Abstract
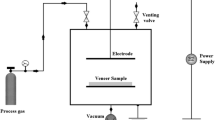
In this study, microwave plasma was used to treat the surface of Pinus yunnanensis wood under the conditions of 220 V of input voltage, 20 μA of filament current, 8.8 mW of output power, 11 mW of reflected power, 2450 MHz of frequency, and 700 Pa of vacuum. The microwave plasma presented very significant treatment effects on the treated surface, even under weak treatment conditions, for example long treatment distance of 120 mm and short treatment time of 60 s. The treated surface showed better surface wettability, and the contact angles on the treated surface measured from deionized water, glycerin, and diiodomethane decreased sharply, even decreased to 0°. The treated surface also presented higher surface free energy, for example, 61.4–62.8 mJ m−2, being greatly improved by microwave plasma compared to that of untreated surface of 46.5 mJ m−2. The bond strength of the treated surface was 7.34 MPa, about 16 % higher than 6.31 MPa for untreated surface. The best treatment effect was obtained for the treatment distance of 120 mm and treatment time of 60–300 s. This technique might be widely used in wood modification and wood processing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aydin I, Demirkir C (2010) Activation of spruce wood surfaces by plasma treatment after long terms of natural surface inactivation. Plasma Chem Plasam Process 30:697–706
Back EL (1991) Oxidative activation of wood surfaces for glue bonding. For Prod J 41:30–36
Bente M, Avramidis G, Förster S, Viöl W (2004) Wood surface modification in dielectric barrier discharges at atmospheric pressure for creating water repellent characteristics. Holz Roh Werkst 62:157–163
Blantocas GQ, Ramos HJ, Wada M (2006) Surface modification of narra wood (Pterocarpus indicus) by ion shower treatment. Jan J Appl Phys 45:8498–8501
Blantocas GQ, Mateum PER, Orille RWM, Ramos RJU, Monasterial JLC, Ramos HJ, Bo-ot LMT (2007) Inhibited flammability and surface inactivation of wood irradiated by low energy hydrogen ion showers (LEHIS). Nucl Instrum Methods B 259:875–883
Cho DL, Sjöblom E (1990) Plasma treatment of wood. J Polym Sci Appl Polym Sym 46:461–472
Cui HW, Du GB (2007) Research advance on functional improvements of wood in China. China For Prod Ind 34:3–7
Cui HW, Du GB (2008a) Advances in plasma modification of wood. World For Res 21:51–55
Cui HW, Du GB (2008b) Influence of surface wettability on Pinus yunnanensis wood treated by microwave plasma. J Northwest For Univ 23:163–166
Cui HW, Du GB (2008c) Advances on wood fire-retardance. World For Res 21:43–48
Cui HW, Kuo SW (2013) Nanocomposites of polybenzoxazine and exfoliated montmorillonite using a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane surfactant and click chemistry. J Polym Res 20:114
Demirkir C, Aydin I, Colak S, Colakoğlu G (2014) Effects of plasma treatment and sanding process on surface roughness of wood veneers. Turk J Agric For 38:663–667
Denes AR, Young RA (1999) Reduction of weathering degradation of wood through plasma-polymer coating. Holzforschung 53:632–640
Du GB, Hua YK, Wang Z (1998) Surface performance of Chinese fir wood treated by microwave plasma. China Wood Ind 12:17–20
Du GB, Hua YK, Wang Z (1999a) Wood surface ablation under microwave plasma. Sci Silvae Sin 35:95–99
Du GB, Hua YK, Cui YJ, Wang Z (1999b) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic (XPS) analysis of wood surface treatment with microwave plasma. Sci Silvae Sin 35:104–109
Du GB, Yang Z, Qiu J, Huang LR (2002) Analysis on wood surface activated by microwave plasma with ESR. China For Sci Technol 16:28–31
Du GB, Yang Z, Qiu J (2004) Study on alnus nepalensis surface treated by microwave plasma with ESR and XPS. Sci Silvae Sin 40:148–151
Fang ZY (2009) On fire retardant and prevention of wood. J Shenyang Coll Educ 11:99–101
Kaboorani A, Riedl B (2011a) Effects of adding nano-clay on performance of polyvinyl acetate (PVA) as a wood adhesive. Compos Part A 42:1031–1039
Kaboorani A, Riedl B (2011b) Improving performance of polyvinyl acetate (PVA) as a binder for wood by combination with melamine based adhesives. Int J Adhes Adhes 31:605–611
Kim S, Kim HJ (2005) Effect of addition of polyvinyl acetate to melamine-formaldehyde resin on the adhesion and formaldehyde emission in engineered flooring. Int J Adhes Adhes 25:456–461
Lux C, Szalay Z, Beikircher W, Kovacik D, Pulker HK (2013) Investigation of the plasma effects on wood after activation by diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge. Eur J Wood Prod 71:539–549
Magalhães WLE, de Souza MF (2002) Solid wood coated with plasma-polymer for water repellence. Surf Coat Technol 155:11–15
Mahlberg R, Niemi HEM, Denes F, Rowell RM (1998) Effect of oxygen and hexamethyldisiloxane plasma on morphology, wettability and adhesion properties of polypropylene and lignocellulosics. Int J Adhes Adhes 18:283–297
Poaty B, Riedl B, Blanchet P, Blanchard V, Stafford L (2013) Improved water repellency of black spruce wood surfaces after treatment in carbon tetrafluoride plasmas. Wood Sci Technol 47:411–422
Podgorski L, Chevet B, Onic L, Merlin A (2000) Modification of wood wettability by plasma and corona treatments. Int J Adhes Adhes 20:103–111
Ramos HJ, Monasterial JLC, Blantocas GQ (2006) Effect of low energy ion beam irradiation on wettability of narra (Pterocarpus indicus) wood chips. Nucl Instrum Methods B 242:41–44
Rehn P, Viöl W (2003) Dielectric barrier discharge treatments at atmospheric pressure for wood surface modification. Holz Roh Werkst 61:145–150
Rehn P, Wolkenhauer A, Bente M, Förster S, Viöl W (2003) Wood surface modification in dielectric barrier discharges at atmospheric pressure. Surf Coat Technol 174–175:515–518
Sakata I, Morita M, Tsuruta N, MoritaI K (1993) Activation of wood surface by corona treatment to improve adhesive bonding. J Appl Polym Sci 49:1251–1258
van Oss CJ, Chaudhury MK, Good RJ (1988) Interfacial Lifshitz-van der Waals and polar interactions in macroscopic systems. Chem Rev 88:927–941
van Oss CJ, Giese RF, Good RJ (1990) Reevaluation of the surface tension components and parameters of polyacetylene from contact angles of liquids. Langmuir 6:1711–1713
Wascher R, Schulze N, Avramidis G, Militz H, Viol W (2014) Increasing the water uptake of wood veneers through plasma treatment at atmospheric pressure. Eur J Wood Prod 72:685–687
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from National Key Technology Support Program (2012BAD24B03) and National Forestry Public Welfare Industry Research Project (210304505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Q., Cui, HW. & Du, GB. Surface wettability, surface free energy, and surface adhesion of microwave plasma-treated Pinus yunnanensis wood. Wood Sci Technol 50, 285–296 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-015-0793-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-015-0793-x