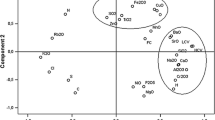
Abstract
The variation in extractives content in sapwood and heartwood was investigated among 12 trees in each of four commercial plantations of Eucalyptus globulus in central Portugal. The study was carried out at the 15% height level and extractions used successively dichloromethane, ethanol and water. At all sites, heartwood had significantly more extractives than sapwood, on average 3.8 and 2.4%, respectively. Most extractives consisted of ethanol soluble material (on average 52% of total extractives). Among the sites, there was a statistically significant difference in the content of extractives but the most important source of variation was the within-tree variation between sapwood and heartwood. Differences in the content of extractives were also observed among trees. A strong relation between extractives content and heartwood proportion was found. The potential loss of pulp yield and problems associated with accumulation of extractives are directly related to the heartwood proportion in the eucalypt stems. Forest management should take into account heartwood development and selection for minimising heartwood extractives.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamapoulos S, Voulgaridis E, Passialis C (2005) Variation of certain chemical properties within the stemwood of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.). Holz Roh Werkst 63:327–333
del Río JC, Gutiérrez A, González-Vila FJ, Martín F, Romero J (1998) Characterization of organic deposits produced in the Kraft pulping of Eucalyptus globulus wood. J Chromatogr A 823:457–465
del Río JC, Gutiérrez A, González-Vila FJ, Martín F (1999) Application of pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to the analysis of pitch deposits and synthetic polymers in pulp and pulp mills. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 49:165–177
Domingues RMA, Sousa GDA, Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Neto CP (2010) Eucalyptus globulus biomass residues from pulping industry as a source of high value triterpenic compounds. Ind Crop Prod 31:65–70
Fengel D, Wegener G (1989) Wood: chemistry ultrastructure reactions. Walter de Gruyter, New York
Freire CSR, Silvestre JD, Neto CP (2005) Lipophilic extractives in Eucalyptus globulus kraft pulps. Behaviour during ECF bleaching. J Wood Chem Technol 25:67–80
Gominho J, Pereira H (2000) Variability of heartwood content in plantation grown Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Wood Fiber Sci 32(2):189–195
Gominho J, Figueira J, Rodrigues JC, Pereira H (2001) Within-tree variation of heartwood, extractives and wood density in the eucalypt hybrid urograndis (Eucalyptus grandis x E. uropylla). Wood Fiber Sci 33(1):3–8
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, González-Vila F (1998) Variation in the composition of wood extractives from Eucalyptus globulus during seasoning. J Wood Chem Technol 18(4):439–446
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Martínez MJ, Martínez A (2001) The biotechnological control of pitch in paper pulp manufactoring. Trends Biotechnol 19(9):340–348
Hillis WE (1971) Distribution, properties and formation of some wood extractives. Wood Sci Technol 5:272–289
Hillis WE (1987) Heartwood and tree exudates. Springer, Berlin
Hillis WE (1991) Eucalypts: chemistry and uses. Appita 44(4):239–244
Jorge MFCTT (1994) Variabilidade anatómica, física e química da madeira da E. globulus Labill. Ph D thesis, Instituto Superior de Agronomia, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa, Lisbon
Lourenço A, Baptista I, Gominho J, Pereira H (2008) The influence of heartwood on the pulping properties of Acacia melanoxylon wood. J Wood Sci 54:464–469
Martínez MJ, Barrasa JM, Gutiérrez A, Rio JC, Martínez AT (1999) Fungal screening for biological removal of extractives from Eucalyptus globulus wood. Can J Bot 77:1513–1522
Mészáros E, Jakab E, Várhegyi G (2007) TG/MS, Py-GC/MS and THM-GC/MS study of the composition and thermal behavior of extractive components of Robinia pseudoacacia. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 79:61–70
Miranda I, Pereira H (2002) Variation of pulpwood quality with provenances and site in Eucalyptus globulus. Ann For Sci 59:283–291
Miranda I, Gominho J, Lourenço A, Pereira H (2006) The influence of irrigation and fertilization on heartwood and sapwood contents in 18-years-old Eucalyptus globulus trees. Can J For Res 36:2675–2683
Miranda I, Gominho J, Lourenço A, Pereira H (2007) Heartwood extractives and pulp yield of three Eucalyptus globulus clones grown in two sites. Appita J 60(6):485–488
Miranda I, Gominho J, Pereira H (2009) Variation of heartwood and sapwood in 18-year-old Eucalyptus globulus trees grown with different spacings. Trees 23:367–372
Morais MC, Pereira H (2007) Heartwood and sapwood variation in Eucalyptus globulus Labill. trees at the end of rotation for pulpwood production. Ann For Sci 64:665–671
Pereira H (1988a) Variability in the chemical composition of plantation eucalypts (Eucalyptus globulus Labill.). Wood Fiber Sci 20:82–89
Pereira H (1988b) The raw-material quality of Eucalyptus globulus. In: Pereira JS, Pereira H (eds) Eucalyptus for biomass production. Commission of the European Communities, Lisbon, pp 294–299
Pereira H, Miranda I (1992) The chemical composition of wood and bark of fast-grown Eucalyptus globulus L. trees during the first 3 years. Appita 37:186–190
Pereira H, Sardinha R (1984) Chemical composition of Eucalyptus globulus. Appita 37(8):661–664
Pereira H, Graça J, Rodrigues JC (2003) Wood chemistry in relation to quality. In: Barnett JR, Jeronimidis G (eds) Wood quality and its biological basis. Blackwell, United Kingdom, pp 53–86
Valente CA, Sousa APM, Furtado FP, Carvalho AP (1992) Improvement program for Eucalyptus globulus at Portucel: technological component. Appita 45(6):403–407
Wilkes J (1984) The influence of rate of growth on the density and heartwood extractives content of eucalypt species. Wood Sci Technol 18:113–120
Wilkins AP (1991) Sapwood, heartwood and bark thickness of silviculturally treated Eucalyptus grandis. Wood Sci Technol 25:415–423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morais, M.C., Pereira, H. Variation of extractives content in heartwood and sapwood of Eucalyptus globulus trees. Wood Sci Technol 46, 709–719 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-011-0438-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-011-0438-7