Abstract
Cementum is the least studied of all mineralized tissues and little is known about mechanisms regulating its formation. Therefore, the goal of this study was to provide new insights into the transcriptional regulation of cementum formation by determining the consequences of the deficiency of the Trps1 transcription factor in cementoblasts. We used Trps1Col1a1 cKO (2.3Co1a1-CreERT2;Trps1fl/fl) mice, in which Trps1 is deleted in cementoblasts. Micro-computed tomography analyses of molars of 4-week-old males and females demonstrated significantly shorter roots with thinner mineralized tissues (root dentin and cementum) in Trps1Col1a1 cKO compared to WT mice. Semi-quantitative histological analyses revealed a significantly reduced area of cellular cementum and localized deficiencies of acellular cementum in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. Immunohistochemical analyses revealed clustering of cementoblasts at the apex of roots, and intermittent absence of cementoblasts on Trps1Col1a1 cKO cementum surfaces. Fewer Osterix-positive cells adjacent to cellular cementum were also detected in Trps1Col1a1 cKO compared to WT mice. Decreased levels of tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP), an enzyme required for proper cementogenesis, were apparent in cementum, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone of Trps1Col1a1 cKO. There were no apparent differences in levels of bone sialoprotein (Bsp) in cementum. Quantitative analyses of picrosirius red-stained periodontal ligament revealed shorter and disorganized collagen fibers in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice demonstrating impaired periodontal structure. In conclusion, this study has identified Trps1 transcription factor as one of the important regulators of cellular and acellular cementum formation. Furthermore, this study suggests that Trps1 supports the function of cementoblasts by upregulating expression of the major proteins required for cementogenesis, such as Osterix and TNAP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Cementum is a mineralized tissue that covers the root of the tooth. It serves as the attachment site for the periodontal ligament that anchors the tooth to the alveolar bone, hence it is crucial for the structural integrity of the periodontium. The cementum at the apical portion of the root contains cementocytes and it is called the cellular cementum, while the acellular cementum is a thin layer of the extracellular matrix (ECM) covering the cervical portion of the root. In comparison with other mineralized tissues, the cementum and the cells that make it–cementoblasts–are far less characterized. The molecular composition of the cementum is similar to the bone and dentin ECM. It consists of the collagen type I network and is enriched in tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP), bone sialoprotein (Bsp), and dentin matrix protein 1 (Dmp1). Due to the similarity of the cementum and the bone tissue, transcriptional mechanisms regulating cementum formation likely share similarities with those in the bone. Accordingly, the major osteogenic transcription factor Osterix (Osx/Sp7) is critical not only for osteogenesis but also for cementogenesis as demonstrated by significantly decreased cellular cementum formation in mice with conditional deletion of Osx/Sp7 in cementoblasts [1]. The acellular cementum, on the other hand, has been shown to be affected by disturbed phosphate/pyrophosphate (Pi/PPi) balance [2,3,4,5,6,7]. This has been demonstrated, for example, in human patients with hypophosphatemic rickets and hypophosphatasia, and was observed in mouse models of these disorders [2, 8,9,10,11]. Even the acellular cementum deficiency in Bsp KO mice has been attributed to the secondary dysregulation of genes controlling Pi/PPi ratio [4]. While the human patients' and animal models’ studies provide strong evidence that the formation and homeostasis of cementum rely on the adequate levels of the Osx/Sp7 transcription factor and proteins regulating Pi and PPi balance, the transcriptional regulation of the cementum is poorly understood.
In our previous in vitro studies of mineralizing cells, we uncovered that the Trps1 transcription factor supports expression of several genes important for cementogenesis, including Osx/Sp7, TNAP, and Bsp [12]. Trps1 is a GATA-type transcription factor involved in endochondral bone development, tooth formation and regulation of the mineralization process [13,14,15,16]. In humans, heterozygous mutations in the TRPS1 gene cause trichorhinophalangeal syndrome – a skeletal dysplasia with low bone mass and dental abnormalities [14]. The broad array of dental phenotypes presented by TRPS patients, which includes supernumerary teeth, microdontia, predisposition to severe dental caries, and delayed tooth eruption, indicates that this transcription factor is involved in multiple aspects of tooth formation [13, 17]. During tooth development, Trps1 is highly expressed in dental mesenchymal cells, including dental follicle cells, which give rise to cementoblasts [13]. Our previous studies of Trps1−/− mice revealed that Trps1 supports proliferation of cells in the developing tooth organ [18], which may contribute to the microdontia phenotype frequently presented in TRPS patients. However, due to neonatal lethality of Trps1−/− mice and mild phenotypes of Trps1+/− mice, the studies addressing the role of Trps1 in formation of the tooth crown and root, and dental mineralized tissues have been very limited.
Recently, we have generated Trps1 conditional knockout (cKO) mice with postnatal deletion of Trps1 driven by tamoxifen-inducible Cre expressed under the control of the 2.3kbCol1a1 promoter (2.3kbCol1a1-CreERT2;Trps1fl/fl a.k.a. Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice). In Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, Trps1 is deleted in osteoblasts, odontoblasts, and cementoblasts. Analyses of the tooth crown revealed wider predentin, decreased volume of dentin, globular pattern of dentin mineralization, as well as localized enamel defects [19], which together suggest that compromised quality of the dentin and enamel contributes to increased susceptibility and severity of dental caries in TRPS patients. Exposed tooth roots were also observed in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, which may be indicative of disrupted periodontal structure.
Based on the previous studies implicating Trps1 in the regulation of the mineralization process [12, 16, 19, 20] and high and specific Trps1 expression in cells giving rise to cementoblasts [13], we hypothesize that Trps1 is involved in cementum formation through regulation of gene expression in cementoblasts. The goal of this study was to determine the consequences of the Trps1 deficiency in cementoblasts on the molecular characteristics of these cells, and their function, i.e., the formation of the cementum in vivo. To this end, we used previously generated Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice [19] and a set of complementary approaches assessing the quantity and mineralization of the cementum, and expression of proteins characteristic for cementoblasts.
Results
Expression of Trps1 in Cementum and Alveolar Bone
In our previous studies, we observed exposed tooth roots in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice [19], which suggests the compromised structure of the periodontal complex. Since the formation of the sound periodontal structure depends on the formation of the cementum as well as alveolar bone, first, we analyzed whether Trps1 is expressed in cells of these tissues. Immunohistochemical staining of the mandibles of 4 wk old WT mice detected the presence of the Trps1 protein in the nuclei of cementocytes and cementoblasts in the cellular cementum, as well as osteoblasts and osteocytes in the alveolar bone (Fig. 1 left panel). In the Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, no specific immunostaining signal was detected in these cells indicating the effective deletion of Trps1 by tamoxifen-induced Cre recombinase (Fig. 1 right panel). In conclusion, these IHC analyses demonstrate high Trps1 expression in cells contributing to the formation and homeostasis of the periodontal complex. Taking into consideration that cementum is a poorly studied tissue, and little is known about the transcriptional regulation of the formation and homeostasis of this tissue, we focused the studies of Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice on the characterization of the cementum.
Efficient depletion of Trps1 from cementoblasts and cementocytes, as well as osteoblasts and osteocytes of the alveolar bone in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. Trps1 immunostaining images showing localization of the Trps1 protein in tooth root and alveolar bone of mandibular first molars in 4 wk old WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. In WT mice, Trps1 is highly expressed in cementoblasts (black arrowheads), cementocytes (black arrows), osteoblasts (blue arrowheads), and osteocytes (blue arrows). Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice have diminished expression of Trps1 in root and alveolar bone. CC–cellular cementum; D–dentin; AB–alveolar bone
Impaired Root Formation in Trps1 Col1a1 cKO Mice
To evaluate the consequences of the Trps1 deficiency in cementoblasts and odontoblasts on tooth root formation, we performed quantitative μCT analyses comparing roots of mandibular first molars of 4 wk old WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. These analyses revealed that Trps1Col1a1 cKO males and females have significantly shorter (Fig. 2A) and overall smaller (Fig. 2B, total root volume) roots than WT mice. Of note, there is no difference in the overall body size and tooth crown size between WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO females [19]. The mineralized tissue (cementum and root dentin) fraction in the roots of Trps1Col1a1cKO males and females was also significantly lower than in WT mice (Fig. 2B). However, there was no difference in the overall mineral density of the root tissues (Fig. 2B). More detailed analyses revealed that the mineralized root tissue thickness ranged from 24 µm to 120 µm with most of the tissue thicker than 60 µm in WT females, while in the Trps1Col1a1 cKO females, the mineralized root tissue thickness ranged from 12 µm to 84 µm with most of the tissue thickness below 60 µm (Fig. 2C). A similar shift of the root mineralized tissue thickness was detected in Trps1Col1a1 cKO males. In Trps1Col1a1 cKO males, most of the root mineralized tissues was thinner than 36 µm, and the thickness ranged from 12 µm to 48 µm, while in the WT males, the tissue thickness ranged from 24 µm to 102 µm with most of the tissue thicker than 36 µm (Fig. 2C). Thus, the quantitative μCT analyses revealed that Trps1 deficiency in odontoblasts and cementoblasts significantly impairs the size of the roots as well as the formation of root mineralized tissues in both male and female mice.
Shorter and thinner tooth roots in Trps1Col1a 1cKO compared with WT mice. Results of quantitative μCT analyses of tooth roots in mandibular first molars 4 wk old WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (n = 5/genotype/sex; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). A Measurements of the distal root length. B Measurements of the root total volume, volume of root dentin and cementum, tissue fraction of root dentin and cementum, and mineral density of root dentin and cementum. C Representative 3D µCT images of the roots. The mineralized tissue was pseudo-colored based on the tissue thickness; the tissue thickness color scale is shown below the images. The graphs below the 3D images show the comparison of the quantity (volume) of the root mineralized tissue with specific thickness in WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice
Reduced Cementum Formation and Abnormal Distribution of Cementoblasts in Trps1 Col1a1 cKO Mice
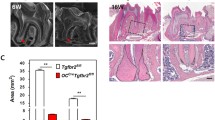
It is difficult to distinguish cementum from dentin using μCT, therefore to determine whether the deficiency of cementum contributes to the decreased mineralized tissue thickness in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, we used histological analyses of root sections stained with toluidine blue, which differentiates between cementum and dentin. These analyses were done in females, because μCT results showed that both sexes are affected in the same way, but the phenotype is more severe in females. Toluidine blue staining of root histological sections was used for semi-quantitative histological analyses of cementum. Low-magnification microscopic images showed shorter distal roots in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, consistent with the μCT results (Fig. 3A). Measurements of the area of the cellular cementum demonstrated significantly reduced area in Trps1Col1a1 cKO compared with WT mice (Fig. 3A). While the measurements of the acellular cementum area did not show the statistically significant difference between WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, an irregular thickness and partial deficit of the acellular cementum in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice was apparent on high magnification images (Fig. 3A, white arrows). Hence, the histological analyses demonstrated that the Trps1 deficiency in cementoblasts affects both the cellular and acellular cementum.
Histological analyses of cementum in mandibular first molars of 4wk old WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO females demonstrating impaired formation of the cellular and acellular cementum, and uneven distribution of cementoblasts in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. A Representative images of toluidine blue-stained root sections and results of semi-quantitative analyses of the cementum area. Left panel: low magnification images showing the general appearance of the roots; middle panel: higher magnification images showing the irregular thickness and partial absence (white arrows) of the acellular cementum (AC) in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice; right panel: higher magnification images showing decreased area of the cellular cementum (CC, outlined by red dotted lines) in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice compared to WT. The graphs show the results of semi-quantitative analyses of the acellular (top) and cellular (bottom) cementum area (n = 5 females/genotype; *p < 0.05). B Results of the IHC for Tubb3 (a cementoblasts marker) in tooth roots showing uneven distribution of cementoblasts in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. The dotted areas on the left-side images indicate the areas showed in higher magnification on the right-side images. Note the surfaces of cellular cementum not covered by Tubb3-positive cells in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. C Fluorescent microscopy images showing mineralized tissues of the tooth root (CC–cellular cementum and D–dentin) and the alveolar bone (AB). The distance between alizarin red and calcein lines indicates the mineralized tissue formed within 7 days. Note the decreased distance between the fluorescent labels in cementum, dentin, and alveolar bone in Trps1Col1a1 cKO compared with WT mice. CC–cellular cementum; AB–alveolar bone; D–dentin
To gain insights about the cause of the cementum defects in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, we first assessed localization of cementoblasts using immunohistostaining detecting Tubb3 (a member of the β tubulin protein family) that has been shown to be a cementoblasts marker [21]. As expected for cementoblasts, Tubb3-positive cells were uniformly lining up along the cellular cementum in WT mice (Fig. 3B). In contrast, in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, cementoblasts were unevenly distributed and clustered at the apical portion of the cementum; at some places, the cementum surface was not covered by cementoblasts (Fig. 3B). In comparison with WT mice, in Trps1Col1a1 cKO, fewer Tubb3-positive cells were observed on the cellular cementum surface beyond the apical end of the root. These analyses suggest that Trps1 deficiency in cementoblasts leads to either defective cementoblast differentiation or premature loss of cementoblasts.
To assess the cementoblast function–the secretion of the organic components of the cementum ECM and its mineralization–we used fluorescent double-labeling (alizarin red followed by calcein) and microscopic imaging of fluorochromes incorporated into mineralizing ECM in a 7-days interval. We observed the decreased distance between the fluorescent labels in the cellular cementum and root dentin of Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice in comparison with WT (Fig. 3C), which indicates that less mineralized ECM was formed in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice than in WT mice in the same period of time. Hence, the Trps1 deficiency in cementoblasts impairs the secretion of the cementum ECM and its mineralization.
Decreased Formation of the Alveolar Bone in Trps1 Col1a1 cKO Mice
The fluorescent double-labeling analyses also revealed the decreased mineral apposition in the alveolar bone of Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (Fig. 3C). Following on this observation, we performed µCT analyses of the alveolar bone of 4wk old male and female mice. These analyses revealed significantly smaller alveolar bones (Total Tissue Volume—TV) and decreased Bone Volume Fraction (BV/TV) in Trps1Col1a1 cKO males and females in comparison with WT mice (Fig. 4). These results suggest that deficiency of the alveolar bone in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice may contribute to the exposed roots phenotype that we reported in our previous study [19].
Differential Effect of Trps1 Deficiency on Expression of the Cementum and Alveolar Bone Proteins
The cementum and bone ECM have similar molecular composition, and Osx has been shown to be a major transcription factor regulating formation of these mineralized tissues. Since our previous in vitro studies demonstrated that Trps1 deficiency in cells producing mineralized ECM results in dramatic downregulation of Osx [12], we first investigated the changes in the Osx protein levels using IHC. Consistent with the previous in vitro data, IHC analyses detected fewer Osx-positive cells in the periodontal ligament area adjacent to the acellular cementum as well as in the cellular cementum of Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice in comparison with WT (Fig. 5A). Furthermore, decreased expression of Osx was also noticeable in osteoblasts on the alveolar bone surface (Fig. 5A). These results demonstrate that Trps1 supports expression of Osx in cementoblasts and osteoblasts of the alveolar bone.
Tissue-specific consequences of Trps1 deficiency on expression of proteins important for cementum formation and alveolar bone. Representative microscopic images of IHC on the tooth root with adjacent periodontal ligament and alveolar bone in 4wk old WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. (A) IHC for Osx showing fewer Osx-positive cells around the acellular and cellular cementum, and on the alveolar bone surface in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice compared to WT mice. (B) IHC for TNAP showing lower TNAP levels around both acellular and cellular cementum and on the alveolar bone surface in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice compared to the WT. (C) IHC for Bsp showing comparable levels of Bsp in acellular and cellular cementum of WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, and notably lower levels of Bsp in the alveolar bone of Trps1Col1a1cKO mice in comparison with WT. Arrows point at the irregularity of the acellular cementum in the Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. AC–acellular cementum; CC–cellular cementum; D–dentin; AB–alveolar bone
Next, we analyzed expression of TNAP, a major enzyme supporting formation of both cementum and bone. In particular, the expression of TNAP in the early root formation stage is essential for formation of the acellular cementum and sound cementum-periodontal ligament interface [22]. As expected, in WT mice, TNAP was widely detected in the periodontal ligament adjacent to acellular and cellular cementum (Fig. 5B). High levels of TNAP were also detected on the surface of the alveolar bone of WT mice. In contrast, the levels of TNAP in the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone were noticeably lower in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (Fig. 5B). This effect of Trps1 deficiency on TNAP expression is also consistent with the previously published in vitro studies [12]. Hence, our data show that Trps1 supports expression of TNAP in the dentoalveolar structure.
Bsp is commonly used as a marker of the acellular cementum, but it is also highly expressed in bone. Bsp expression is also critical for formation of the acellular cementum [23, 24]. Since defects in the acellular cementum were detected in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (Fig. 3A), we compared Bsp levels in Trps1Col1a1 cKO and WT mice. Although the IHC analyses did not show an apparent difference in Bsp levels in the acellular and cellular cementum of WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, the distribution of the Bsp protein accentuated the irregularity of the acellular cementum in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (Fig. 5C). Notably, the IHC analyses detected a striking difference in Bsp levels in the alveolar bone of WT mice and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (Fig. 5C) with overall lower levels of Bsp in Trps1Col1a1 cKO alveolar bone. Moreover, while high levels of Bsp were detected throughout the alveolar bone ECM of WT mice, only the margins of the alveolar bone ECM were positive for the Bsp in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (Fig. 5C). Hence, Trps1 deficiency affects Bsp expression differently in the cementum and alveolar bone tissues. In summary, the results of IHC analyses of major proteins important for cementum and alveolar bone formation revealed tissue-specific consequences of Trps1 deficiency.
Impaired Organization of Collagen Fibers in Periodontal Ligament in Trps1 Col1a1 cKO Mice
Cementum serves as the attachment site for the periodontal ligament anchoring the tooth to the alveolar bone. Based on the results showing irregular acellular cementum and decreased levels of TNAP, which causes loss of attachment in hypophosphatasia patients, we speculated that the periodontal ligament may also be impaired in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. To assess the organization of collagen fibers in the periodontal ligament, Picrosirius red staining was performed. Picrosirius red-stained collagen fibers appear as bright yellow or orange under polarized light when densely packed and thick, while thin collagen fibers are green. Microscopic imaging under polarized light revealed that in WT mice, the periodontal ligament was composed of regularly oriented dense orange/yellow collagen fibers connecting the root to the alveolar bone (Fig. 6B, D). On the other hand, there were fewer yellow collagen fibers in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (Fig. 6B, D), indicating thinner and less organized collagen. Quantitative analyses demonstrated a significantly reduced area occupied by well-organized thick alveolar crest fibers in the cervical portion of the periodontal ligament (Fig. 6B, C) as well as the oblique fibers in the apical portion of the periodontal ligament (Fig. 6D, E) in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice in comparison with WT.
Impaired organization of collagen fibers in periodontal ligament of Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. A A representative image of Picrosirius red-stained a molar root viewed under a light microscope (bright field). The black boxes indicate areas imaged under the polarized light in the comparative analyses of WT vs. Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. B Images of the Picrosirius red-stained cervical region of the periodontal ligament of WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice viewed under the polarized light. The dotted white line demarcates the alveolar bone/periodontal ligament interface. C Quantification of thick collagen fibers in the cervical region expressed as the percentage of the yellow area in the total periodontal ligament area in the analyzed region. D Images of the Picrosirius red-stained apical region of the periodontal ligament of WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice viewed under the polarized light. The dotted white line demarcates the alveolar bone/periodontal ligament interface. E Quantification of thick collagen fibers in the apical region expressed as the percentage of the yellow area in the total periodontal ligament area in the analyzed region. Data were obtained from analyses of 3 females/genotype; results from each mouse and mean values ± standard deviation are shown. AC–acellular cementum; CC–cellular cementum; D–dentin; AB–alveolar bone
Discussion
Cementum is the least studied tissue of all mammalian mineralized tissues. Although, its molecular composition is fairly well characterized, little is known about the transcriptional regulation of the cementum formation. Here, using a conditional KO mouse approach with Trps1 deletion in cementoblasts (Fig. 1), we demonstrate that the Trps1 transcription factor is required for the proper formation of the tooth root and cementum in both male and female mice, as well as for the distribution and function of cementoblasts. Our study revealed that deletion of Trps1 in cementoblasts impairs formation of the cellular and acellular cementum, and results in compromised periodontal structure with less organized collagen fibers. Furthermore, our data suggest that this function of Trps1 is executed, at least in part, through supporting the expression of Osx – the major transcription factor involved in cementogenesis, and TNAP – the enzyme regulating Pi/PPi balance in the local, cellular environment. Hence, this study broadens the knowledge on the regulation of function of cementoblasts, which are the least studied cells producing mineralized ECM. In addition, this study provides some insights into reported association of Trps1 with colonization of periodontal pathogens [25] by demonstrating that Trps1 deficiency results in defective structure of periodontium. Such compromised structure may make the periodontium susceptible to oral bacteria invasion.
The molecular composition of the cementum ECM shares some similarities with bone and dentin suggesting that similar molecular mechanisms govern the formation of these tissues. Recently, we have demonstrated that Trps1 is required for the formation of the sound dentin—teeth of Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice have reduced dentin layer, expanded predentin, and globular dentin mineralization pattern, which is characteristic for disturbed phosphate homeostasis [19]. Furthermore, our previous in vitro data from the analyses of cells derived from preodontoblasts revealed that expression of many genes required for formation of mineralized ECM of dentin and bone is supported by Trps1 [12]. Since many of these genes are also important for the cementum formation, and this tissue is highly sensitive to Pi/PPi balance, these data prompted us to examine the consequences of Trps1 deficiency on cementum. Indeed, the µCT analyses of tooth roots of 4 wk old mice revealed significantly reduced thickness of mineralized tissue and the length of the roots in Trps1Col1a1cKO males and females (Fig. 2). These data, together with the fluorescent double-labeling of mineralized tissues (Fig. 3C) showing less cementum deposited within the 7 days period in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, demonstrate the importance of Trps1 for the formation of mineralized tissues in tooth roots. The subsequent histological analyses that allowed for a detailed examination of cementum revealed significantly reduced area of the cellular cementum and irregular thickness of a thin layer of the acellular cementum (Fig. 3). Hence, these data together with our previously published dentin phenotype in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, establish Trps1 as one of the transcription factors important for both dentin and cementum formation. It is important to note that, while Trps1Col1a1 cKO males are significantly smaller than WT, there is no significant difference in the overall body size and crown size between WT and Trps1Col1a1 cKO females as we reported previously [19]. This indicates that the effect of Trps1 deficiency on the tooth root size reflects the role of Trps1 specifically in tooth root formation. This is further supported by reduced number of cementoblasts (Fig. 3B) and reduced cementum formation in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (Fig. 3C).
In mice, the formation of cementum continues after 4wk of age (the age analyzed in this study). Although we have not analyzed older mice, the cementoblasts abnormalities (Fig. 3B), and reduced cementum formation rate (Fig. 3C) suggest that the deficiencies in cementum in 4wk old Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice do not reflect a simple delay of the tissue formation. The uneven distribution of cementoblasts with their clustering at the apex of the root and their deficit beyond the apical portion of the root (Fig. 3B) suggest that Trps1 deficiency in cementoblasts leads to their premature loss. Alternatively to the premature cementoblasts apoptosis hypothesis, and based on well demonstrated (in many cell types) function of Trps1 as a pro-proliferative transcription factor [16, 18, 26, 27], it is possible that Trps1-deficient cementoblasts prematurely cease the proliferation. Regardless of the mechanism underlying the cementoblast deficit, it is likely that the deficiency of cementum and shorter roots phenotype would persist at later age in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice.
In this study, we also provide some insights into the molecular pathology underlying the tooth root abnormalities in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice—likely, the reduced expression of Osx (Fig. 5A) likely is a contributor to the root phenotype in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. Osx has been identified as one of the major transcription factors supporting cementogenesis and tooth root formation as demonstrated by studies of cKO mice with deletion of Osx in cementoblasts [1, 28]. Osx cKO mice have significantly shorter roots due to failed root elongation and deficiency of cellular cementum, but no obvious defects in the tooth crown. Osx regulates the cellular cementum formation through activation of Dkk and subsequent downregulation of Wnt/βcatenin signaling [29]. Importantly, Wnt signaling is important for cementum and root formation [30, 31], and Trps1 has been shown to regulate Wnt signaling in endochondral ossification and hair follicles [32, 33]. Further studies are needed to determine whether Trps1 regulates Osx expression directly or indirectly in cementoblasts, and if Wnt signaling pathway is regulated by Trps1 during cementogenesis. However, the striking similarities between Trps1Col1a1 cKO and Osx cKO tooth root abnormalities and lower than in WT expression of Osx in Trps1-deficient cementoblasts strongly suggests that the tooth root phenotype in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice is at least partly caused by the Osx deficiency. Thus, these data together with our previous in vitro studies of odontoblast-like cells [12], place Trps1 upstream of the Osx transcription factor and demonstrate the cell-autonomous requirement of Trps1 for Osx expression in cells committed to formation of mineralized ECM.
Human patients and animal models studies suggest that acellular cementum is more sensitive than cellular cementum to changes in the Pi/PPi balance [2, 10, 22, 34,35,36]. For example, acellular cementum deficiency with a concomitant loss of continuity between the root and periodontal ligament have been reported in hypophosphatasia patients [10, 37] and in Alpl−/− mice [22, 35, 38] with genetic deficiency of TNAP enzymatic activity, which is a major regulator of the Pi/PPi ratio in the local extracellular compartment. Similarly, reduced acellular cementum thickness and detachment of periodontal ligament have been described in individuals with genetic forms of hypophosphatemia and in Hyp mice (a model of X-linked hypophosphatemia) [34, 40]. Acellular cementum is also compromised by Trps1 deficiency in cementoblasts (Fig. 3A). This is accompanied by reduced TNAP levels throughout the periodontal ligament as well as the cementum and alveolar bone surfaces (Fig. 5B). Interestingly, levels of Bsp in cementum do not seem to be affected by Trps1 deficiency (Fig. 5C). Since Bsp supports cementum formation through mechanisms independent of Pi/PPi balance, the results of immunohistochemical analyses suggest that the disturbed Pi/PPi balance due to TNAP deficiency is likely one of the underlying causes of the acellular cementum pathology in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice. Of note unlike in TNAP KO and Bsp KO mice, no detachment of the periodontal ligament was detected in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, demonstrating a milder periodontal structure impairment than in the cases of TNAP or Bsp deficiency.
The importance of the cementum for the function and homeostasis of the periodontium is underscored by periodontal pathologies in individuals with impaired or deficient cementum. For example, individuals with hypophosphatasia demonstrate insufficient periodontal attachment and premature tooth loss due to acellular cementum hypoplasia [8,9,10,11]. Consistently, disorganization of periodontal ligament is also apparent in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice (Fig. 6). Although no ligament detachment has been observed in Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice, the disorganization of collagen fibers suggests a compromised periodontal structure, which may predispose to accumulation of oral bacteria. Interestingly, GWAS studies identified TRPS1 as one of the loci associated with periodontal pathogen colonization [25]. The impaired organization of collagen fibers in Trps1Col1a1 cKO periodontal ligament suggests that this association may, in part, reflect the role of Trps1 in the structural integrity of the periodontium. However, recent studies have identified Trps1 as one of the key transcription factors regulating TI-Treg cells in the context of cancer malignancy [41]. This points to a new interesting function of Trps1 in the immune response, which may contribute to the periodontal health.
Our analyses of alveolar bone along with cementum revealed differences in the regulation of these two mineralized tissues. Deposition of mineralized extracellular matrix and tissue volume was decreased in both tissues by Trps1 deficiency (Figs. 3 and 4), so were the levels of Osx and TNAP (Fig. 5A, B). However, changes in the distribution of Bsp in the extracellular matrix were apparent only in alveolar bone of Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice in comparison with WT (Fig. 5C). While cementum and bone share many similarities, some features are found in bone only. For example, cementum remodeling does not occur under physiological conditions, however it can occur in response to excessive occlusal stress. The observed changes of Bsp distribution in alveolar bone of Trps1Col1a1 cKO mice highlight the differences between formation and homeostasis of cementum and bone.
In summary, this study identifies the Trps1 transcription factor as a major regulator of the cementoblast function and cementum formation. Furthermore, it expands the knowledge on the role of Trps1 in formation of dental mineralized tissues revealing that not only the proper formation of the tooth crown [19] but also root mineralized tissues require Trps1. Furthermore, the differential effect of Trps1 deficiency on Bsp levels in cementum and alveolar bone revealed differences in transcriptional regulation of cementum and alveolar bone formation. Importantly, we have demonstrated that expression of Trps1 in cementoblasts supports expression of another major cementoblast-regulating transcription factor (Osterix), and a major enzyme involved in cementum and periodontal ligament formation (TNAP). Hence, this study provides a better understanding of the transcriptional regulation of cellular and acellular cementum formation, which has been very poorly understood so far.
Materials and Methods
Animals
All animal experiments were approved by the University of Pittsburgh Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol #22091787) and conducted in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Preparation and genotyping of 2.3kbCol1a1-CreERT2;Trps1fl/fl conditional knockout (Trps1Col1a1 cKO) was described previously [19]. Experimental Trps1Col1a1 cKO and control WT (Trps1fl/fl) mice were administered with tamoxifen (0.1 mg/g body weight/day, via intraperitoneal injection) at postnatal days (P)1, P2, P9, P16 and P23, and P30 to induce deletion of Trps1 in specific cells. Mice were euthanized by CO2 inhalation for the collection of tissues for the analyses. Male and female mice were used in this study, and analyzed separately.
Micro-Computed Tomography (μCT) Analysis
Hemimandibles (n = 5/ genotype/sex) of 4 wk old mice were imaged using the Scanco μCT 50 (Scanco Medical, Brüttisellen, Switzerland) system. Specimens were scanned in 70% ethanol at 55 KVp, 0.36 degrees rotation step (180 degrees angular range) and a 1,500 ms exposure per view, and 6-μm voxel size. Measurements of tissue mineral density (TMD), thickness (Th), volume (BV), dentin and cementum tissue fraction (BV/TV) in the total tooth root volume (TV), and alveolar bone were done as described before [19].
Fluorescent Double-Labeling
For the analyses of the cementum formation, P27 mice were intraperitoneally injected with alizarin red (25 mg/kg; A3882 Sigma) followed by an injection of calcein (25 mg/kg; C0875 Sigma) 6 days later. Mice were sacrificed 48 h after the second injection, and hemimandibles were collected for analysis. Hemimandibles were fixed with 10% formalin (Fisher, #S7100-4) overnight, dehydrated with ethanol followed by xylene, and then embedded in methyl methacrylate. Seven μm sections of embedded tissues were imaged under fluorescent microscope (Zeiss AxioCam on a Zeiss Axioskop A1 microscope) and images were processed by ZEN software.
Histology and Semi-Quantitative Analyses of Cementum and Periodontal Ligament
Hemimandibles (n = 5/genotype/sex) were dissected, fixed with 10% formalin overnight, decalcified with 10% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA, pH 7.4) for 14 days, and embedded in paraffin. Seven μm sagittal sections were stained with toluidine blue (TB, Fisher, AC348600250) or picrosirius red (PR, Fisher, NC9908782) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Images of TB- and PR-stained sections were captured by Zeiss AxioCam on a Zeiss Axioskop A1 microscope and Nikon TE2000 microscope with polarizing filters, respectively. BIOQUANT software (BIOQUANT Image Analysis Corporation, Nashville, TN USA) was used to measure cementum area and alignment of collagen fibers. The area of the acellular and cellular cementum was measured on tissue sections (n = 5 mice/females/genotype) stained with TB, which allows to distinguish cementum (light blue color) from dentin (darker blue color) [40, 42,43,44,45]. The organization of the collagen fibers in periodontal ligament was assessed in the area between 200 μm from cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) and 200 μm from the root apex, on tissue sections stained with picrosirius red. The organization of the collagen fibers was expressed as the percentage of red/orange area (labeling long well-organized fibers) in the total analyzed periodontal ligament area (n = 3 females/genotype).
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed on paraffin sections using heat-induced antigen retrieval in sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0). The following primary antibodies were used: anti-TRPS1 (1:100, OriGene, TA314642), anti-βIII Tubulin (Tubb3, 1:500, Abcam, ab18207), anti-Osx (1:500, Abcam, ab22552), anti-TNAP (1:100, Abcam, ab65834), anti-Bsp (1:500, kindly provided by Dr. Renny Franceschi, University of Michigan). Sections for diaminobenzidine visualizing system were immersed in methanol containing 1% of hydrogen peroxide. The Vectastatin Elite ABC kit (Vector Laboratories Inc., PK-6101) was used for secondary antibody and avidin–biotin peroxidase system, followed by visualization with DAB Substrate Kit (Vector Laboratories Inc., SK-4100). Counterstaining was performed using hematoxylin or methyl green staining. For immunofluorescence, sections were incubated with Alexa Fluor 546-conjugated secondary antibody (1:500, Thermo Fisher Scientific, A-11035) and DAPI. Images were captured with Zeiss AxioCam on a Zeiss Axioskop A1 microscope and ZEN software.
Statistical Analyses
Five mice/genotype/sex were used in the experiments, unless otherwise stated. Males and females were analyzed separately. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). Statistically significant differences were determined using the Student’s t-test. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All values are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
References
Cao Z, Zhang H, Zhou X, Han X, Ren Y, Gao T, Xiao Y, de Crombrugghe B, Somerman MJ, Feng JQ (2012) Genetic evidence for the vital function of osterix in cementogenesis. J Bone Miner Res 27:1080–1092
Biosse Duplan M, Coyac BR, Bardet C, Zadikian C, Rothenbuhler A, Kamenicky P, Briot K, Linglart A, Chaussain C (2017) Phosphate and vitamin D prevent periodontitis in X-linked hypophosphatemia. J Dent Res 96:388–395
Nociti FH Jr, Berry JE, Foster BL, Gurley KA, Kingsley DM, Takata T, Miyauchi M, Somerman MJ (2002) Cementum: a phosphate-sensitive tissue. J Dent Res 81:817–821
Ao M, Chavez MB, Chu EY, Hemstreet KC, Yin Y, Yadav MC, Millan JL, Fisher LW, Goldberg HA, Somerman MJ, Foster BL (2017) Overlapping functions of bone sialoprotein and pyrophosphate regulators in directing cementogenesis. Bone 105:134–147
Nagasaki A, Nagasaki K, Chu EY, Kear BD, Tadesse WD, Ferebee SE, Li L, Foster BL, Somerman MJ (2021) Ablation of pyrophosphate regulators promotes periodontal regeneration. J Dent Res 100:639–647
Zweifler LE, Patel MK, Nociti FH Jr, Wimer HF, Millan JL, Somerman MJ, Foster BL (2015) Counter-regulatory phosphatases TNAP and NPP1 temporally regulate tooth root cementogenesis. Int J Oral Sci 7:27–41
Chu EY, Vo TD, Chavez MB, Nagasaki A, Mertz EL, Nociti FH, Aitken SF, Kavanagh D, Zimmerman K, Li X, Stabach PR, Braddock DT, Millan JL, Foster BL, Somerman MJ (2020) Genetic and pharmacologic modulation of cementogenesis via pyrophosphate regulators. Bone 136:115329
Beumer J 3rd, Trowbridge HO, Silverman S Jr, Eisenberg E (1973) Childhood hypophosphatasia and the premature loss of teeth. a clinical and laboratory study of seven cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 35:631–640
Lundgren T, Westphal O, Bolme P, Modeer T, Noren JG (1991) Retrospective study of children with hypophosphatasia with reference to dental changes. Scand J Dent Res 99:357–364
van den Bos T, Handoko G, Niehof A, Ryan LM, Coburn SP, Whyte MP, Beertsen W (2005) Cementum and dentin in hypophosphatasia. J Dent Res 84:1021–1025
Foster BL, Ramnitz MS, Gafni RI, Burke AB, Boyce AM, Lee JS, Wright JT, Akintoye SO, Somerman MJ, Collins MT (2014) Rare bone diseases and their dental, oral, and craniofacial manifestations. J Dent Res 93:7S-19S
Kuzynski M, Goss M, Bottini M, Yadav MC, Mobley C, Winters T, Poliard A, Kellermann O, Lee B, Millan JL, Napierala D (2014) Dual role of the Trps1 transcription factor in dentin mineralization. J Biol Chem 289:27481–27493
Kantaputra P, Miletich I, Ludecke HJ, Suzuki EY, Praphanphoj V, Shivdasani R, Wuelling M, Vortkamp A, Napierala D, Sharpe PT (2008) Tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome with supernumerary teeth. J Dent Res 87:1027–1031
Momeni P, Glockner G, Schmidt O, von Holtum D, Albrecht B, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Hennekam R, Meinecke P, Zabel B, Rosenthal A, Horsthemke B, Ludecke HJ (2000) Mutations in a new gene, encoding a zinc-finger protein, cause tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome type I. Nat Genet 24:71–74
Maas SM, Shaw AC, Bikker H, Ludecke HJ, van der Tuin K, Badura-Stronka M, Belligni E, Biamino E, Bonati MT, Carvalho DR, Cobben J, de Man SA, Den Hollander NS, Di Donato N, Garavelli L, Gronborg S, Herkert JC, Hoogeboom AJ, Jamsheer A, Latos-Bielenska A, Maat-Kievit A, Magnani C, Marcelis C, Mathijssen IB, Nielsen M, Otten E, Ousager LB, Pilch J, Plomp A, Poke G, Poluha A, Posmyk R, Rieubland C, Silengo M, Simon M, Steichen E, Stumpel C, Szakszon K, Polonkai E, van den Ende J, van der Steen A, van Essen T, van Haeringen A, van Hagen JM, Verheij JB, Mannens MM, Hennekam RC (2015) Phenotype and genotype in 103 patients with tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome. Eur J Med Genet 58:279–292
Napierala D, Sam K, Morello R, Zheng Q, Munivez E, Shivdasani RA, Lee B (2008) Uncoupling of chondrocyte differentiation and perichondrial mineralization underlies the skeletal dysplasia in tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 17:2244–2254
Bennett CG, Hill CJ, Frias JL (1981) Facial and oral findings in trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 (characteristics of TRPS 1). Pediatr Dent 3:348–352
Goss M, Socorro M, Monier D, Verdelis K, Napierala D (2019) Trps1 transcription factor regulates mineralization of dental tissues and proliferation of tooth organ cells. Mol Genet Metab 126:504–512
Socorro M, Hoskere P, Roberts C, Lukashova L, Verdelis K, Beniash E, Napierala D (2022) Deficiency of mineralization-regulating transcription factor Trps1 compromises quality of dental tissues and increases susceptibility to dental caries. Front Dent Med. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdmed.2022.875987
Wang L, Lu W, Zhang L, Huang Y, Scheib R, Liu X, Myers L, Lu L, Farber CR, Liu G, Wang CY, Deng H, Williams RW, Wang Y, Gu W, Jiao Y (2014) Trps1 differentially modulates the bone mineral density between male and female mice and its polymorphism associates with BMD differently between women and men. PLoS ONE 9:e84485
Nagata M, Chu AKY, Ono N, Welch JD, Ono W (2021) Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals developmental relationships and specific markers of mouse periodontium cellular subsets. Front Dent Med. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdmed.2021.679937
Beertsen W, VandenBos T, Everts V (1999) Root development in mice lacking functional tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase gene: inhibition of acellular cementum formation. J Dent Res 78:1221–1229
Foster BL, Soenjaya Y, Nociti FH Jr, Holm E, Zerfas PM, Wimer HF, Holdsworth DW, Aubin JE, Hunter GK, Goldberg HA, Somerman MJ (2013) Deficiency in acellular cementum and periodontal attachment in bsp null mice. J Dent Res 92:166–172
Foster BL, Ao M, Willoughby C, Soenjaya Y, Holm E, Lukashova L, Tran AB, Wimer HF, Zerfas PM, Nociti FH Jr, Kantovitz KR, Quan BD, Sone ED, Goldberg HA, Somerman MJ (2015) Mineralization defects in cementum and craniofacial bone from loss of bone sialoprotein. Bone 78:150–164
Divaris K, Monda KL, North KE, Olshan AF, Lange EM, Moss K, Barros SP, Beck JD, Offenbacher S (2012) Genome-wide association study of periodontal pathogen colonization. J Dent Res 91:21S-28S
Suemoto H, Muragaki Y, Nishioka K, Sato M, Ooshima A, Itoh S, Hatamura I, Ozaki M, Braun A, Gustafsson E, Fassler R (2007) Trps1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes through Stat3 signaling. Dev Biol 312:572–581
Fantauzzo KA, Kurban M, Levy B, Christiano AM (2012) Trps1 and its target gene Sox9 regulate epithelial proliferation in the developing hair follicle and are associated with hypertrichosis. PLoS Genet 8:e1003002
Kim TH, Bae CH, Lee JC, Kim JE, Yang X, de Crombrugghe B, Cho ES (2015) Osterix regulates tooth root formation in a site-specific manner. J Dent Res 94:430–438
Cao Z, Liu R, Zhang H, Liao H, Zhang Y, Hinton RJ, Feng JQ (2015) Osterix controls cementoblast differentiation through downregulation of Wnt-signaling via enhancing DKK1 expression. Int J Biol Sci 11:335–344
Bae CH, Choi H, You HK, Cho ES (2017) Wnt activity is associated with cementum-type transition. J Periodontal Res 52:334–341
Bae CH, Lee JY, Kim TH, Baek JA, Lee JC, Yang X, Taketo MM, Jiang R, Cho ES (2013) Excessive Wnt/β-catenin signaling disturbs tooth-root formation. J Periodontal Res 48:405–410
Fantauzzo KA, Christiano AM (2012) Trps1 activates a network of secreted Wnt inhibitors and transcription factors crucial to vibrissa follicle morphogenesis. Development 139:203–214
Wuelling M, Schneider S, Schrother VA, Waterkamp C, Hoffmann D, Vortkamp A (2020) Wnt5a is a transcriptional target of Gli3 and Trps1 at the onset of chondrocyte hypertrophy. Dev Biol 457:104–118
Coyac BR, Falgayrac G, Baroukh B, Slimani L, Sadoine J, Penel G, Biosse-Duplan M, Schinke T, Linglart A, McKee MD, Chaussain C, Bardet C (2017) Tissue-specific mineralization defects in the periodontium of the Hyp mouse model of X-linked hypophosphatemia. Bone 103:334–346
Foster BL, Kuss P, Yadav MC, Kolli TN, Narisawa S, Lukashova L, Cory E, Sah RL, Somerman MJ, Millan JL (2017) Conditional Alpl ablation phenocopies dental defects of hypophosphatasia. J Dent Res 96:81–91
Baab DA, Page RC, Ebersole JL, Williams BL, Scott CR (1986) Laboratory studies of a family manifesting premature exfoliation of deciduous teeth. J Clin Periodontol 13:677–683
Chavez MB, Kramer K, Chu EY, Thumbigere-Math V, Foster BL (2020) Insights into dental mineralization from three heritable mineralization disorders. J Struct Biol 212:107597
Foster BL (2012) Methods for studying tooth root cementum by light microscopy. Int J Oral Sci 4:119–128
Foster BL, Nagatomo KJ, Nociti FH Jr, Fong H, Dunn D, Tran AB, Wang W, Narisawa S, Millán JL, Somerman MJ (2012) Central role of pyrophosphate in acellular cementum formation. PLoS ONE 7:e38393
Zhang H, Chavez MB, Kolli TN, Tan MH, Fong H, Chu EY, Li Y, Ren X, Watanabe K, Kim DG, Foster BL (2020) Dentoalveolar defects in the Hyp mouse model of x-linked hypophosphatemia. J Dent Res 99:419–428
Obradovic A, Ager C, Turunen M, Nirschl T, Khosravi-Maharlooei M, Iuga A, Jackson CM, Yegnasubramanian S, Tomassoni L, Fernandez EC, McCann P, Rogava M, DeMarzo AM, Kochel CM, Allaf M, Bivalacqua T, Lim M, Realubit R, Karan C, Drake CG, Califano A (2023) Systematic elucidation and pharmacological targeting of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cell master regulators. Cancer Cell 41(933–949):e911
Nottmeier C, Decker MG, Luther J, von Kroge S, Kahl-Nieke B, Amling M, Schinke T, Petersen J, Koehne T (2020) Accelerated tooth movement in Rsk2-deficient mice with impaired cementum formation. Int J Oral Sci 12:35
Carpenter KA, Alkhatib DO, Dulion BA, Guirado E, Patel S, Chen Y, George A, Ross RD (2023) Sclerostin antibody improves alveolar bone quality in the Hyp mouse model of X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH). Int J Oral Sci 15:47
Koehne T, Jeschke A, Petermann F, Seitz S, Neven M, Peters S, Luther J, Schweizer M, Schinke T, Kahl-Nieke B, Amling M, David JP (2016) Rsk2, the kinase mutated in coffin-lowry syndrome, controls cementum formation. J Dent Res 95:752–760
Lim JC, Bae SH, Lee G, Ryu CJ, Jang YJ (2020) Activation of β-catenin by TGF-β1 promotes ligament-fibroblastic differentiation and inhibits cementoblastic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. Stem Cells. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.3275
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Catherine Roberts and Jin Gao for technical assistance. The authors thank Dr. Renny Franceschi for providing anti-Bsp antibodies. This work was supported by National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, and National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under awards number DE023083 and AR074981, respectively (to DN); and National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research award F32DE029096 (to MS).
Funding
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, DE023083, Dobrawa Napierala, F32DE029096, Mairobys Socorro, National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, AR074981, Dobrawa Napierala.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.F. contributed to the design of the study, performed most of the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the data, drafted and revised the manuscript. M.S. contributed to the design of the study, performed μCT analysis, interpreted the data and revised the manuscript. L.L. and K.V. contributed to μCT data acquisition, analysis and interpretation. P.H. and P.K contributed to the analyses of the alveolar bone μCT data, D.N contributed to conception, design, data analyses and interpretation, drafted and revised the manuscript. The authors gave final approval and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Kaoru Fujikawa, Mairobys Socorro, Lyudmila Lukashova, Priyanka Hoskere, Paulina Keskinidis, Kostas Verdelis, Dobrawa Napierala, there is no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Fujikawa, K., Socorro, M., Lukashova, L. et al. Deficiency of Trps1 in Cementoblasts Impairs Cementogenesis and Tooth Root Formation. Calcif Tissue Int (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-024-01277-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-024-01277-2