Abstract
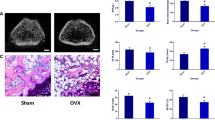
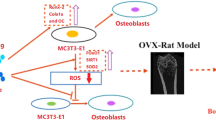
Osteoporosis-related bone defects are a major public health concern. Considering poor effects of a singular pharmacological treatment, many have sought combination therapies, including local treatment combined with systemic intervention. Based on recent evidence that selenium and silibinin increase bone formation and bone mineral density, it is hypothesized that systemic administration with silibinin plus local treatment with selenium may have an additive effect on bone regeneration in an OVX rat model with bone defects. To verify this hypothesis, 3-month-old ovariectomized Sprague- Dawley rats (n = 10/gp) were intraperitoneally with a dose of 50 mg/kg silibinin with selenium hydrogel scaffolds implanted into femoral metaphysis bone defect. Moreover, the MC3T3-E1 cells were co-cultured with selenium and silibinin, and observed any change of cell viability, ROS, and osteogenic activity. Experiment results show that the cell mineralization and osteogenic activity of silibinin plus selenium (SSe) group is enormously higher than the control (Con) group and selenium (Se) group, while ROS appears to be immensely reduced. Osteogenic protein expressions such as SIRT1, SOD2, RUNX-2 and OC of SSe group are significantly higher than Con group and Se group. Micro-CT and Histological analysis evaluation display that group SSe, compared with Con group and Se group, presents the strongest effect on bone regeneration, bone mineralization and higher expression of SIRT1 and SOD2. RT-qPCR analysis indicates that SSe group manifests increased SIRT1, SOD1, SOD2 and CAT than the Con group and Se group (p < 0.05). Our current study demonstrates that systemic administration with SIL plus local treatment with Se is a scheme for rapid repair of femoral condylar defects, and these effects may be achieved via reducing the oxidative stress pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cosman F (2020) Anabolic therapy and optimal treatment sequences for patients with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture. Endocr Pract 26(7):777–786
Abidin N, Mitra S (2020) Total vs. bioavailable: determining a better 25(OH)D index in association with bone density and muscle mass in postmenopausal women. Metabolites 11(1):23
Tao Z, Zhou W, Wu X et al (2019) Single-dose local administration of parathyroid hormone (1–34, PTH) with β-tricalcium phosphate/collagen (β-TCP/COL) enhances bone defect healing in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Metab 37(1):28–35
Liu X, Chin J, Qu X et al (2017) The beneficial effect of praeruptorin C on osteoporotic bone in ovariectomized mice via suppression of osteoclast formation and bone resorption. Front Pharmacol 8:627
Liang B, Shi Q, Xu J et al (2020) Poly (glycerol sebacate)-based bio-artificial multiporous matrix for bone regeneration. Front Chem 8:603577
Schmidt A (2021) Autologous bone graft: is it still the gold standard? Injury 52:S18–S22
Bharadwaz A, Jayasuriya A (2021) Osteogenic differentiation cues of the bone morphogenetic protein-9 (BMP-9) and its recent advances in bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C 120:111748
Lee B, Lobanov A, Marino S et al (2011) A 4-selenocysteine, 2-selenocysteine insertion sequence (SECIS) element methionine sulfoxide reductase from metridium senile reveals a non-catalytic function of selenocysteines. J Biol Chem 286(21):18747–18755
Dumitrescu AM, Liao XH, Abdullah MS et al (2005) Mutations in SECISBP2 result in abnormal thyroid hormone metabolism. Nat Genet 37(11):1247–1252
Schoenmakers E, Agostini M, Mitchell C et al (2010) Mutations in the selenocysteine insertion sequence-binding protein 2 gene lead to a multisystem selenoprotein deficiency disorder in humans. J Clin Investig 120(12):4220–4235
Murphy E, Gluer CC, Reid DM et al (2010) Thyroid function within the upper normal range is associated with reduced bone mineral density and an increased risk of nonvertebral fractures in healthy euthyroid postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(7):3173–3181
Hoeg A, Gogakos A, Murphy E et al (2012) Bone turnover and bone mineral density are independently related to selenium status in healthy euthyroid postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(11):4061–4070
Song J, Jeon Y, Tian J et al (2019) Evaluation of silymarin/duck’s feet-derived collagen/hydroxyapatite sponges for bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C 97:347–355
Shen Y, Zhao H, Wang Z et al (2019) Silibinin declines blue light-induced apoptosis and inflammation through MEK/ERK/CREB of retinal ganglion cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47(1):4059–4065
Rajalakshmi S, Vimalraj S, Saravanan S et al (2018) Synthesis and characterization of silibinin/phenanthroline/neocuproine copper(II) complexes for augmenting bone tissue regeneration: an in vitro analysis. J Biol Inorg Chem 23(5):753–762
Vimalraj S, Rajalakshmi S, Saravanan S et al (2018) Synthesis and characterization of zinc-silibinin complexes: a potential bioactive compound with angiogenic, and antibacterial activity for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B 167:134–143
Ying X, Sun L, Chen X et al (2013) Silibinin promotes osteoblast differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells via bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 721:225–230
Wang T, Cai L, Wang Y et al (2017) The protective effects of silibinin in the treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetic osteoporosis in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 89:681–688
Ying X, Chen X, Liu H et al (2015) Silibinin alleviates high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells via antioxidant effect and PI3K/Akt signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 765:394–401
Zhang W, Sun C, Zhu J et al (2020) 3D printed porous titanium cages filled with simvastatin hydrogel promotes bone ingrowth and spinal fusion in rhesus macaques. Biomater Sci 8(15):4147–4156
Tao ZS, Lv YX, Cui W et al (2016) Effect of teriparatide on repair of femoral metaphyseal defect in ovariectomized rats. Z Gerontol Geriatr 49(5):423–428
Tao ZS, Wu XJ, Zhou WS et al (2019) Local administration of aspirin with beta-tricalcium phosphate/poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (beta-TCP/PLGA) could enhance osteoporotic bone regeneration. J Bone Miner Metab 37(6):1026–1035
Tao ZS, Zhou WS, Xu HG et al (2020) Aspirin modified strontium-doped beta-tricalcium phosphate can accelerate the healing of femoral metaphyseal defects in ovariectomized rats. Biomed Pharmacother 132:110911
Tao ZS, Zhou WS, Wu XJ et al (2019) Single-dose local administration of parathyroid hormone (1–34, PTH) with beta-tricalcium phosphate/collagen (beta-TCP/COL) enhances bone defect healing in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Metab 37(1):28–35
Alsaggar M, Bdour S, Ababneh Q et al (2020) Silibinin attenuates adipose tissue inflammation and reverses obesity and its complications in diet-induced obesity model in mice. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 21(1):8
Li YF, Li XD, Bao CY et al (2013) Promotion of peri-implant bone healing by systemically administered parathyroid hormone (1–34) and zoledronic acid adsorbed onto the implant surface. Osteoporos Int 24(3):1063–1071
Gabet Y, Kohavi D, Kohler T et al (2008) Trabecular bone gradient in rat long bone metaphyses: mathematical modeling and application to morphometric measurements and correction of implant positioning. J Bone Miner Res 23(1):48–57
Hao Y, Yingjie H, Zhang G et al (2007) Changes of microstructure and mineralized tissue in the middle and late phase of osteoporotic fracture healing in rats. Bone 41(4):631–638
He Y, Zhang G, Pan X et al (2011) Impaired bone healing pattern in mice with ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis: a drill-hole defect model. Bone 48(6):1388–1400
Xue D, Chen E, Zhong H et al (2018) Immunomodulatory properties of graphene oxide for osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Int J Nanomed 13:5799–5810
Zhao F, Yao D, Guo R et al (2015) Composites of polymer hydrogels and nanoparticulate systems for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland) 5(4):2054–2130
Syed D, Afaq F, Sarfaraz S et al (2008) Delphinidin inhibits cell proliferation and invasion via modulation of Met receptor phosphorylation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 231(1):52–60
Shafiee A, Kehtari M, Zarei Z et al (2021) An in situ hydrogel-forming scaffold loaded by PLGA microspheres containing carbon nanotube as a suitable niche for neural differentiation. Materi Sci Eng C 120:111739
Mahmoud A, Ibrahim H, El-Sawi M et al (2020) Effects of silymarin and mesenchymal stem cells on hematological and some biochemical changes induced by gamma radiation in albino rats. Int J Radiat Biol 96(2):220–227
Faedmaleki F, Shirazi F, Ejtemaeimehr S et al (2016) Study of silymarin and vitamin E protective effects on silver nanoparticle toxicity on mice liver primary cell culture. Acta Med Iran 54(2):85–95
Wang Y, Hao H, Zhang S (2016) Lysozyme loading and release from Se doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Materi Sci Eng C 61:545–552
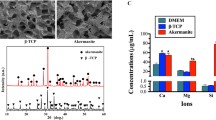
Li T, Tao Z, Wu X et al (2021) Selenium-modified calcium phosphate cement can accelerate bone regeneration of osteoporotic bone defect. J Bone Miner Metab 39(6):934–943
Kim J, Kang S, Kang M et al (2012) Osteoblastogenesis and osteoprotection enhanced by flavonolignan silibinin in osteoblasts and osteoclasts. J Cell Biochem 113(1):247–259
Honoki K (2017) Preventing aging with stem cell rejuvenation: feasible or infeasible? World J Stem Cells 9(1):1–8
Nasto L, Robinson A, Ngo K et al (2013) Mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a causal role in aging-related intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res 31(7):1150–1157
Liu C, Zhu R, Liu H et al (2018) Aqueous extract of mori folium exerts bone protective effect through regulation of calcium and redox homeostasis via PTH/VDR/CaBP and AGEs/RAGE/Nox4/NF-κB signaling in diabetic rats. Front Pharmacol 9:1239
Shao J, Liu S, Zheng X et al (2021) Berberine promotes peri-implant osteogenesis in diabetic rats by ROS-mediated IRS-1 pathway. BioFactors (Oxford, England) 47(1):80–92
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (82002322), Funding of “Peak” Training Program and “Panfeng” Innovation Team Project for Scientific Research of Yijishan Hospital, Wannan Medical College (Grant No. GF2019G04, PF2019005, GF2019T02 and PF2019007) and Young and Middle-aged Key Project of Wannan Medical College (WK2020ZF16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Zhoushan Tao, Tian-Lin Li, Min Yang and Hong-Guang Xu declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Research involving Human and Animal Rights
All aspects of this research were conducted in accordance with the Chinese Guidelines for Animal Welfare and Experimental Protocols. All animal experiments were performed under the approval of the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wannan Medical College, Yijishan Hospital.
Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, Z., Li, TL., Yang, M. et al. Silibinin Can Promote Bone Regeneration of Selenium Hydrogel by Reducing the Oxidative Stress Pathway in Ovariectomized Rats. Calcif Tissue Int 110, 723–735 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-021-00936-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-021-00936-y