Abstract
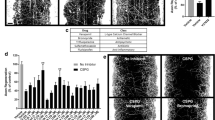
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a bioactive lysophospholipid that causes neuronal growth cones to collapse and neurites to retract through a RhoA-ROCK mediated pathway. It has been reported that the NSAID ibuprofen improves regeneration after spinal cord injury through a mechanism of inhibiting RhoA. This leads to the hypothesis that ibuprofen should block LPA-mediated growth cone collapse. We tested this hypothesis by treating embryonic chick retinal neurons with ibuprofen followed by LPA. Retinal growth cones collapsed with LPA in the presence of ibuprofen similar to control; however, growth cone collapse was effectively blocked by a ROCK inhibitor. Thus, our results do not support the designation of ibuprofen as a direct RhoA inhibitor.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files]. Any other materials available upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Benowitz LI, He Z, Goldberg JL (2017) Reaching the brain: advances in optic nerve regeneration. Exp Neurol 287:365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.12.015
Bertrand J, Winton MJ, Rodriguez-Hernandez N, Campenot RB, McKerracher L (2005) Application of Rho antagonist to neuronal cell bodies promotes neurite growth in compartmented cultures and regeneration of retinal ganglion cell axons in the optic nerve of adult rats. J Neurosci 25:1113–1121
Birgbauer E (2021) Lysophosphatidic Acid Signalling in Nervous System Development and Function. Neuromolecular Med 23:68–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-020-08630-2
Birgbauer E, Chun J (2010) Lysophospholipid receptors LPA1–3 are not required for the inhibitory effects of LPA on mouse retinal growth cones. Eye and Brain 2010:1–13
Campbell DS, Holt CE (2001) Chemotropic responses of retinal growth cones mediated by rapid local protein synthesis and degradation. Neuron 32:1013–1026
Campbell DS, Holt CE (2003) Apoptotic pathway and MAPKs differentially regulate chemotropic responses of retinal growth cones. Neuron 37:939–952
Choi JW, Chun J (2013) Lysophospholipids and their receptors in the central nervous system. Biochim Biophys Acta 1831:20–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.07.015
Crair MC, Mason CA (2016) Reconnecting eye to brain. J Neurosci 36:10707–10722. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1711-16.2016
Dergham P, Ellezam B, Essagian C, Avedissian H, Lubell WD, McKerracher L (2002) Rho signaling pathway targeted to promote spinal cord repair. J Neurosci 22:6570–6577. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-15-06570.2002 (20026637)
Dill J, Patel AR, Yang X-L, Bachoo R, Powell CM, Li S (2010) A molecular mechanism for ibuprofen-mediated RhoA inhibition in neurons. J Neurosci 30:963–972. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5045-09.2010
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420:629–635
Fawcett JW (2020) The struggle to make CNS axons regenerate: why has it been so difficult? Neurochem Res 45:144–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02844-y
Fehlings MG, Theodore N, Harrop J et al (2011) A phase I/IIa clinical trial of a recombinant Rho protein antagonist in acute spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 28:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2011.1765
Ferrera P, Zepeda A, Arias C (2017) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs attenuate amyloid-beta protein-induced actin cytoskeletal reorganization through Rho signaling modulation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:1311–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0467-3
Fincher J, Whiteneck C, Birgbauer E (2014) G-protein-coupled receptor cell signaling pathways mediating embryonic chick retinal growth cone collapse induced by lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine-1-phosphate. Dev Neurosci 36:443–453. https://doi.org/10.1159/000364858
Fu Q, Hue J, Li S (2007) Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Promote Axon Regeneration via RhoA Inhibition. J Neurosci 27:4154–4164. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4353-06.2007
Fujita Y, Yamashita T (2014) Axon growth inhibition by RhoA/ROCK in the central nervous system. Front Neurosci 8:338. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2014.00338
Govek EE, Newey SE, Van Aelst L (2005) The role of the Rho GTPases in neuronal development. Genes Dev 19:1–49
Hall A, Lalli G (2010) Rho and Ras GTPases in axon growth, guidance, and branching. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:a001818. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a001818
Huang LT, Lin CH, Chou HC, Chen CM (2014) Ibuprofen protects ventilator-induced lung injury by downregulating Rho-kinase activity in rats. Biomed Res Int 2014:749097. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/749097
Huber AB, Kolodkin AL, Ginty DD, Cloutier JF (2003) Signaling at the growth cone: ligand-receptor complexes and the control of axon growth and guidance. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:509–563
Jalink K, Eichholtz T, Postma FR, van Corven EJ, Moolenaar WH (1993) Lysophosphatidic acid induces neuronal shape changes via a novel, receptor-mediated signaling pathway: similarity to thrombin action. Cell Growth Differ 4:247–255
Jalink K, van Corven EJ, Hengeveld T, Morii N, Narumiya S, Moolenaar WH (1994) Inhibition of lysophosphatidate- and thrombin-induced neurite retraction and neuronal cell rounding by ADP ribosylation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J Cell Biol 126:801–810
Kihara Y, Maceyka M, Spiegel S, Chun J (2014) Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature review: IUPHAR Review 8. Br J Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12678
Kopp MA, Liebscher T, Niedeggen A et al (2012) Small-molecule-induced rho-inhibition: NSAIDs after spinal cord injury. Cell Tissue Res 349:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-012-1334-7
Kopp MA, Liebscher T, Watzlawick R et al (2016) SCISSOR-spinal cord injury study on small molecule-derived rho inhibition: a clinical study protocol. BMJ Open 6:e010651. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010651
Kozma R, Sarner S, Ahmed S, Lim L (1997) Rho family GTPases and neuronal growth cone remodelling: relationship between increased complexity induced by Cdc42Hs, Rac1, and acetylcholine and collapse induced by RhoA and lysophosphatidic acid. Mol Cell Biol 17:1201–1211
Laha B, Stafford BK, Huberman AD (2017) Regenerating optic pathways from the eye to the brain. Science 356:1031–1034. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal5060
Lehmann JM, Lenhard JM, Oliver BB, Ringold GM, Kliewer SA (1997) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma are activated by indomethacin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Biol Chem 272:3406–3410
Lehmann M, Fournier A, Selles-Navarro I et al (1999) Inactivation of Rho signaling pathway promotes CNS axon regeneration. J Neurosci 19:7537–7547
Li X, Du J, Xu S, Lin X, Ling Z (2013) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist rosiglitazone reduces secondary damage in experimental spinal cord injury. J Int Med Res 41:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060513476601
Luo L (2000) Rho GTPases in neuronal morphogenesis. Nat Rev Neurosci 1:173–180
Madura T, Tomita K, Terenghi G (2011) Ibuprofen improves functional outcome after axotomy and immediate repair in the peripheral nervous system. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64:1641–1646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2011.07.014
McKerracher L, Higuchi H (2006) Targeting Rho to stimulate repair after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 23:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2006.23.309
Miglio G, Rattazzi L, Rosa AC, Fantozzi R (2009) PPARgamma stimulation promotes neurite outgrowth in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Lett 454:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.014
Narumiya S, Thumkeo D (2018) Rho signaling research: history, current status and future directions. FEBS Lett 592:1763–1776. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13087
Park SW, Yi JH, Miranpuri G, Satriotomo I, Bowen K, Resnick DK, Vemuganti R (2007) Thiazolidinedione class of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists prevents neuronal damage, motor dysfunction, myelin loss, neuropathic pain, and inflammation after spinal cord injury in adult rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:1002–1012. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.113472
Patel P, Parikh M, Shah H, Gandhi T (2016) Inhibition of RhoA/Rho kinase by ibuprofen exerts cardioprotective effect on isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 791:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.08.015
Pelham CJ, Ketsawatsomkron P, Groh S et al (2012) Cullin-3 regulates vascular smooth muscle function and arterial blood pressure via PPARgamma and RhoA/Rho-kinase. Cell Metab 16:462–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.08.011
Ramirez SH, Heilman D, Morsey B, Potula R, Haorah J, Persidsky Y (2008) Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) suppresses Rho GTPases in human brain microvascular endothelial cells and inhibits adhesion and transendothelial migration of HIV-1 infected monocytes. J Immunol 180:1854–1865. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.180.3.1854
Redondo-Castro E, Navarro X (2014) Chronic ibuprofen administration reduces neuropathic pain but does not exert neuroprotection after spinal cord injury in adult rats. Exp Neurol 252:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.11.008
Roloff F, Scheiblich H, Dewitz C, Dempewolf S, Stern M, Bicker G (2015) Enhanced neurite outgrowth of human model (NT2) neurons by small-molecule inhibitors of Rho/ROCK signaling. PLoS ONE 10:e0118536. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118536
Saito S (1997) Effects of lysophosphatidic acid on primary cultured chick neurons. Neurosci Lett 229:73–76
Scheiblich H, Bicker G (2017) Regulation of microglial phagocytosis by RhoA/ROCK-inhibiting drugs. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:461–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0379-7
Schill EM, Lake JI, Tusheva OA et al (2016) Ibuprofen slows migration and inhibits bowel colonization by enteric nervous system precursors in zebrafish, chick and mouse. Dev Biol 409:473–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.09.023
Sharp KG, Yee KM, Stiles TL, Aguilar RM, Steward O (2013) A re-assessment of the effects of treatment with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (ibuprofen) on promoting axon regeneration via RhoA inhibition after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 248:321–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.06.023
Tigyi G, Fischer DJ, Sebok A, Marshall F, Dyer DL, Miledi R (1996a) Lysophosphatidic acid-induced neurite retraction in PC12 cells: neurite-protective effects of cyclic AMP signaling. J Neurochem 66:549–558
Tigyi G, Fischer DJ, Sebok A, Yang C, Dyer DL, Miledi R (1996b) Lysophosphatidic acid-induced neurite retraction in PC12 cells: control by phosphoinositide-Ca2+ signaling and Rho. J Neurochem 66:537–548
Ueyama T (2019) Rho-family small GTPases: from highly polarized sensory neurons to cancer cells. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020092
Villapol S (2018) Roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma on brain and peripheral inflammation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0554-5
Wakino S, Hayashi K, Kanda T et al (2004) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands inhibit Rho/Rho kinase pathway by inducing protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2. Circ Res 95:e45-55. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000142313.68389.92
Wang X, Budel S, Baughman K, Gould G, Song K-H, Strittmatter SM (2009) Ibuprofen enhances recovery from spinal cord injury by limiting tissue loss and stimulating axonal growth. J Neurotrauma 26:81–95. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2007.0464
Watabe-Uchida M, Govek EE, Van Aelst L (2006) Regulators of Rho GTPases in neuronal development. J Neurosci 26:10633–10635
Watanabe M (2010) Regeneration of optic nerve fibers of adult mammals. Dev Growth Differ 52:567–576. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-169X.2010.01203.x
Watzlawick R, Sena ES, Dirnagl U et al (2014) Effect and reporting bias of RhoA/ROCK-blockade intervention on locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol 71:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.4684
Xing B, Li H, Wang H, Mukhopadhyay D, Fisher D, Gilpin CJ, Li S (2011) RhoA-inhibiting NSAIDs promote axonal myelination after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 231:247–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.06.018
Zhou Y, Su Y, Li B et al (2003) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can lower amyloidogenic Abeta42 by inhibiting Rho. Science 302:1215–1217. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1090154
Acknowledgements
We thank Eva Hermanova and Allison Reed for assistance with blind observer counts.
Funding
This research was supported by grant REY024453A from the National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health to E.B. and P20GM103499 (SC INBRE) from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, National Institutes of Health and from Winthrop University Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by all authors; JV and EB performed and analyzed growth cone collapse assay data and AA and EB performed and analyzed time-lapse data. The first draft of the manuscript was written by EB and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent for publication.
Additional information
Communicated by Thomas Deller.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Movie 1 Time-lapse imaging of the chick retinal growth cone from Figure 5. A growth cone is observed growing initially under control conditions, then ibuprofen is added at 50 µM and the growth cone continues to grow. Finally, LPA is added to a concentration of 100 nM and the growth cone collapses and the neurite retracts. The time-lapse displayed encompasses 51 minutes with frames at 30 second intervals
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinton, J., Aninweze, A. & Birgbauer, E. Ibuprofen does not inhibit RhoA-mediated growth cone collapse of embryonic chicken retinal axons by LPA. Exp Brain Res 239, 2969–2977 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-021-06172-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-021-06172-y