Abstract
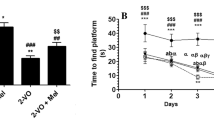
Professionals and mountaineers often face the problem of reperfusion injury due to re-oxygenation, upon their return to sea-level after sojourn at high altitude. Small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (SK channels) have a role in regulating hippocampal synaptic plasticity. However, the role of SK channels under hypoxia-reoxygenation (H/R) is unknown. The present study hypothesized that SK channels play a significant role in H/R induced cognitive dysfunction. Sprague–Dawley rats were exposed to simulated HH (25,000 ft) continuously for 7 days followed by reoxygenation periods 3, 6, 24, 48, 72 and 120 h. It was observed that H/R exposure caused impairment in spatial memory as indicated by increased latency (p < 0.001) and pathlength (p < 0.001). The SK1 channel expression increased upon HH exposure (102.89 ± 7.055), which abrogated upon reoxygenation. HH exposure results in an increase in SK2 (CA3, 297.67 ± 6.69) and SK3 (CA1, 246 ± 5.13) channels which continued to increase gradually upon reoxygenation. The number of pyknotic cells (24 ± 2.03) (p < 0.01) and the expression of caspase-3 increased with HH exposure, which continued in the reoxygenation group (177.795 ± 1.264). Similar pattern was observed in lipid peroxidation (p < 0.001), LDH activity (p < 0.001) and ROS production (p < 0.001). A positive correlation of memory, cell death and oxidative stress indicates that H/R exposure increases oxidative stress coupled with SK channel expression, which may play a role in H/R-induced cognitive decline and neurodegeneration.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Na.
References
Adelman JP, Maylie J, Sah P (2012) Small-Conductance Ca 2+ -Activated K + channels: form and function. Annu Rev Physiol 74:245–269. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-020911-153336
Baeyens D, Meier M (1978) Effects of hyperbaric hypoxia on some enzyme systems in the mammalian liver. J Ark Acad Sci 32:22–24
Ballanyi K (2004) Protective role of neuronal K ATP channels in brain hypoxia. J Exp Biol 207:3201–3212. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01106
Barhwal K, Singh SB, Hota SK et al (2007) Acetyl- L -Carnitine ameliorates hypobaric hypoxic impairment and spatial memory deficits in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 570:97–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.05.063
Biswal S, Sharma D, Kumar K et al (2016) Global hypoxia induced impairment in learning and spatial memory is associated with precocious hippocampal aging. Neurobiol Learn Mem 133:157–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2016.05.011
Bloodgood BL, Sabatini BL (2007) Nonlinear regulation of unitary synaptic by CaV2.3 voltage- sensitive calcium channels located in dendritic spines. Neuron 53:249–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.12.017
Bock T, Stuart GJ, Martina M (2016) The impact of BK channels on cellular excitability depends on their subcellular location. Front Cell Neurosci 10:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00206
Boero JA, Ascher J, Arregui A et al (1999) Increased brain capillaries in chronic hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 86:1211–1219. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1999.86.4.1211
Bond CT, Maylie J, Adelman JP (1999) Small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci 868:370–378. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb11298.x
Bond CT, Sprengel R, Bissonnette JM, et al (2000) Respiration and Pafiurition Affected by Conditional Overexpression of the Ca2+- Activated K+ Channel Subunit, SK3
Bond CT, Maylie J, Adelman JP (2005) SK channels in excitability, pacemaking and synaptic integration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2005.05.001
Borutaite V, Jekabsone A, Morkuniene R, Brown GC (2003) Inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition prevents mitochondrial dysfunction, cytochrome c release and apoptosis induced by heart ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol 35:357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2828(03)00005-1
Boyle LM (2013) A neuroplasticity hypothesis of chronic stress in the basolateral amygdala. Yale J Biol Med 86:117–125
Brandies R, Brandys Y, Yehuda S (1989) The use of the morris water maze in the study of memory and learning. Int J Neurosci 48:29–69. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207458909002151
Buchanan KA, Petrovic MM, Chamberlain SEL et al (2010) Facilitation of long-term potentiation by muscarinic M 1 receptors is mediated by inhibition of SK channels. Neuron 68:948–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.018
Cai J, Yang J, Jones DP (1998) Mitochondrial control of apoptosis: the role of cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1366:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(98)00109-1
Conforti L, Millhorn DE (2000) Regulation of Shaker- Type Potassium Channels by Hypoxia. In: Lahiri S, Prabhakar NR, Forster RE (eds) Oxygen Sensing. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 475th edn. Springer, Boston, MA, Boston, pp 265–274
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Faber ESL, Sah P (2003) Calcium-activated potassium channels: multiple contributions to neuronal function. Neuroscientist 9:181–194. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858403252673
Faber ESL, Sah P (2005) Independent roles of calcium and voltage-dependent potassium currents in controlling spike frequency adaptation in lateral amygdala pyramidal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 22:1627–1635. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04357.x
Faber ESL, Sah P (2007) Functions of SK channels in central neurons. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34:1077–1083. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04725.x
Gao Y, Zhang Y, Dong Y et al (2020) Dexmedetomidine mediates neuroglobin up-regulation and alleviates the hypoxia / reoxygenation injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis in developing rats. Front Pharmacol 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.555532
Haglund U (1988) Hypoxia and reoxygenation—two mechanisms for tissue injury in ischemia and shock. Ups J Med Sci 93:127–129. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009738809178533
Hamanaka RB, Chandel NS (2009) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate hypoxic signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:894–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2009.08.005
Hammond RS, Bond CT, Strassmaier T et al (2006) Small-Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ channel type 2 (SK2) modulates hippocampal learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 26:1844–1853. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4106-05.2006
Hooge RD, De DPP (2001) Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res Rev 36:60–90
Hota SK, Barhwal K, Singh SB, Ilavazhagan G (2007) Differential temporal response of hippocampus, cortex and cerebellum to hypobaric hypoxia: a biochemical approach. Neurochem Int 51:384–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2007.04.003
Hota SK, Barhwal K, Ray K et al (2008a) Ceftriaxone rescues hippocampal neurons from excitotoxicity and enhances memory retrieval in chronic hypobaric hypoxia. Neurobiol Learn Mem 89:522–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2008.01.003
Hota SK, Barhwal K, Singh SB, Sairam M (2008b) NR1 and GluR2 expression mediates excitotoxicity in chronic hypobaric hypoxia. J Neurosci Res 86:1142–1152. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21554
Hou Y, Wang X, Chen X et al (2019) Establishment and evaluation of a simulated high-altitude hypoxic brain injury model in SD rats. Mol Med Rep 19:2758–2766. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.9939
Huppert FA (1982) Memory impairment associated with chronic hypoxia. Thorax 37:858–860. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.37.11.858
Inan SY, Aksu F, Baysal F (2000) The effects of some K+ channel blockers on scopolamine- or electroconvulsive shock-induced amnesia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 407:159–164
Jain V, Baitharu I, Barhwal K et al (2012) Enriched environment prevents hypobaric hypoxia induced neurodegeneration and is independent of antioxidant signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:599–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9807-5
Jain V, Baitharu I, Prasad D, Ilavazhagan G (2013) Enriched environment prevents hypobaric hypoxia induced memory impairment and neurodegeneration: role of BDNF / PI3K / GSK3 b pathway coupled with CREB activation. PLoS ONE 8:e62235. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0062235
Jensen BOS, Strøbæk D, Christophersen P et al (1998) Characterization of the cloned human intermediate-conductance Ca 2+ -activated K+ channel. Am J Physiol 275:C848–C856. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.1998.275.3.C848
Jung SH, Brownlow ML, Pellegrini M, Jankord R (2017) Divergence in morris water maze-based cognitive performance under chronic stress is associated with the hippocampal whole transcriptomic modification in mice. Front Mol Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00275
Kass IS, Liptont P (1986) Calcium and long-term transmission damage following anoxia in dentate gyrus and CA1 regions of the rat hippocampal slice. J Physiol 378:313–334. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016221
Kawasaki K, Traynelis SF, Dingledine R (1990) Different responses of CA1 and CA3 regions to hypoxia in rat hippocampal slice. J Neurophysiol 63:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1990.63.3.385
Kelly MJ, Rønnekleiv OK, Ibrahim N et al (2002) Estrogen modulation of K +channel activity in hypothalamic neurons involved in the control of the reproductive axis. Steroids 67:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-128X(01)00181-7
Krnjević K (1999) Early effects of hypoxia on brain cell function. Croat Med J 40:375–380
Kushwah N, Jain V, Deep S et al (2016) Neuroprotective role of intermittent hypobaric hypoxia in unpredictable chronic mild stress induced depression in rats. PLoS ONE 11:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149309
Kushwah N, Jain V, Dheer A et al (2018) Hypobaric Hypoxia induced learning and memory impairment: elucidating the role of small conductance Ca 2 + activated K + channels. Neuroscience 388:418–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.07.026
Lafuente JV, Bermudez G, Camargo- Arce L, Bulnes S (2016) Blood-brain barrier changes in high altitude. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 15:1188–1197. https://doi.org/10.2174/18715273156661609201239
LaManna JC, Vendel LM, Farrell RM (1992) Brain adaptation to chronic hypobaric hypoxia in rats. J Appl Physiol 72:2238–2243. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1992.72.6.2238
Lebel CP, Ali SF, McKee M, Bondy SC (1990) Organometal-induced increases in oxygen reactive species: the potential of 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescin diacetate as an index of neurotoxic damage. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 104:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-008X(90)90278-3
Li X, Fang P, Mai J et al (2013) Targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as novel therapy for inflammatory diseases and cancers. J Hematol Oncol 6:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-6-19
Litt M, Lamorticella D, Bond CT, Adelman JP (1999) Gene structure and chromosome mapping of the human small-conductance calcium- activated potassium channel SK1 gene. Cytogenet Cell Genet 86:70–73. https://doi.org/10.1159/000015415
Lochhead JJ, Mccaffrey G, Quigley CE et al (2010) Oxidative stress increases blood – brain barrier permeability and induces alterations in occludin during hypoxia – reoxygenation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1625–1636. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2010.29
Maiti P, Singh SB, Sharma AK et al (2006) Hypobaric hypoxia induces oxidative stress in rat brain. Neurochem Int 49:709–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2006.06.002
Maiti P, Muthuraju S, Ilavazhagan G, Singh SB (2008a) Hypobaric hypoxia induces dendritic plasticity in cortical and hippocampal pyramidal neurons in rat brain. Behav Brain Res 189:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2008.01.007
Maiti P, Singh SB, Mallick B et al (2008b) High altitude memory impairment is due to neuronal apoptosis in hippocampus, cortex and striatum. J Chem Neuroanat 36:227–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2008.07.003
Maiti P, Singh SB, Ilavazhagan G (2010) Nitric oxide system is involved in hypobaric hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in rat brain. Acta Histochem 112:222–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2008.10.005
McCord JM (1985) Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med 312:159–163. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM198501173120305
Mishra OP, Delivoria-papadopoulos M (1989) Lipid peroxidation in developing fetal guinea pig brain during normoxia and hypoxia. Dev Brain Res 45:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-3806(89)90014-X
Muthuraju S, Pati S (2014) Effect of hypobaric hypoxia on cognitive functions and potential therapeutic agents. Malaysian J Med Sci 21:41–45
Muthuraju S, Maiti P, Solanki P et al (2009) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors enhance cognitive functions in rats following hypobaric hypoxia. Behav Brain Res 203:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.03.026
Muthuraju S, Maiti P, Pati S et al (2011) Role of cholinergic markers on memory function of rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia. Eur J Pharmacol 672:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.08.023
Naghdi N, Majlessi N, Bozorgmehr T (2003) The effects of anisomycin (a protein synthesis inhibitor ) on spatial learning and memory in CA1 region of rats hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 139:69–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(02)00060-8
Ngo-anh TJ, Bloodgood BL, Lin M et al (2005) SK channels and NMDA receptors form a Ca 2 + -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines. Nat Neurosci 8:642–649. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1449
Pedarzani P, Stocker M (2008) Molecular and cellular basis of small- and intermediate-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channel function in the brain. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:3196–3217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8216-x
Pedarzani P, Mccutcheon JE, Rogge G et al (2005) Specific enhancement of SK channel activity selectively potentiates the afterhyperpolarizing current I AHP and modulates the firing properties of hippocampal pyramidal neurons*. J Biol Chem 280:41404–41411. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M509610200
Peng D, Pan X, Cui J et al (2013) Hyperphosphorylation of tau protein in hippocampus of central insulin- resistant rats is associated with cognitive impairment. Cell Physiol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1159/000356579
Pinson A, Tirosh R (1996) Reversible and irreversible damage in reoxygenated “ischemic” ventricular myocytes in culture. Mol Cell Biochem 160–161:137–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00240043
Quaife RA, Kohmoto O, Barry WH (1991) Mechanisms of reoxygenation injury in cultured ventricular myocytes. Circulation 83:566–577. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.83.2.566
Sailer CA, Hu H, Kaufmann WA et al (2002) Regional differences in distribution and functional expression of small-conductance Ca 2+ -Activated K + channels in rat brain. J Neurosci 22:9698–9707. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-22-09698.2002
Schoch HJ, Fischer S, Marti HH (2002) Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression causes vascular leakage in the brain. Brain 125:2549–2557. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awf257
Schurr A, West CA, Rigor BM (1989) Electrophysiology of energy metabolism and neuronal function in the hippocampal slice preparation. J Neurosci Methods 28:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(89)90004-6
Shi X, Liu Z, Li J (2020) Protective effects of dexmedetomidine on hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in cardiomyocytes by regulating the CHOP signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 22:3307–3315. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11442
Shukitt-hale B, Banderet LE, Lieberman HR (1998) Elevation-dependent symptom, mood, and performance changes produced by exposure to hypobaric hypoxia. Int J Aviat Psychol 8:319–334. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327108ijap0804_1
Šimonová Z, Štˇ K, Brožek G, Syková E (2003) Postnatal hypobaric hypoxia in rats impairs water maze learning and the morphology of neurones and macroglia in cortex and hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 141:195–205
Souza A, Dussan-Sarria JA, Medeiros LF et al (2014) Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy reduces c-Fos activation in the rat hippocampus: evidence of a long-lasting effect. Int J Dev Neurosci 38:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2014.09.003
Stackman RW, Hammond RS, Linardatos E et al (2002) Small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels modulate synaptic plasticity and memory encoding. J Neurosci 22:10163–10171. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-23-10163.2002
Stackman RW Jr, Bond CT, Adelman JP (2008) Contextual memory deficits observed in mice overexpressing small conductance Ca 2 + -activated K + type 2 (K Ca 2. 2, SK2) channels are caused by an encoding deficit. Learn Mem 4:208–213. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.906808.These
Vannucci RC, Brucklacher RM, Vannucci SJ (2001) Intracellular calcium accumulation during the evolution of hypoxic – ischemic brain damage in the immature rat. Dev Brain Res 126:117–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-3806(00)00135-8
Villalobos C, Shakkottai VG, Chandy KG et al (2004) SK Ca Channels mediate the medium but not the slow calcium-activated afterhyperpolarization in cortical neurons. J Neurosci 24:3537–3542. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0380-04.2004
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1:848–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.116
Wagner EJ, Rønnekleiv OK, Kelly MJ (2001) The noradrenergic inhibition of an apamin-sensitive, small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel in hypothalamic y-aminobutyric acid neurons : pharmacology, estrogen sensitivity, and relevance to the control of the reproductive axis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:21–30
Wang L, Zhu Q, Wang G et al (2011) The protective roles of mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels during hypoxia – ischemia – reperfusion in brain. Neurosci Lett 491:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.12.065
Watson BD (1993) Evaluation of the concomitance of lipid peroxidation in experimental models of cerebral ischemia and stroke. In: Kogure K, Hossmann K-A, Siesjö BK (eds) Progress in Brain Research, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 69–95
Wei W, Peng J, Li J (2019) Curcumin attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced myocardial injury. Mol Med Rep 20:4821–4830. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10742
Wolfart J, Roeper J (2002) Selective coupling of T-type calcium channels to SK potassium channels prevents intrinsic bursting in dopaminergic midbrain neurons. J Neurosci 22:3404–3413. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-09-03404.2002
Womack MD, Khodakhah K (2003) Cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurosci 23:2600–2607. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02600.2003
Wong CHY, Crack PJ (2008) Modulation of neuro-inflammation and vascular response by oxidative stress following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Med Chem 15:1–14. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986708783330665
Wu S, Tamaki N, Nagashima T, Yamaguchi M (1998) Reactive oxygen species in reoxygenation injury of rat brain capillary endothelial cells: commentaries. Neurosurgery 43:584. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199809000-00102
Xie J, Cheng C, Jie Y et al (2019) Expression of lactate dehydrogenase is induced during hypoxia via HIF-1 in the mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 225:108563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2019.108563
Ying S, Goldstein PA (2005) Propofol-block of SK channels in reticular thalamic neurons enhances GABaergic inhibition in relay neurons. J Neurophysiol 93:1935–1948. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.01058.2004
Zhao RZ, Jiang S, Zhang L, Bin YuZ (2019) Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling (Review). Int J Mol Med 44:3–15. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2019.4188
Zhu P, Yang M, He H et al (2019) Curcumin attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury by downregulating Notch signaling. Mol Med Rep 20:1541–1550. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10371
Funding
This work was supported by Grant [No: DIP-263 (NK)] from DRDO, Ministry of Defence, Government of India. NK and MK received fellowship from DRDO, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NK conceived and coordinated the study, assisted in data analysis. MK designed the study, performed and analyzed the experiments. MK, NK wrote the manuscript. NK, SP contributed with hypobaric hypoxia exposures. DP, BK and UP helped in administrative processing of the manuscript and reviewed the manuscript before submission. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of “Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals” of the government of India. Protocols for experiments and animal care were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee for Animal Care and Use (ICACU). (27/40/RBi/SL/99/CPCSEA).
Consent to participate
Na.
Consent for publication
Na.
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Communicated by Sreedharan Sajikumar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadam, M., Perveen, S., Kushwah, N. et al. Elucidating the role of hypoxia/reoxygenation in hippocampus-dependent memory impairment: do SK channels play role?. Exp Brain Res 239, 1747–1763 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-021-06095-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-021-06095-8