Abstract
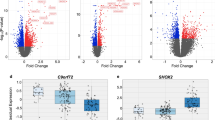
The mechanisms by which environmental influences lead to the development of complex neurodegenerative diseases are largely unknown. It is known, however, that epigenetic mechanisms can mediate alterations in transcription due to environmental influences. In order to identify genes susceptible to regulation in the adult cortex by one type of epigenetic mechanism, histone, and protein acetylation, we treated mice with the histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A (TSA). After 1 week of treatment with TSA, RNA was extracted from the brain cortices of mice and gene expression differences were analyzed by microarray profiling. The altered genes were then compared with genes differentially expressed in microarray studies of disease by database and literature searches. Genes regulated by TSA were found to significantly overlap with differentially expressed genes in the Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain. Several TSA-regulated genes involved in chromatin remodeling and epigenetic reprogramming including histone cluster 1, H4 h (Hist1H4 h), methionine adenosyltransferase II, alpha (Mat2a), and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate homocysteine reductase (Mtrr) overlapped with genes altered in early-stage AD in gray matter. We also show that the expression of hemoglobin, which has been shown to be altered in neurons in the AD brain, is regulated by TSA treatment. This analysis suggests involvement of epigenetic mechanisms in neurons in early stages of AD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anekonda TS, Reddy PH (2006) Neuronal protection by sirtuins in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 96:305–313. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03492.x
Ballas N, Mandel G (2005) The many faces of REST oversee epigenetic programming of neuronal genes. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:500–506
Ben-Porath I, Thomson MW, Carey VJ, Ge R, Bell GW, Regev A, Weinberg RA (2008) An embryonic stem cell-like gene expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nat Genet 40:499–507
Berger SL (2007) The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 447:407–412. doi:10.1038/nature05915
Biagioli M, Pinto M, Cesselli D et al (2009) Unexpected expression of α- and β-globin in mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons and glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:15454–15459
Blacker D, Bertram L, Saunders AJ et al (2003) Results of a high-resolution genome screen of 437 Alzheimer’s disease families. Hum Mol Genet 12:23–32
Blalock EM, Geddes JW, Chen KC et al (2004) Incipient Alzheimer’s disease: microarray correlation analyses reveal major transcriptional and tumor suppressor responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2173–2178
Blalock EM, Buechel HM, Popovic J, Geddes JW, Landfield PW (2011) Microarray analyses of laser-captured hippocampus reveal distinct gray and white matter signatures associated with incipient Alzheimer’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 42:118–126
Bossers K, Wirz KTS, Meerhoff GF et al (2010) Concerted changes in transcripts in the prefrontal cortex precede neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 133:3699–3723. doi:10.1093/brain/awq258
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–59 (review)
Brickell KL, Leverenz JB, Steinbart EJ et al (2007) Clinicopathological concordance and discordance in three monozygotic twin pairs with familial Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 78:1050–1055. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2006.113803
Broadwater L, Pandit A, Azzam S, Clements R, Vadnal J, Yong VW, Freeman EJ, Gregory RB, McDonough J (2011) Analysis of the mitochondrial proteome in multiple sclerosis cortex. BBA Mol Bas Dis 1812:630–641
Camelo S, Iglesias AH, Hwang D et al (2005) Transcriptional therapy with the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 164:10
Chouliaras L, Rutten BPF, Kenis G et al (2010) Epigenetic regulation in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 90:498–510. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.01.002
Colangelo V, Schurr J, Ball MJ, Pelaez RP, Bazan NG, Lukiw WJ (2002) Gene expression profiling of 12633 genes in Alzheimer hippocampal CA1: transcription and neurotrophic factor down-regulation and up-regulation of apoptotic and pro-inflammatory signaling. J Neurosci Res 70:462–473
Combs CK, Karlo JC, Kao SC, Landreth GE (2001) beta-Amyloid stimulation of microglia and monocytes results in TNFalpha-dependent expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 21:1179–1188
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ et al (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261:921–923
Cyr AR, Domann FE (2011) The redox basis of epigenetic modifications: from mechanisms to functional consequences. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:551–589. doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3492
Delacourte A, Sergeant N, Champain D et al (2002) Nonoverlapping but synergetic tau and APP pathologies in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 59:398–407
Ding H, Dolan PJ, Johnson GV (2008) Histone deacetylase 6 interacts with the microtubule-associated protein tau. J Neurochem 106:2119–2130. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05564.x
Doyle K, Fitzpatrick FA (2010) Redox signaling, alkylation (carbonylation) of conserved cysteines inactivates class I histone deacetylases 1, 2, and 3 and antagonizes their transcriptional repressor function. J Biol Chem 285:17417–17424. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.089250
Drake J, Petroze R, Castegna A et al (2004) 4-Hydroxynonenal oxidatively modifies histones: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 356:155–158. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2003.11.047
Dunckley T, Beach TG, Ramsey KE et al (2006) Gene expression correlates of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:1359–1371. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.08.013
Fathallah H, Portnoy G, Atweh GF (2008) Epigenetic analysis of the human alpha- and beta-globin gene clusters. Blood Cells Mol Dis 40:166–173
Ferrante RJ, Kubilus JK, Lee J et al (2003) Histone deacetylase inhibition by sodium butyrate chemotherapy ameliorates the neurodegenerative phenotype in Huntington’s Disease mice. J Neurosci 23:9418–9427
Ferrer I, Gómez A, Carmona M, Huesa G, Porta S, Riera-Codina M, Biagioli M, Gustincich S, Aso E (2011) Neuronal hemoglobin is reduced in Alzheimer’s disease, argyrophilic grain disease, Parkinson’s disease, and dementia with Lewy bodies. J Alzheimers Dis 23:537–550
Francis YI, Fà M, Ashraf H, Zhang H, Staniszewski A, Latchman DS, Arancio O (2009) Dysregulation of histone acetylation in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 18:131–139
Fuso A, Nicolia V, Cavallaro RA, Ricceri L, D’Anselmi F, Coluccia P, Calamandrei G, Scarpa S (2008) B-vitamin deprivation induces hyperhomocysteinemia and brain S-adenosylhomocysteine, depletes brain S-adenosylmethionine, and enhances PS1 and BACE expression and amyloid-beta deposition in mice. Mol Cell Neurosci 37:731–746
Fuso A, Nicolia V, Pasqualato A, Fiorenza MT, Cavallaro RA, Scarpa S (2011) Changes in Presenilin 1 gene methylation pattern in diet-induced B vitamin deficiency. Neurobiol Aging 32:187–199
Gardian G, Browne SE, Choi D-K et al (2005) Neuroprotective effects of phenylbutyrate in the N171–82Q transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. J Biol Chem 280:556–563
Gatz M, Reynolds CA, Fratiglioni L et al (2006) Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatr 63:168–174. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.2.168
Ginsberg SD, Alldred MJ, Che S (2012) Gene expression levels assessed by CA1 pyramidal neuron and regional hippocampal dissections in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 45:99–107
Goate A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Mullan M et al (1991) Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 349:704–706. doi:10.1038/349704a0
Gräff J, Rei D, Guan JS et al (2012) An epigenetic blockade of cognitive functions in the neurodegenerating brain. Nature 483:222–226
Green KN, Steffan JS, Martinez-Coria H et al (2008) Nicotinamide restores cognition in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice via a mechanism involving sirtuin inhibition and selective reduction of Thr231-phosphotau. J Neurosci 28:11500–11510
Gregory PD, Wagner K, Hörz W (2001) Histone acetylation and chromatin remodeling. Exp Cell Res 265:195–202. doi:10.1006/excr.2001.5187
Guan JS, Haggarty SJ, Giacometti E, Dannenberg JH, Joseph N, Gao J, Nieland TJ, Zhou Y, Wang X, Mazitschek R, Bradner JE, DePinho RA, Jaenisch R, Tsai LH (2009) HDAC2 negatively regulates memory formation and synaptic plasticity. Nature 459(7243):55–60
Hirai K, Aliev G, Nunomura A et al (2001) Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 21:3017–3023
Ito K, Hanazawa T, Tomita K et al (2004) Oxidative stress reduces histone deacetylase 2 activity and enhances IL-8 gene expression: role of tyrosine nitration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 315:240–245. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.01.046
Kennedy BP, Bottiglieri T, Arning E, Ziegler MG, Hansen LA, Masliah E (2004) Elevated S-adenosylhomocysteine in Alzheimer brain: influence on methyltransferases and cognitive function. J Neural Transm 111:547–567
Lane AA, Chabner BA (2009) Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 10(27):5459–5468
Lathrop MJ, Hsu M, Richardson CA, Olivier EN, Qiu C, Bouhassira EE, Fiering S, Lowrey CH (2009) Developmentally regulated extended domains of DNA hypomethylation encompass highly transcribed genes of the human beta-globin locus. Exp Hematol 37:807–813
Li G, Jiang H, Chang M, Xie H, Hu L (2011) HDAC6 α-tubulin deacetylase: a potential therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurol Sci 304(1–2):1–8
Liang WS, Dunckley T, Beach TG et al (2008) Altered neuronal gene expression in brain regions differentially affected by Alzheimer’s disease: a reference data set. Physiol Genomics 33:240–256
Lindgren D, Liedberg F, Andersson A et al (2006) Molecular characterization of early-stage bladder carcinomas by expression profiles, FGFR3 mutation status, and loss of 9q. Oncogene 25:2685–2696
Lithner CU, Hernandez CM, Nordberg A, Sweatt JD (2009) Epigenetic changes related to beta-amyloid-implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dementia 5:P304. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2009.04.457
Mastroeni D, Grover A, Delvaux E, Whiteside C, Coleman PD, Rogers J (2011) Epigenetic mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 32:1161–1180
Mehler MF (2008) Epigenetic principles and mechanisms underlying nervous system functions in health and disease. Prog Neurobiol 86:305
Moreira PI, Santos MS, Oliveira CR et al (2008) Alzheimer disease and the role of free radicals in the pathogenesis of the disease. CNS Neurol Disord: Drug Targets 7:3–10
Peleg S, Sananbenesi F, Zovoilis A, Burkhardt S, Bahari-Javan S, Agis-Balboa RC, Cota P, Wittnam JL, Gogol-Doering A, Opitz L, Salinas-Riester G, Dettenhofer M, Kang H, Farinelli L, Chen W, Fischer A (2010) Altered histone acetylation is associated with age-dependent memory impairment in mice. Science 328:753–756
Perez M, Santa-Maria I, Gomez de Barreda E et al (2009) Tau–an inhibitor of deacetylase HDAC6 function. J Neurochem 109:1756–1766. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06102.x
Qin B, Cartier L, Dubois-Dauphin M et al (2006) A key role for the microglial NADPH oxidase in APP-dependent killing of neurons. Neurobiol Aging 27:1577–1587. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.09.036
Qin W, Haroutunian V, Katsel P, Cardozo CP, Ho L, Buxbaum JD, Pasinetti GM (2009) PGC-1alpha expression decreases in the Alzheimer disease brain as a function of dementia. Arch Neurol 66:352–361
Ricciarelli R, d’Abramo C, Massone S, Marinari U, Pronzato M, Tabaton M (2004) Microarray analysis in Alzheimer’s disease and normal aging. IUBMB Life 56:349–354
Richter F, Meurers BH, Zhu C, Medvedeva VP, Chesselet M-F (2009) Neurons express hemoglobin α- and β-chains in rat and human brains. J Comp Neurol 515:538–547
Ricobaraza A, Cuadrado-Tejedor M, Pérez-Mediavilla A et al (2009) Phenylbutyrate ameliorates cognitive deficit and reduces tau pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:1721–1732. doi:10.1038/npp.2008.229
Ryu H, Lee J, Olofsson BA et al (2003) Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent oxidative neuronal death independent of expanded polyglutamine repeats via an Sp1-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:4281–4286
Schelshorn DW, Schneider A, Kuschinsky AW, Weber D, Kruger C, Dittgen T, Burgers HF, Sabouri F, Gassler N, Bach A, Martin H, Maurer MH (2009) Expression of hemoglobin in rodent neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 29:585–595
Selkoe DJ (1996) Amyloid beta-protein and the genetics of Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 271:18295–18298
Selkoe DJ (2004) Cell biology of protein misfolding: the examples of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Nat Cell Biol 6:1054–1061. doi:10.1038/ncb1104-1054
Shahbazian MD, Grunstein M (2007) Functions of site-specific histone acetylation and deacetylation. Annu Rev Biochem 76:75–100 (review)
Shaw T, Martin P (2009) Epigenetic reprogramming during wound healing: loss of polycomb-mediated silencing may enable upregulation of repair genes. EMBO Rep 10:881–886. doi:10.1038/embor.2009.102
Smith MA, Richey Harris PL, Sayre LM et al (1997) Widespread peroxynitrite-mediated damage in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 17:2653–2657
Stilling RM, Fischer A (2011) The role of histone acetylation in age-associated memory impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Learn Mem 96:19–26. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2011.04.002 (review)
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:15545–15550. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Szyf M, McGowan P, Meaney MJ (2008) The social environment and the epigenome. Environ Mol Mut 49:46–60
Tan MG, Chua W-T, Esiri MM et al (2010) Genome wide profiling of altered gene expression in the neocortex of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Res 88:1157–1169
van Vliet J, Oates N, Whitelaw E (2007) Epigenetic mechanisms in the context of complex diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1531–1538
Wang X, Michaelis ML, Michaelis EK (2010) Functional genomics of brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease: focus on selective neuronal vulnerability. Curr Genomics 11:618–633
Weeraratna AT, Kalehua A, Deleon I et al (2007) Alterations in immunological and neurological gene expression patterns in Alzheimer’s disease tissues. Exp Cell Res 313:450–461
Wilkinson BL, Landreth GE (2006) The microglial NADPH oxidase complex as a source of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflamm 3:30. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-3-30
Williams C, Mehrian Shai R, Wu Y et al (2009) Transcriptome analysis of synaptoneurosomes identifies neuroplasticity genes overexpressed in incipient Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 4:e4936. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004936
Yang J, Kong X, Martins-Santos ME, Aleman G, Chaco E, Liu GE, Wu SY, Samols D, Hakimi P, Chiang CM, Hanson RW (2009) Activation of SIRT1 by resveratrol represses transcription of the gene for the cytosolic form of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) by deacetylating hepatic nuclear factor 4alpha. J Biol Chem 284(40):27042–27053
Yao PJ, Zhu M, Pyun EI, Brooks AI, Therianos S, Meyers VE, Coleman PD (2003) Defects in expression of genes related to synaptic vesicle trafficking in frontal cortex of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 12:97–109
Acknowledgments
This study was funded in part by NIH Grant NS058921 (JM) and by a Grant from the Ohio Board of Regents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
221_2012_3172_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary Figure 1. Genes modulated by TSA overlap with genes involved in chromatin remodeling, DNA repair, and methionine metabolism. Supplementary material 1 (DOCX 231 kb)
221_2012_3172_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Table 1. Differential gene expression in adult mouse cortex, p < 0.05. Supplementary material 2 (PDF 396 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vadnal, J., Houston, S., Bhatta, S. et al. Transcriptional signatures mediated by acetylation overlap with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Brain Res 221, 287–297 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3172-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3172-y