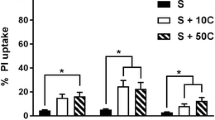
Abstract
The role of the neutral amino acid glycine in excitotoxic neuronal injury is unclear. Glycine coactivates glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors by binding to a distinct recognition site on the NR1 subunit. Purely excitatory glycine receptors composed of NR1 and NR3/NR4 NMDA receptor subunits have recently been described, raising the possibility of excitotoxic effects mediated by glycine alone. We have previously shown that exposure to high concentrations of glycine causes extensive neurotoxicity in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures by activation of NMDA receptors. In the present study, we investigated further properties of in vitro glycine-mediated toxicity. Agonists of the glycine recognition site of NMDA receptors (D-serine and D-alanine) did not have any toxic effect in hippocampal cultures, whereas competitive blockade of the glycine site by 7-chlorokynurenic acid was neuroprotective. Stimulation (taurine, β-alanine) or inhibition (strychnine) of the inhibitory strychnine-sensitive glycine receptors did not produce any neurotoxicity. The toxic effects of high-dose glycine were comparable in extent to those produced by the excitatory amino acid glutamate in our model. When combined with sublethal hypoxia/hypoglycemia, the threshold of glycine toxicity was decreased to less than 1 mM, which corresponds to the range of concentrations of excitatory amino acids measured during in vivo cerebral ischemia. Taken together, these results further support the assumption of an active role of glycine in excitotoxic neuronal injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers GW, Clark WM, Atkinson RP, Madden K, Data JL, Whitehouse MJ (1999) Dose escalation study of the NMDA glycine-site antagonist licostinel in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 30:508–513
Baker AJ, Zornow MH, Scheller MS, Yaksh TL, Stilling SR, Smullin DH, Larson AA, Kuczenski R (1991) Changes in extracellular concentrations of glutamate, aspartate, glycine, dopamine, serotonin, and dopamine metabolites after transient global ischemia in the rabbit brain. J Neurochem 57:1370–1379
Castillo J, Davalos A, Naveiro J, Noya M (1996) Neuroexcitatory amino acids and their relation in infarct size and neurological deficit in ischemic stroke. Stroke 27:1060–1065
Castillo J, Davalos A, Noya M (1997) Progression of ischaemic stroke and excitotoxic aminoacids. Lancet 349:79–83
Chatterton JE, Awobuluyl M, Premkumar LS, Takahashi H, Talantova M, Shin Y, Cul J, Tu S, Sevarino KA, Nakanishi N, Tong G, Lipton SA, Zhang D (2002) Excitatory glycine receptors containing the NR3 family of NMDA receptor subunits. Nature 415:793–798
Choi DW, Rothman SM (1990) The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Annu Rev Neurosci 13:171–182
Cull-Candy S, Brickley S, Farrant M (2001) NMDA receptor subunits: diversity, development and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:327–335
Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D, Traynelis SF (1999) The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol Rev 51:7–61
Fadda E, Danisz W, Wroblewski JT, Costa E (1988) Glycine and D-serine increase the affinity of N-methyl-D-aspartate sensitive glutamate binding sites in rat brain synaptic membranes. Neuropharmacology 27:1183–1185
Faden AL, Demediuck P, Panter SS, Vink R (1989) The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science 244:798–800
Foucaud B, Laube B, Schemm R, Kreimeyer A, Goeldner M, Betz H (2003) Structural model of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor glycine site probed by site-directed chemical coupling. J Biol Chem 278:24011–24017
Globus MYT, Busto R, Martinez E, Valdes I, Dietrich WD, Ginsberg MD (1991a) Comparative effect of transient global ischemia on extracellular levels of glutamate, glycine, and γ-aminobutyric acid in vulnerable and nonvulnerable brain regions in the rat. J Neurochem 57:470–478
Globus MYT, Ginsberg MD, Busto R (1991b) Excitotoxic index—a biochemical marker of selective vulnerability. Neurosci Lett 127:39–42
Graham SH, Shiraishi K, Panter SS, Simon RP, Faden AI (1990) Changes in extracellular amino acid neurotransmitters produced by focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett 110:124–130
Hirai H, Kirsch J, Laube B, Betz H, Kuhse J (1996) The glycine binding site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR1: identification of novel determinants of co-agonist potentiation in the extracellular M3-M4 loop region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:6031–6036
Hood WF, Compton RP, Monahan JB (1990) N-methyl-D-aspartate recognition site ligands modulate activity at the coupled glycine recognition site. J Neurochem 54:1040–1046
Ikonomidou C, Turski L (2002) Why did NMDA receptor antagonists fail clinical trials for stroke and traumatic brain injury? Lancet Neurol 1:383–386
Johnson JW, Ascher P (1987) Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature 325:529–531
Kanthan R, Shuaib A (1995) Clinical evaluation of extracellular amino acids in severe head trauma by intracerebral in vivo microdialysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 59:326–327
Kaplita PV, Ferkany JW (1990) Evidence for direct interactions between the NMDA and glycine recognition sites in brain. Eur J Pharmacol 188:175–179
Kleckner NW, Dingledine R (1988) Requirement for glycine in activation of NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Science 241:835–837
Kutsawada T, Kashiwabuchi N, Mori H, Sakimura K, Kushiya E, Araki K, Meduro H, Masaki H, Kumanishi T, Arakawa M, Mishina M (1992) Molecular diversity of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature 358:36–41
Larson AA, Beitz AJ (1988) Glycine potentiates strychnine-induced convulsions: role of NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 8:3822–3826
Lees KR, Asplund K, Carolei A, Davis SM, Diener HC, Kaste M, Orgogozo JM, Whitehead J (2000) Glycine antagonist (gavestinel) in neuroprotection (GAIN International) in patients with acute stroke: a randomised controlled trial. GAIN International Investigators. Lancet 255:1949–1954
Lipton SA, Rosenberg PA (1994) Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med 330:613–622
Madden K (2002) NMDA receptor antagonists and glycine site NMDA antagonists. Curr Med Res Opin 18 [Suppl 2]:27–31
Matsumoto K, Graf R, Rosner G, Taguchi J, Heiss WD (1993) Elevation of neuroactive substances in the cortex of cats during prolonged focal ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13:586–594
McBain CJ, Mayer ML (1994) N-methyl-D-aspartatic acid receptor structure and function. Physiol Rev 74:723–760
McNamara D, Dingledine R (1990) Dual effect of glycine on NMDA-induced neurotoxicity in rat cortical cultures. J Neurosci 10:3970–3976
Meguro H, Mori H, Araki K, Kushiya E, Kutsuwada T, Yamazaki M, Kumanishi T, Arakawa M, Sakimura K, Mishina M (1992) Functional characterization of a heteromeric NMDA receptor channel expressed from cloned cDNAs. Nature 357:70–74
Monahan JB, Biesterfeldt JP, Hood WF, Compton RP, Cordi AA, Vazquez MI, Lanthorn TH, Wood PL (1990) Differential modulation of the associated glycine recognition site by competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists. Mol Pharmacol 37:780–784
Newell DW, Barth A, Papermaster V, Malouf AT (1995a) Glutamate and non-glutamate receptor mediated toxicity caused by oxygen and glucose deprivation in organotypic hippocampal cultures. J Neurosci 15:7702–7711
Newell DW, Barth A, Malouf AT (1995b) Glycine site NMDA receptor antagonists provide protection against ischemia-induced neuronal damage in hippocampal slice cultures. Brain Res 675:38–44
Newell DW, Barth A, Ricciardi TN, Malouf AT (1997) Glycine causes increased excitability and neurotoxicity by activation of NMDA receptors in the hippocampus. Exp Neurol 145:235–244
Obrenovitch TP, Richards DA (1995) Extracellular neurotransmitter changes in cerebral ischemia. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 7:1–54
Obrenovitch TP, Hardy AM, Urenjak J (1997) High extracellular glycine does not potentiate N-methyl-D-aspartate-evoked depolarization in vivo. Brain Res 746:190–194
Pace JR, Martin BM, Paul SM, Rogawski MA (1992) High concentrations of neutral amino acids activate NMDA receptor currents in rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett 141:97–100
Patel J, Zinkand WC, Thompson C, Keith R, Salama A (1990) Role of glycine in the N-methyl-D-aspartate-mediated neuronal cytotoxicity. J Neurochem 54:849–854
Perry TL, Hansen S (1981) Amino acid abnormalities in epileptogenic foci. Neurology 31:872–876
Sandberg M, Butcher SP, Hagberg H (1986) Extracellular overflow of neuroactive amino acids during severe insulin-induced hypoglycemia: in vivo dialysis of the rat hippocampus. J Neurochem 47:178–184
Saransaari P, Oja SS (2001) Characteristics of hippocampal glycine release in cell-damaging conditions in the adult and developing mouse. Neurochem Res 26:845–852
Shalaby I, Chenard B, Prochniak M (1989) Glycine reverses 7-chlorokynurenate blockade of glutamate neurotoxicity in cell culture. Eur J Pharmacol 160:309–311
Shoham S, Javitt DC, Heresco-Levy U (2001) Chronic high-dose glycine nutrition: effects on rat brain cell morphology. Biol Psychiatry 49:876–885
Sierra-Paredes G, Senra-Vidal A, Sierra-Marcuno G (2001) Effect of extracellular long-time microperfusion of high concentrations of glutamate and glycine on picrotoxin seizure thresholds in the hippocampus of freely moving rats. Brain Res 888:19–25
Stoppini L, Buchs PA, Muller D (1991) A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods 37:173–182
Sucher NJ, Awobuluyi M, Choi YB, Lipton SA (1996) NMDA receptors: from genes to channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci 17:348–355
Thomson AM (1990) Glycine is a coagonist at the NMDA receptor/channel complex. Prog Neurobiol 35:53–74
von Essen C, Rydenhag B, Nyström B, Mozzi R, van Gelder N, Hamberger A (1996) High levels of glycine and serine as a cause of the seizure symptoms of cavernous angiomas? J Neurochem 67:260–264
Wallis RA, Panizzon KL, Nolan JP (1995) Glycine-induced CA1 excitotoxicity in the rat hippocampal slice. Brain Res 685:225–235
Waziri R, Baruah S (1999) A hyperglycinergic rat model for the pathogenesis of schizophrenia: preliminary findings. Schizophr Res 37:205–215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barth, A., Nguyen, L.B., Barth, L. et al. Glycine-induced neurotoxicity in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Exp Brain Res 161, 351–357 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-2079-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-2079-7