Abstract
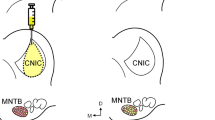
Norepinephrine is believed to modulate important functions of the cochlear nuclear complex (CNC) such as the detection of signals in noise and the processing of timing cues. To better understand the impact of the noradrenergic system in the CNC, we used neurotransmitter immunohistochemistry combined with retrograde tract-tracing to identify the noradrenrgic cell groups that project to the CNC. Here we present data showing that the CNC receives noradrenergic inputs from the A1 cell group located in the ventrolateral medulla. The projection from A1 to the CNC may be part of a system-wide modulation by the noradrenergic system based on stress and arousal level, or it may be part of a separate circuit that modulates its targets during survival behaviors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman AL (1968) The brain stem of the cat. University of Wisconsin Press, Madison
Blessing WW, Frost P, Furness JB (1980) Catecholamine cell groups of the cat medulla oblongata. Brain Res 192:69–75
Carlton SM, Honda CN, Denoroy L (1989) Distribution of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase cell bodies, axons, and terminals in monkey brainstem: an immunohistochemical mapping study. J Comp Neurol 287:273–285
Chikamori Y, Sasa M, Fujimoto S, Takaori S, Matsuoka I (1980) Locus coeruleus-induced inhibition of dorsal cochlear nucleus neurons in comparison with lateral vestibular nucleus neurons. Brain Res 184:53–63
Ciriello JM Caverson M, Polosa C (1986) Function of the ventrolateral medulla in the control of the circulation. Brain Res Rev 11:359–391
Comis SD, Whitfield IC (1968) Influence of centrifugal pathways on unit activity in the cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 31:62–68
Dahlström A, Fuxe K (1964) Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neruons in the central nervous system. I. Demonstration of monoamines in the cell bodies of brain stem neurons. Acta Physiol Scand 62:1–55
Dayas CV, Buller KM, Crane JW, Xu Y, Day TA (2001) Stressor categorization: acute physical and psychological stressors elicit distinctive recruitment patterns in the amygdala and in medullary noradrenergic cell groups. Eur J Neurosci 14:1143–1152
Ebert U (1996) Noradrenaline enhances the activity of cochlear nucleus neurons in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 8:1306–1314
Floody OR, Lisk RD (1987) Effects of sex and reproductive state on acoustic responsiveness in hamsters. Brain Res Bull 18:235–242
Haenggeli CA, Doucet JR, Ryugo DK (2002) Projections of the spinal trigeminal nucleus to the cochlear nucleus. In: Proceedings of the Scientific Program, Central Auditory Processing: Integration of Auditory and Non-Auditory Information, Monté Verita, Switzerland. Abstract P36
Herbert H, Saper CB (1992) Organization of medullary adrenergic and noradrenergic projections to the periaqueductal gray matter in the rat. J Comp Neurol 315:34–52
Hökfelt T, Johansson O, Goldstein M (1984) Central catecholamine neurons as revealed by immunohistochemistry with special reference to adrenaline neurons. In: Bjorklund A, Hökfelt T (eds) Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, Vol 2: Classical Transmitters in the CNS. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 157–276
Klepper A, Herbert H (1991) Distribution and origin of noradrenergic and serotonergic fibers in the cochlear nucleus and inferior colliculus of the rat. Brain Res 557:190–201
Klop EM, Mouton LJ, Holstege G. (2002) Nucleus retroambiguus projections to the periaqueductal gray in the cat. J Comp Neurol 445:47–58
Kössl M, Vater M (1989) Noradrenaline enhances temporal auditory contrast and neuronal timing precision in the cochlear nucleus of the mustached bat. J Neurosci 9:4169–4178
Kössl M, Vater M, Schweizer H (1988) Distribution of catecholamine fibers in the cochlear nucleus of horseshoe bats and mustache bats. J Comp Neurol 269:523–534
Kromer LF, Moore RY (1976) Cochlear nucleus innervation by central norepinephrine neurons in the rat. Brain Res 118:531–537
Llewllyn-Smith IJ, Pilowsky P, Minson JB (1992) Retrograde tracers for light and electron microscopy. In: Bolam JP (ed) Experimental Neuroanatomy: a Practical Approach. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 31–59
Matta SG, Foster CA, Sharp BM (1993) Nicotine stimulates the expression of cFos protein in the parvocellular paraventricular nucleus and brainstem catecholaminergic regions. Endocrinology 132:2149–2156
McKellar S, Loewy AD (1982) Efferent projections of the A1 catecholamine cell group in the rat: an autoradiographic study. Brain Res 241:11–29
Milner TA, Pickel VM, Giuliano R, Reis DJ (1989) Ultrastructural localization of choline acetyltransferase in the rat rostral ventrolateral medulla: evidence for major synaptic relations with non-catecholaminergic neurons. Brain Res 500:67–89
Onaka T, Yamashita T, Liu X, Honda K, Saito T, Yagi K (2001) Medullary A1 noradrenergic neurones may mediate oxytocin release after noxious stimuli. Neuroreport 12:2499–2502
Pacak K, Palkovits M, Kvetnansky R, Kopin IJ, Goldstein DS (1993) Stress-induced norepinephrine release in the paraventricular nucleus of rats with brain-stem hemisections: a microdialysis study. Neuroendocrinology 58:196–201
Pasquier DA, Gold MA, Jacobowitz DM (1980) Noradrenergic perikarya (A5–A7, subcoeruleus) projections to the rat cerebellum. Brain Res 196:270–275
Pau KY, Yu JH, Lee CJ, Spies HG (1998) Topographic localization of neuropeptide Y mRNA in the monkey brainstem. Regul Pept 75–76:145–153
Pickles JO (1976) The noradrenaline-containing innervation of the cochlear nucleus and the detection of signals in noise. Brain Res 105:591–596
Pickles JO, Comis SD (1973) Role of centrifugal pathways to cochlear nucleus in detection of signals in noise. J.Neurophysiol 36:1131–1137
Poitras D, Parent A (1978) Atlas of the distribution of monoamine-containing nerve cell bodies in the brain stem of the cat. J Comp Neurol 179:699–718
Reiner PB, Vincent SR (1986) The distribution of tyrosine hydroxylase, dopamine-β-hydroxylase, and phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase immunoreactive neurons in the feline medulla oblongata. J Comp Neurol 248:518–531
Rinaman L (2001) Postnatal development of catecholamine inputs to the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in rats. J Comp Neurol 438:411–422
Roder S, Ciriello J (1993) Innervation of the amygdaloid complex by catecholaminergic cell groups of the ventrolateral medulla. J Comp Neurol 332:105–122
Ruggiero DA, Meeley MP, Anwar M, Reis DJ (1985) Newly identified GABAergic neurons in regions of the ventrolateral medulla which regulate blood pressure. Brain Res 339:171–177
Rusnak M, Kvetnansky R, Jelokova J, Palkovits M (2001) Effect of novel stressors on gene expression of tyrosine hydroxylase and monoamine transporters in brainstem noradrenergic neurons of long-term repeatedly immobilized rats. Brain Res 899:20–35
Schuerger RJ, Balaban CD (1993) Immunohistochemical demonstration of regionally selective projections from locus coeruleus to the vestibular nuclei in rats. Exp Brain Res 92:351–359
Thompson AM (1998) Heterogeneous projections of the cat posteroventral cochlear nucleus. J Comp Neurol 390:439–453
Thompson, AM (2003) Pontine sources of norepinephrine in cat cochlear nucleus. J Comp Neurol 457:374–383
Thompson AM, Moore KR, Thompson GC (1995) Distribution and origin of serotoninergic afferents to guinea pig cochlear nucleus. J Comp Neurol 351:104–116
Woulfe JM, Flumerfelt BA, Hrycyshyn AW (1990) Efferent connections of the A1 noradrenergic cell group: A DBH immunohistochemical and PHA-L anterograde tracing study. Exp Neurol 109:308–322
Yang SP, Voogt JL (2001) Mating-activated brainstem catecholaminergic neurons in the female rat. Brain Res 894:159–166
Acknowledgements
Supported by the Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology (HR99-060). The author thanks Dr. Staci Myers for her technical assistance and Dr. Glenn Thompson for his helpful editorial comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, A.M. A medullary source of norepinephrine in cat cochlear nuclear complex. Exp Brain Res 153, 486–490 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1681-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1681-4