Abstract.
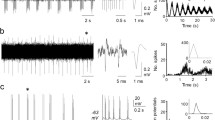
Extracellular recordings of neuronal activity made in the lumbosacral spinal segments of the anesthetized cat have disclosed the existence of a set of neurons in Rexed's laminae III–VI that discharged in a highly synchronized manner during the occurrence of spontaneous negative cord dorsum potentials (nCDPs) and responded to stimulation of low-threshold cutaneous fibers (<1.5×T) with mono- and polysynaptic latencies. The cross-correlation between the spontaneous discharges of pairs of synchronic neurons was highest when they were close to each other, and decreased with increasing longitudinal separation. Simultaneous recordings of nCDPs from several segments in preparations with the peripheral nerves intact have disclosed the existence of synchronized spontaneous nCDPs in segments S1–L4. These potentials lasted between 25 and 70 ms and were usually larger in segments L7–L5, where they attained amplitudes between 50 and 150 µV. The transection of the intact ipsilateral hindlimb cutaneous and muscle nerves, or the section of the dorsal columns between the L5 and L6, or between the L6 and L7 segments in preparations with already transected nerves, had very small effects on the intersegmental synchronization of the spontaneous nCDPs and on the power spectra of the cord dorsum potentials recorded in the lumbosacral enlargement. In contrast, sectioning the ipsilateral dorsal horn and the dorsolateral funiculus at these segmental levels strongly decoupled the spontaneous nCDPs generated rostrally from those generated caudally to the lesion and reduced the magnitude of the power spectra throughout the whole frequency range. These results indicate that the lumbosacral intersegmental synchronization between the spontaneous nCDPs does not require sensory inputs and is most likely mediated by intra- and intersegmental connections. It is suggested that the occurrence of spontaneous synchronized nCDPs is due to the activation of tightly coupled arrays of neurons, each comprising one or several spinal segments. This system of neurons could be involved in the modulation of the information transmitted by cutaneous and muscle afferents to functionally related, but rostrocaudally distributed spinal interneurons and motoneurons, as well as in the selection of sensory inputs during the execution of voluntary movements or during locomotion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manjarrez, .E., Jiménez, .I. & Rudomin, .P. Intersegmental synchronization of spontaneous activity of dorsal horn neurons in the cat spinal cord. Exp Brain Res 148, 401–413 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-002-1303-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-002-1303-6