Abstract
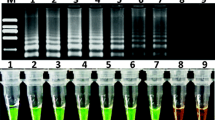
The determination of the presence of genetically modified plant material by the detection of expressed genetically engineered proteins using lateral flow protein strip tests has been evaluated in different matrices. The presence of five major genetically engineered proteins (CP4-EPSPS, CryIAb, Cry9C, PAT/pat and PAT/bar protein) was detected at low levels in seeds, seed/leaf powder and leaf tissue from genetically modified soy, maize or oilseed rape. A comparison between “protein strip test” (PST) and “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) analysis of genetically modified food/feed samples demonstrates complementarities of both techniques.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
James C (2004) Global status of commercialized transgenic crops: 2004. ISAAA Brief, no. 32. Ithaca, New York
EC (2001) Directive 2001/18/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 March 2001 on the deliberate release into the environment of genetically modified organisms and repealing Council Directive 90/220/EEC. Off J Eur Communities L106:1–39
EC (2003a) Regulation (EC) 1829/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2003 on genetically modified food and feed. Off J Eur Communities L268:1–23
EC (2003b) Regulation (EC) 1830/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2003 concerning the traceability and labelling of genetically modified organisms and the traceability of food and feed products produced from genetically modified organisms and amending Directive 2001/18/EC Off J Eur Communities L268:24–28
Holst-Jensen AH, Berdal KG (2004) The modular analytical procedure and validation approach and the units of measurement for genetically modified materials in foods and feeds. J AOAC Int 87:927–936
Anklam E, Heinze P, Kay S, Van den Eede G (2002) Validation studies and proficiency testing. J AOAC Int 85(3):809–815
Bertheau Y, Diolez A, Kobilinsky A, Magin K (2002) Detection methods and performance criteria for genetically modified organisms. J AOAC Int 85(3):801–808
Stave J (2002) Protein immunoassays methods for detection of biotech crops: applications, limitations and practical considerations. J AOAC Int 85(3):780–786
Barry G, Kishore G, Padgette S, Taylor M, Kolacz K, Weldon M, Re D, Eichholtz D, Fincher K, Hallas L (1992) Inhibitors of amino acid biosynthesis: strategies for imparting glyphosate tolerance to crop plants. In: Singh et al. (eds) Biosynthesis and molecular regulation of amino acids in plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, pp 139–145
Koziel MG, Carozzi NB, Currier TC, Warren GW, Evola S (1993) The insecticidal crystal proteins of bacillus thuringiensis: past, present and future uses. In: Tombs MP (ed) Biotechnology and genetic engeneering reviews, vol. 11. Intercept, Andover, UK, pp 171–228
Wohlleben W, Arnold W, Broer I, Hillemann D, Strauch E, Pühler A (1988) Nucleotide sequence of the phosphinotricine N-acetyltransferase gene from Streptomyces viridochromogenes Tü494 and its expression in Nicotiana tabacum. Gene 70:25–37
De Block M, Botterman J, Vandewiele M, Dockx J, Thoen C, Gosselé V, Movva NR, Thompson C, Van Montagu M, Leemans J (1987) Engineering herbicide resistance in plants by expression of a detoxifying enzyme. EMBO J 6:2513–2518
Hüpfer C, Hotzel H, Sachse K, Engel KH (1998) Detection of the genetic modification in heat-treated products by BT-maize polymerase chain reaction. Zeitschrift für Lebensmittel-Untersuchnung und –Forschung A206:203–207
Odell JT, Nagy F, Chua NH (1985) Identification of DNA sequences required for the activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. Nature 313:810–812
Depicker A, Stachel S, Dhaese P, Seurinck J, Deboeck F, De Greve H, Lemmers M, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1982) Nopaline synthase: transcript mapping and DNA sequence. J Mol Appl Genet 1:1–573
Lipp M, Bluth A, Euquem F, Kruse L, Schimmel H, Van den Eede G, Anklam E (2001) Validation of a method based on polymerase chain reaction for the detection of genetically modified organisms in various processed foodstuffs. Eur Food Res Technol 212:497–504
Pietsch K, Waiblinger HU, Brodmann P, Wurz A (1997) Screeningverfahren zur Identifizierung “genetisch veränderter” pflanzlicher Lebensmittel. Deutsche Lebensmittel-Rundschau 93(2):35–38
Studer E, Dahinden I, Lüthy J, Hübner P (1997) Nachweis des genetisch veränderten “Maximizer”-Mais mittels der polymerase-Kettenreaktion (PCR). Mitteilungen aus dem Gebiet der Lebensmittel und Hygiene 88:515–524
Kuribara H, Matsuoka T, Takuba K, Futo S, Hirao T, Akiyama H, Goda Y, Toyoda M, Hino A (2002) Novel reference molecules for quantification of genetically modified maize and soy. J AOAC Int 85(5):1077–1089
Ma BL, Subedi K, Evenson L, Stewart G (2005) Evaluation of detection methods for genetically modified traits in genotypes resistant to European Corn Borer and Herbicides. J Environ Sci Health B 40:633–644
EC (2004) Commission Recommendation 787/2004 on technical guidance for sampling and detection of genetically modified organisms and material produced from genetically modified organisms as or in the context of Regulation (EC) 1830/2003. Off J Eur Communities L348:18–26
Lin H-Y, Chiang J-W, Shih DY-C (2001) Detection of genetically modified soybeans by PCR method and immunoassay kits. J Food Drug Anal 9(3):160–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van den Bulcke, M., De Schrijver, A., De Bernardi, D. et al. Detection of genetically modified plant products by protein strip testing: an evaluation of real-life samples. Eur Food Res Technol 225, 49–57 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-006-0381-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-006-0381-2