Abstract
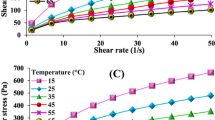
The rheological properties of syrups prepared using bulk sweeteners such as sorbitol and bulking agents like maltodextrin and polydextrose along with aspartame were studied. The apparent viscosity, consistency index, yield stress, and flow behavior index were determined from the shear stress versus shear rate data. The Herschel–Bulkley model was found to adequately describe the flow behavior of the syrups. The activation energy for all the syrups at different concentrations was determined from the Arrhenius equation. The yield stress, flow behavior index, and consistency index were dependent on the temperature and concentration of the syrups. The apparent viscosity increased from 8.8 to 129 mPa·s for sugar and sorbitol syrups, respectively, over the concentration range from 35 to 65%. In general, the rheological characteristic of sorbitol syrup was similar to that of sugar syrup, while syrups made with polydextrose and its mixture with maltodextrin were significantly different from those of sugar syrup.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saravacos GD (1970) J Food Sci 35:122–125
Collins JL, Dincer B (1973) J Food Sci 38:489–492
Chirife J, Bruera MP (1997) J Food Eng 33:221–226
Ozdemir M, Sadikoglu H (1998) Int J Food Sci Tech 33:439–444
Savage RM (2000) Food Hydrocolloids 14:209–215
Hyvonen L, Torma R (1983) J Food Sci 48:183–185
Gerdes DL, Burns EE, Harrow LS (1987) Lebensm Wiss Technol 20:282–286
Ibarz A, Pagan J, Miguelsanz R (1992) J Food Eng 15:63–73
Gunjal BB, Waghmare NJ (1987) J Food Sci Technol India 24:20–23
Holdsworth SD (1971) J Texture Stud 2:393–418
Rao MA, Cooley HJ (1983) J Food Process Eng 6:159–173
Parades MDC, Rao MA, Bourne MC (1989) J Texture Stud 20:235–240
Monohar B, Ramakrishna P, Udayashankar K (1991) J Food Eng 10:241–258
Bhandari B, D’Arcy B, Chow S (1999) J Food Eng 41:65–86
Mossel B, Bhandar B, D’Arcy B, Caffin A (2000). Lebensm Wiss Technol 35:545–552
Rao MA, Cooley HJ, Vitali AA (1984) Food Technol 38:113–119
Khalil KE, Ramakrishna P, Nanjundaswamy AM, Patwardhan MV (1989) J Food Eng 10:231–240
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. B.R. Lokesh, Dr. K.N. Gurudatt, heads of the departments, and Dr. V. Prakash, Director of the Institute for their keen interest in the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chetana, R., Krishnamurthy, S. & Yella Reddy, S.R. Rheological behavior of syrups containing sugar substitutes. Eur Food Res Technol 218, 345–348 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-004-0876-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-004-0876-7