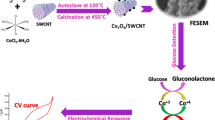
Abstract
The development of cost-effective and highly efficient electrocatalysts is critical to help electrochemical non-enzymatic sensors achieve high performance. Here, a new class of catalyst, Ru single atoms confined on Cu nanotubes as a single-atom alloy (Ru1Cu NTs), with a unique electronic structure and property, was developed to construct a novel electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor for the first time. The Ru1Cu NTs with a diameter of about 24.0 nm showed a much lower oxidation potential (0.38 V) and 9.0-fold higher response (66.5 μA) current than Cu nanowires (Cu NWs, oxidation potential 0.47 V and current 7.4 μA) for glucose electrocatalysis. Moreover, as an electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor, Ru1Cu NTs not only exhibited twofold higher sensitivity (54.9 μA mM−1 cm−2) and wider linear range (0.5–8 mM) than Cu NWs, but also showed a low detection limit (5.0 μM), excellent selectivity, and great stability. According to theoretical calculation results, the outstanding catalytic and sensing performance of Ru1Cu NTs could be ascribed to the upshift of the d-band center that helped promote glucose adsorption. This work presents a new avenue for developing highly active catalysts for electrochemical non-enzymatic sensors.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liao K-F, Kuo Y-H, Lai S-W. Diabetes mellitus in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(8):e134–e134. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216221.
Huang M, He D, Wang M, Jiang P. NiMoO4 nanosheet arrays anchored on carbon cloth as 3D open electrode for enzyme-free glucose sensing with improved electrocatalytic activity. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(30):7921–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1413-z.
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA, Ogurtsova K, Shaw JE, Bright D, Williams R. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843.
Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, Paik JM, Srishord M, Fukui N, Qiu Y, Burns L, Afendy A, Nader F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2019;71(4):793–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021.
Dervisevic M, Alba M, Yan L, Senel M, Gengenbach TR, Prieto-Simon B, Voelcker NH. Transdermal electrochemical monitoring of glucose via high-density silicon microneedle array patch. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(3):2009850. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202009850.
Saha T, Del Caño R, Mahato K, De la Paz E, Chen C, Ding S, Yin L, Wang J. Wearable electrochemical glucose sensors in diabetes management: a comprehensive review. Chem Rev. 2023;123(12):7854–89. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00078.
Lin Y, Bariya M, Nyein HYY, Kivimäki L, Uusitalo S, Jansson E, Ji W, Yuan Z, Happonen T, Liedert C, Hiltunen J, Fan Z, Javey A. Porous enzymatic membrane for nanotextured glucose sweat sensors with high stability toward reliable noninvasive health monitoring. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(33):1902521. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201902521.
Bihar E, Wustoni S, Pappa AM, Salama KN, Baran D, Inal S. A fully inkjet-printed disposable glucose sensor on paper. npj Flexible Electron. 2018;2(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-018-0044-y.
Zhou J, Pan K, Qu G, Ji W, Ning P, Tang H, Xie R. rGO/MWCNTs-COOH 3D hybrid network as a high-performance electrochemical sensing platform of screen-printed carbon electrodes with an ultra-wide detection range of Cd(II) and Pb(II). Chem Eng J. 2022;449:137853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137853.
Farid A, Zhonghua C, Khan AS, Javid M, Khan IA, Khan AA, Fan Z, Pan L. Ni3V2O8 nanosheets grafted on 3D helical-shaped carbon nanocoils as a binder-free hierarchical composite for efficient non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Adv Funct Mater. 2023;33(33):2301727. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202301727.
Zhang M, Wang G, Chen J, Lu X. Single atom catalysts for sensors. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2023;169:117399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2023.117399.
Gurusamy L, Karuppasamy L, Anandan S, Barton SC, Chuang Y-H, Liu C-H, Wu JJ. Review of oxygen-vacancies nanomaterials for non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors application. Coord Chem Rev. 2023;484:215102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215102.
Tan M, Ni M, Liu X, Qu B, Lin X, Jiang D, Yuan Y, Du H. Surface adsorption guided design of semicrystalline nickel-iron hydroxide for highly-sensitive glucose sensing. Chem Eng J. 2023;451:138963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138963.
Zhang L, Ye C, Li X, Ding Y, Liang H, Zhao G, Wang Y. A CuNi/C nanosheet array based on a metal–organic framework derivate as a supersensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Nano-Micro Lett. 2017;10(2):28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-017-0178-9.
Zhang Y, Li N, Xiang Y, Wang D, Zhang P, Wang Y, Lu S, Xu R, Zhao J. A flexible non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on copper nanoparticles anchored on laser-induced graphene. Carbon. 2020;156:506–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.10.006.
Ullah H, Ahmad R, Khan AA, Khaliq N, Khan M, Ali G, Karim S, Yi X, Cho SO. A sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on MgO entangled nanosheets decorated with CdS nanoparticles: experimental and DFT study. J Mol Liq. 2022;360:119366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119366.
Liu F, Wang P, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Liu Y, Zheng Z, et al. Porous Co3O4 nanosheets as a high-performance non-enzymatic sensor for glucose detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(29):7663–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1380-4.
Mao J, Yin J, Pei J, Wang D, Li Y. Single atom alloy: an emerging atomic site material for catalytic applications. Nano Today. 2020;34:100917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100917.
Chen C-H, Wu D, Li Z, Zhang R, Kuai C-G, Zhao X-R, Dong C-K, Qiao S-Z, Liu H, Du X-W. Ruthenium-based single-atom alloy with high electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution. Adv Energy Mater. 2019;9(20):1803913. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201803913.
Xie H, Wan Y, Wang X, Liang J, Lu G, Wang T, Chai G, Adli NM, Priest C, Huang Y, Wu G, Li Q. Boosting Pd-catalysis for electrochemical CO2 reduction to CO on Bi-Pd single atom alloy nanodendrites. Appl Catal B. 2021;289:119783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119783.
Xu Z, Ao Z, Yang M, Wang S. Recent progress in single-atom alloys: synthesis, properties, and applications in environmental catalysis. J Hazard Mater. 2022;424:127427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127427.
Marcinkowski MD, Darby MT, Liu J, Wimble JM, Lucci FR, Lee S, Michaelides A, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M, Stamatakis M, Sykes ECH. Pt/Cu single-atom alloys as coke-resistant catalysts for efficient C-H activation. Nat Chem. 2018;10(3):325–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2915.
Andersen M, Levchenko SV, Scheffler M, Reuter K. Beyond scaling relations for the description of catalytic materials. ACS Catal. 2019;9(4):2752–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b04478.
Pérez-Ramírez J, López N. Strategies to break linear scaling relationships. Nat Catal. 2019;2(11):971–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-019-0376-6.
Han L, Zhang L, Wu H, Zu H, Cui P, Guo J, Guo R, Ye J, Zhu J, Zheng X, Yang L, Zhong Y, Liang S, Wang L. Anchoring Pt single atoms on Te nanowires for plasmon-enhanced dehydrogenation of formic acid at room temperature. Adv Sci. 2019;6(12):1900006. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201900006.
Zhou L, Martirez JMP, Finzel J, Zhang C, Swearer DF, Tian S, Robatjazi H, Lou M, Dong L, Henderson L, Christopher P, Carter EA, Nordlander P, Halas NJ. Light-driven methane dry reforming with single atomic site antenna-reactor plasmonic photocatalysts. Nat Energy. 2020;5(1):61–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-019-0517-9.
Zhang S, Rong H, Yang T, Bai B, Zhang J. Ultrafine PtRu dilute alloy nanodendrites for enhanced electrocatalytic methanol oxidation. Chem - Eur J. 2020;26(18):4025–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201904229.
Zhao Y, Jiang Y, Mo Y, Zhai Y, Liu J, Strzelecki AC, Guo X, Shan C. Boosting electrochemical catalysis and nonenzymatic sensing toward glucose by single-atom Pt supported on Cu@CuO core–shell nanowires. Small. 2023;19(18):2207240. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202207240.
Lyu Z, Zhu S, Xie M, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Chen R, Tian M, Chi M, Shao M, Xia Y. Controlling the surface oxidation of Cu nanowires improves their catalytic selectivity and stability toward C2+ products in CO2 reduction. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60(4):1909–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202011956.
Yang H, Bao J, Qi Y, Zhao J, Hu Y, Wu W, Wu X, Zhong D, Huo D, Hou C. A disposable and sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on 3D graphene/Cu2O modified carbon paper electrode. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1135:12–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.08.010.
Zheng X, Tang J, Gallo A, Garrido Torres JA, Yu X, Athanitis CJ, Been EM, Ercius P, Mao H, Fakra SC, Song C, Davis RC, Reimer JA, Vinson J, Bajdich M, Cui Y. Origin of enhanced water oxidation activity in an iridium single atom anchored on NiFe oxyhydroxide catalyst. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2021;118(36):e2101817118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2101817118.
Shimoyama Y, Ishizuka T, Kotani H, Shiota Y, Yoshizawa K, Mieda K, Ogura T, Okajima T, Nozawa S, Kojima T. A Ruthenium(III)–oxyl complex bearing strong radical character. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016;55(45):14041–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201607861.
Kim J, Shih P-C, Tsao K-C, Pan Y-T, Yin X, Sun C-J, Yang H. High-performance pyrochlore-type yttrium ruthenate electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction in acidic media. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139(34):12076–83. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b06808.
Liu Q, Zheng W, Su X, Zhang X, Han N, Wang Z, Luo J, Lu Z, Fransaer J. Synergistic effect of different configurations on the anionic redox reaction in Na-deficient oxides for sodium ion batteries. Chem Eng J. 2023;452:139337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139337.
Acknowledgements
Changsheng Shan acknowledges the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22274036, 21874031) and “Chu-Tian Scholar” Program of Hubei Province. Y. Zhao thanks the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 22302059). The numerical calculations in this paper have been done on the supercomputing system in the Supercomputing Center of Wuhan University. Part of the work performed at the Advanced Photon Source, U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science User Facilities, was supported by the U.S. DOE, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. J.L. and X.G. also acknowledge the WSU-PNNL Nuclear Science and Technology Institute, and Alexandra Navrotsky Institute for Experimental Thermodynamics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuang Zhang: experiment, methodology, investigation, drawing, writing the original draft. Yunhao Jian: experiment, investigation. Wenlin Lei: investigation. Juejing Liu: experiment, writing the original draft. Xingyi Lyu: resources. Tao Li: resources. Yueming Zhai: resources. Xiaofeng Guo: resources, supervision, writing — review and editing. Yuanmeng Zhao: supervision, funding acquisition, writing — review and editing. Changsheng Shan: resources, supervision, funding acquisition, writing — review and editing. Li Niu: resources, writing — review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection featuring Nanozymes with guest editors Vipul Bansal, Sudipta Seal, and Hui Wei.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Jiang, Y., Lei, W. et al. Tailoring the d-band center on Ru1Cu single-atom alloy nanotubes for boosting electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Anal Bioanal Chem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05284-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05284-y