Abstract
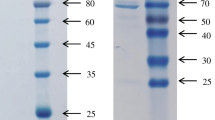
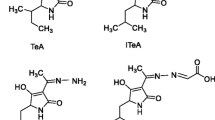
Deoxynivalenol (DON) is a mycotoxin that widely distributes in various foods and seriously threatens food safety. To minimize the consumers’ dietary exposure to DON, there is an urgent demand for developing rapid and sensitive detection methods for DON in food. In this study, a bifunctional single-chain variable fragment (scFv) linked alkaline phosphatase (ALP) fusion protein was developed for rapid and sensitive detection of deoxynivalenol (DON). The scFv gene was chemically synthesized and cloned into the expression vector pET25b containing the ALP gene by homologous recombination. The prokaryotic expression, purification, and activity analysis of fusion proteins (scFv-ALP and ALP-scFv) were well characterized and performed. The interactions between scFv and DON were investigated by computer-assisted simulation, which included hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and van der Waals forces. The scFv-ALP which showed better bifunctional activity was selected for developing a direct competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (dc-ELISA) for DON in cereals. The dc-ELISA takes 90 min for one test and exhibits a half inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 11.72 ng/mL, of which the IC50 was 3.08-fold lower than that of the scFv-based dc-ELISA. The developed method showed high selectivity for DON, and good accuracy was obtained from the spike experiments. Furthermore, the detection results of actual cereal samples analyzed by the method correlated well with that determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (R2=0.97165). These results indicated that the scFv-ALP is a promising bifunctional probe for developing the one-step colorimetric immunoassay, providing a new strategy for rapid and sensitive detection of DON in cereals.
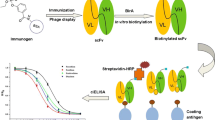
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yörük E, Tunali B, Kansu B, Ölmez F, Uz G, Zümrüt IM, Sarıkaya A, Meyva G. Characterization of high-level deoxynivalenol producer Fusarium graminearum and F. culmorum isolates caused head blight and crown rot diseases in Turkey. J Plant Dis Protect. 2016;123:177–86.
Ganesan AR, Mohan K, Karthick Rajan D, Pillay AA, Palanisami T, Sathishkumar P, Conterno L. Distribution, toxicity, interactive effects, and detection of ochratoxin and deoxynivalenol in food: a review. Food Chem. 2022;378:131978.
Yao Y, Long M. The biological detoxification of deoxynivalenol: a review. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;145:111649.
Chen C, Turna NS, Wu F. Risk assessment of dietary deoxynivalenol exposure in wheat products worldwide: Are new codex DON guidelines adequately protective? Trends Food Sci Tech. 2019;89:11–25.
Jurisic N, Schwartz-Zimmermann H, Kunz-Vekiru E, Reisinger N, Klein S, Caldwell D, Fruhmann P, Schatzmayr D, Berthiller F. Deoxynivalenol-3-sulphate is the major metabolite of dietary deoxynivalenol in eggs of laying hens. World Mycotoxin J. 2019;12(3):245–55.
Lee H-M, Song S-O, Cha S-H, Wee S-B, Bischoff K, Park S-W, Son S-W, Kang H-G, Cho M-H. Development of a monoclonal antibody against deoxynivalenol for magnetic nanoparticle-based extraction and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Vet Sci. 2013;14(2):143–50.
Rocha DFdL, Oliveira MdS, Furlong EB, Junges A, Paroul N, Valduga E, Backes GT, Zeni J, Cansian RL. Evaluation of the TLC quantification method and occurrence of deoxynivalenol in wheat flour of southern Brazil. Food Addit Contam: Part A. 2017;34(12):2220–9.
Şahin S, Eyupoğlu OE, Yaman M, Doğan TÇ, Korkmaz BİO, Omurtag GZ. Investigation of the deoxynivalenol and ochratoxin A levels by high-performance liquid chromatography of cereals sold in the markets in Türkiye. Food Sci Technol. 2023;43:e89822.
Tahoun IF, Gab-Allah MA, Yamani RN, Shehata AB. Development and validation of a reliable LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of deoxynivalenol and T-2 toxin in maize and oats. Microchem J. 2021;169:106599.
Li Y, Chen A, Mao X, Sun M, Yang S, Li J, You Y, Wu Y, Jiang G. Multiple antibodied based immunoaffinity columns preparation for the simultaneous analysis of deoxynivalenol and T-2 toxin in cereals by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2021;337:127802.
Xu Y, Huang Z-B, He Q-H, Deng S-Z, Li L-S, Li Y-P. Development of an immunochromatographic strip test for the rapid detection of deoxynivalenol in wheat and maize. Food Chem. 2010;119(2):834–9.
Narenderan S, Meyyanathan S, Babu B. Review of pesticide residue analysis in fruits and vegetables. Pre-treatment, extraction and detection techniques. Food Res Int. 2020;133:109141.
Jeanson A, Cloes J-M, Bouchet M, Rentier B. Comparison of conjugation procedures for the preparation of monoclonal antibody-enzyme conjugates. J Immunol Methods. 1988;111(2):261–70.
Xie G, Lu Y, Li W, He Z, Sun Z, Xie X, Liu X. Simultaneous heptamerization of nanobody and alkaline phosphatase by self-assembly and its application for ultrasensitive immunodetection of small molecular contaminants in agro-products. Food Control. 2022;141:109156.
Burkin MA, Nuriev RI, Wang Z, Galvidis IA. Development of sandwich double-competitive ELISA for sulfonamides. Comparative analytical characteristics and matrix effect resistance. Food Anal Methods. 2018;11:663–74.
Yan T, Zhang Q, Wang D, Li P, Tang X, Zhang W. Determination of deoxynivalenol by ELISA and immunochromatographic strip assay based on monoclonal antibodies. Toxin Rev. 2021;40(3):285–91.
Mokhtar HE, Xu A, Xu Y, Fadlalla MH, Wang S. Preparation of monoclonal antibody against deoxynivalenol and development of immunoassays. Toxins. 2022;14(8):533.
Zhang Y, Yang J, Lu Y, Ma D-Y, Qi MG, Wang S. A competitive direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the rapid detection of deoxynivalenol: development and application in agricultural products and feedstuff. Food Agric Immunol. 2017;28(3):516–27.
Nikolova G, Georgieva Y, Atanasova A, Radulova G, Kapogianni A, Tsacheva I. Autoinduction as means for optimization of the heterologous expression of recombinant single-chain Fv (scFv) antibodies. Mol Biotechnol. 2021;63(11):1049–56.
Ren W, Xu Y, Huang Z, Li Y, Tu Z, Zou L, He Q, Fu J, Liu S, Hammock BD. Single-chain variable fragment antibody-based immunochromatographic strip for rapid detection of fumonisin B1 in maize samples. Food Chem. 2020;319:126546.
Maragos CM, Li L, Chen D. Production and characterization of a single chain variable fragment (scFv) against the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol. Food Agric Immunol. 2012;23(1):51–67.
Min W-K, Kweon D-H, Park K, Park Y-C, Seo J-H. Characterisation of monoclonal antibody against aflatoxin B1 produced in hybridoma 2C12 and its single-chain variable fragment expressed in recombinant Escherichia coli. Food Chem. 2011;126(3):1316–23.
Sompunga P, Pruksametanan N, Rangnoi K, Choowongkomon K, Yamabhai M. Generation of human and rabbit recombinant antibodies for the detection of zearalenone by phage display antibody technology. Talanta. 2019;201:397–405.
Kadkhoda J, Akrami-Hasan-Kohal M, Tohidkia MR, Khaledi S, Davaran S, Aghanejad A. Advances in antibody nanoconjugates for diagnosis and therapy: a review of recent studies and trends. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;185:664–78.
Kim H-Y, Lee J-H, Kim MJ, Park SC, Choi M, Lee W, Ku KB, Kim BT, Changkyun Park E, Kim HG, Kim SI. Development of a SARS-CoV-2-specific biosensor for antigen detection using scFv-Fc fusion proteins. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021;175:112868.
Mahalakshmi N, Ravishankaran R, Kamatchi R, Sangith N, Kaliraj P, Meenakshisundaram S. Molecular evolution of single chain fragment variable (scFv) for diagnosis of lymphatic filariasis. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46:5409–18.
He Q, Yang L, Lin M, Yang H, Cui X, McCoy MR, Hammock BD, Fang Y, Zhao S. Generation of bioluminescent enzyme immunoassay for ferritin by single-chain variable fragment and its NanoLuc luciferase fusion. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022;414(23):6939–46.
Oyama H, Kiguchi Y, Morita I, Miyashita T, Ichimura A, Miyaoka H, Izumi A, Terasawa S, Osumi N, Tanaka H, Niwa T, Kobayashi N. NanoLuc luciferase as a suitable fusion partner of recombinant antibody fragments for developing sensitive luminescent immunoassays. Analytica Chim Acta. 2021;1161:238180.
Dong J, Li Z, Wang Y, Jin M, Shen Y, Xu Z, Abd El-Aty A, Gee SJ, Hammock BD, Sun Y. Generation of functional single-chain fragment variable from hybridoma and development of chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for determination of total malachite green in tilapia fish. Food Chem. 2021;337:127780.
Hanyu Y, Kato M. Screening antibody libraries with colony assay using scFv-alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins. Molecules. 2020;25(12):2905.
Rangnoi K, Jaruseranee N, O’Kennedy R, Pansri P, Yamabhai M. One-step detection of aflatoxin-B1 using scFv-alkaline phosphatase-fusion selected from human phage display antibody library. Mol Biotechnol. 2011;49:240–9.
Pranomphon R, Srila W, Yamabhai M. Generation of recombinant scFv antibody against ochratoxin A (OTA). Indones J Biotechnol. 2018;22(2):107–13.
He J, Tao X, Wang K, Ding G, Li J, Li QX, Gee SJ, Hammock BD, Xu T. One-step immunoassay for the insecticide carbaryl using a chicken single-chain variable fragment (scFv) fused to alkaline phosphatase. Anal Biochem. 2019;572:9–15.
Li C, He J, Ren H, Zhang X, Du E, Li X. Preparation of a chicken scFv to analyze gentamicin residue in animal derived food products. Anal Chem. 2016;88(7):4092–8.
Leivo J, Vehniäinen M, Lamminmäki U. Phage display selection of an anti-idiotype-antibody with broad-specificity to deoxynivalenol mycotoxins. Toxins. 2021;13:18.
Han L, Li Y-T, Jiang J-Q, Li R-F, Fan G-Y, Lv J-M, Zhou Y, Zhang W-J, Wang Z-L. Development of a direct competitive ELISA kit for detecting deoxynivalenol contamination in wheat. Molecules. 2019;25(1):50.
Xu Y, Yang H, Huang Z, Li Y, He Q, Tu Z, Ji Y, Ren W. A peptide/maltose-binding protein fusion protein used to replace the traditional antigen for immunological detection of deoxynivalenol in food and feed. Food Chem. 2018;268:242–8.
Qiu Y-L, He Q-H, Xu Y, Bhunia AK, Tu Z, Chen B, Liu Y-Y. Deoxynivalenol-mimic nanobody isolated from a naïve phage display nanobody library and its application in immunoassay. Analytica Chim Acta. 2015;887:201–8.
Li Y, Liu G, Fu X, He J, Wang Z, Hou J, Cao X, Shi W, Zhang S. High-sensitive chemiluminescent ELISA method investigation for the determination of deoxynivalenol in rice. Food Anal Methods. 2015;8(3):656–60.
Yu S, Yu F, Li Y, Liu L, Zhang H, Qu L, Wu Y. Magnetic nanoparticles replacing microplate as immobile phase could greatly improve the sensitivity of chemiluminescence enzymatic immunoassay for deoxynivalenol. Food Control. 2016;60:500–4.
Duan N, Li C, Song M, Ren K, Wang Z, Wu S. Deoxynivalenol fluorescence aptasensor based on AuCu bimetallic nanoclusters and MoS2. Microchim Acta. 2022;189(8):296.
Zhou S, Xu L, Kuang H, Xiao J, Xu C. Fluorescent microsphere immunochromatographic sensor for ultrasensitive monitoring deoxynivalenol in agricultural products. Microchem J. 2021;164:106024.
Qin M, Zhang X, Zhao X, Song Y, Zhang J, Xia X, Han Q. Complementary chain competition and fluorescence quenching detection of deoxynivalenol and analytical applications using a novel aptamer. CyTA-J Food. 2021;19(1):257–64.
Jiang X, Wang Y, Zhao L, Li X, Dong Y. Development of aptamer-based au nanoparticle lateral flow test strips for the detection of deoxynivalenol in corn. ACS Food Sci Technol. 2023;3(1):182–90.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (323QN251, 824MS074), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32102067), and the Education Department of Hainan Province (Hnky2023-74).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Xing Liu. Methodology: Li Wen, Yirui Huang. Formal analysis: Li Wen, Yirui Huang, Shiyuan Shi, and Xiaoxia Xie. Investigation: Li Wen, Yirui Huang, Zhichang Sun, and Shiyuan Shi. Validation: Yirui Huang, Xiaoxia Xie. Data curation: Zhenyun He. Project administration: Zhichang Sun, Zhenyun He, and Xing Liu. Writing—original draft preparation: Li Wen. Writing—review and editing: Zhenyun He and Xing Liu. Funding acquisition: Zhenyun He, Xing Liu. Resources: Xing Liu. Supervision: Xing Liu.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, L., Huang, Y., Sun, Z. et al. Development of alkaline phosphatase-linked single-chain variable fragment fusion proteins for one-step immunodetection of deoxynivalenol in cereals. Anal Bioanal Chem 416, 2929–2939 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05241-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05241-9