Abstract
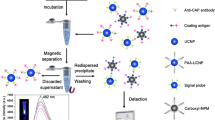
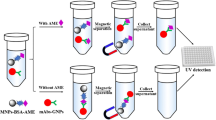
Zearalenone (ZEN), produced by Fusarium species, is a potential risk to human health. Traditional enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is restricted due to low sensitivity for the detection of ZEN. Herein, enzyme nanocomposites (ALP-SA-Bio-ssDNA, ASBD) were prepared with the self-assembly strategy based on streptavidin-labeled alkaline phosphatase (SA-ALP) and dual-biotinylated ssDNA (B2-ssDNA). The enzyme nanocomposites improved the loading amount of ALP and catalyzed more ascorbic acid 2-phosphate to generate ascorbic acid (AA). Subsequently, Cu2+ could be reduced to copper nanoclusters (CuNCs) having strong fluorescence signal by AA with poly T. Benefiting from the high enzyme load of nanocomposites and the strong signal of CuNCs, the fluorescence ELISA was successfully established for the detection of ZEN. The proposed method exhibited lower limit of detection (0.26 ng mL−1) than traditional ELISA (1.55 ng mL−1). The recovery rates ranged from 92.00% to 108.38% (coefficient of variation < 9.50%) for the detection of zearalenone in corn and wheat samples. In addition, the proposed method exhibited no cross reaction with four other mycotoxins. This proposed method could be used in trace detection for food safety.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that has been used is confidential.
References
Anfossi L, Baggiani C, Giovannoli C, D’Arco G, Giraudi G. Lateral-flow immunoassays for mycotoxins and phycotoxins: a review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013;405(2–3):467–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6033-4.
Smith MC, Madec S, Coton E, Hymery N. Natural co-occurrence of mycotoxins in foods and feeds and their in vitro combined toxicological effects. Toxins. 2016;8(4):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040094.
Xu SL, Zhang GG, Fang BL, Xiong QR, Duan HW, Lai WH. Lateral flow immunoassay based on polydopamine-coated gold nanoparticles for the sensitive detection of zearalenone in maize. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2019;11(34):31283–90. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b08789.
Kong WJ, Li JY, Qiu F, Wei JH, Xiao XH, Zheng YG, Yang MH. Development of a sensitive and reliable high performance liquid chromatography method with fluorescence detection for high-throughput analysis of multi-class mycotoxins in Coix seed. Anal Chim Acta. 2013;799:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.08.042.
Cho HD, Suh JH, Feng S, Eom T, Kim J, Hyun SM, Kim J, Wang Y, Han SB. Comprehensive analysis of multi-class mycotoxins in twenty different species of functional and medicinal herbs using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control. 2019;96:517–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.10.007.
Gonzalez-Jartin JM, Alfonso A, Rodriguez I, Sainz MJ, Vieytes MR, Botana LM. A QuEChERS based extraction procedure coupled to UPLC-MS/MS detection for mycotoxins analysis in beer. Food Chem. 2019;275:703–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.162.
Cheng Z, Li MH, Marriott PJ, Zhang XX, Wang SP, Li JG, Ma LY. Chemometric analysis of the volatile compounds generated by Aspergillus carbonarius strains isolated from grapes and dried vine fruits. Toxins. 2018;10(2):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020071.
Zhu WY, Ji GN, Chen RP, Xiang YF, Ji SF, Zhang SL, Gao ZX, Liu H, Wang Y, Han T. A fluorescence aptasensor based on hybridization chain reaction for simultaneous detection of T-2 toxins and zearalenone1. Talanta. 2023;255:124249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.124249.
Tang XQ, Li PW, Zhang Q, Zhang ZW, Zhang W, Jiang J. Time-resolved fluorescence immunochromatographic assay developed using two idiotypic nanobodies for rapid, quantitative, and simultaneous detection of aflatoxin and zearalenone in Maize and Its Products. Anal Chem. 2017;89(21):11520–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02794.
Lin XF, Li CX, Tong XY, Duan N, Wang ZP, Wu SJ. A portable paper-based aptasensor for simultaneous visual detection of two mycotoxins in corn flour using dual-color upconversion nanoparticles and Cu-TCPP nanosheets. Food Chem. 2023;404:134750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134750.
Jia YX, Zhao SQ, Li DS, Yang JL, Yang L. Portable chemiluminescence optical fiber aptamer-based biosensors for analysis of multiple mycotoxins. Food Control. 2023;144:109361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109361.
Guan Y, Ma JN, Neng J, Yang BL, Wang Y, Xing FG. A Novel and label-free chemiluminescence detection of zearalenone based on a truncated aptamer conjugated with a G-quadruplex DNAzyme. Biosensors-Basel. 2023;13(1):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010118.
Wu SJ, Liu LH, Duan N, Li Q, Zhou Y, Wang ZP. Aptamer-based lateral flow test strip for rapid detection of zearalenone in corn samples. J Agr Food Chem. 2018;66(8):1949–54. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05326.
Yan JX, Hu WJ, You KH, Ma ZE, Xu Y, Li YP, He QH. Biosynthetic mycotoxin conjugate mimetics-mediated green strategy for multiplex mycotoxin immunochromatographic assay. J Agr Food Chem. 2020;68(7):2193–200. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06383.
Ma TY, Liu KX, Yang X, Yang JY, Pan MF, Wang S. Development of indirect competitive ELISA and visualized multicolor ELISA based on gold nanorods growth for the determination of zearalenone. Foods. 2021;10(11):2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112654.
Liu ZJ, Wang XY, Ren XX, Li WB, Sun JF, Wang XW, Huang YQ, Guo YG, Zeng HW. Novel fluorescence immunoassay for the detection of zearalenone using HRP-mediated fluorescence quenching of gold-silver bimetallic nanoclusters. Food Chem. 2021;355:129633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129633.
Zhang FY, Liu B, Sheng W, Zhang Y, Liu Q, Li SJ, Wang S. Fluoroimmunoassays for the detection of zearalenone in maize using CdTe/CdS/ZnS quantum dots. Food Chem. 2018;255:421–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.060.
Li RY, Liu Q, Jin Y, Li BX. Fluorescent enzyme-linked immunoassay strategy based on enzyme-triggered in-situ synthesis of fluorescent copper nanoclusters. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2019;281:28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.128.
Xiong Y, Leng YK, Li XM, Huang XL, Xiong YH. Emerging strategies to enhance the sensitivity of competitive ELISA for detection of chemical contaminants in food samples. Trac-Trend Anal Chem. 2020;126:115861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115861.
Xu CC, Liu QQ, Chu S, Li P, Wang FX, Si YM, Mao GJ, Wu CF, Wang H. A microdots array-based fluoremetric assay with superwettability profile for simultaneous and separate analysis of iron and copper in red wine. Anal Chim Acta. 2023;1254:341045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2023.341045.
Wang ZX, Guo YR, Xianyu YL. Applications of self-assembly strategies in immunoassays: a review. Coordin Chem Rev. 2023;478:214974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214974.
Men D, Zhang TT, Hou LW, Zhou J, Zhang ZP, Shi YY, Zhang JL, Cui ZQ, Deng JY, Wang DB, Zhang XE. Self-assembly of ferritin nanoparticles into an enzyme nanocomposite with tunable size for ultrasensitive immunoassay. ACS Nano. 2015;9(11):10852–60. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b03607.
Li ZW, Fan QS, Yin YD. Colloidal self-assembly approaches to smart nanostructured materials. Chem Rev. 2022;122(5):4976–5067. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00482.
Li XY, Liu XW, Liu XG. Self-assembly of colloidal inorganic nanocrystals: nanoscale forces, emergent properties and applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2021;50(3):2074–101. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cs00436g.
Hou L, Huang JJ, Liu SD, Lin TR, Zhao SL. Magneto-controlled fluorescent immunosensor for sensitive determination of biomarker via three-dimensional AuNCs/liposome networks. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2021;342:130075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130075.
Li XH, Lin LY, Wang KY, Li J, Feng L, Song LJ, Liu XK, He JH, Sakthivel R, Chung RJ. Streptavidin-functionalized-polyethyleneimine/chitosan/HfO2-Pr6O11 nanocomposite using label-free electrochemical immunosensor for detecting the hunger hormone ghrelin. Compos Part B-Eng. 2021;224:109231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109231.
Weber PC, Ohlendorf DH, Wendoloski JJ, Salemme FR. Structural origins of high-affinity biotin binding to streptavidin. Science. 1989;243(4887):85–8. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2911722.
Fang BL, Peng J, Zhang G, Xing KY, Chen WY, Liu DF, Shan S, Xiong YH, Lai WH. I-2/I–mediated fluorescence quenching of an Ag+-doped gold nanocluster-based immunoassay for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk. J Dairy Sci. 2022;105(4):2922–30. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2021-21281.
Wu J, Chen YP, Yang MZ, Wang Y, Zhang C, Yang M, Sun JS, Xie MX, Jiang XY. Streptavidin-biotin-peroxidase nanocomplex-amplified microfluidics immunoassays for simultaneous detection of inflammatory biomarkers. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;982:138–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.05.031.
Song CM, Zhi AM, Liu QT, Yang JF, Jia GC, Shervin J, Tang L, Hu XF, Deng RG, Xu CL, Zhang GP. Rapid and sensitive detection of beta-agonists using a portable fluorescence biosensor based on fluorescent nanosilica and a lateral flow test strip. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;50:62–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.06.022.
Shao YN, Duan H, Guo L, Leng YK, Lai WH, Xiong YH. Quantum dot nanobead-based multiplexed immunochromatographic assay for simultaneous detection of aflatoxin B-1 and zearalenone. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1025:163–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.03.041.
An Y, Ren Y, Bick M, Dudek A, Waworuntu EHW, Tang J, Chen J, Chang BS. Highly fluorescent copper nanoclusters for sensing and bioimaging (vol 154, 112078, 2020). Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;156:112127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112127.
Mu J, Peng Y, Shi Z, Zhang DW, Jia Q. Copper nanocluster composites for analytical (bio)-sensing and imaging: a review. Microchim Acta. 2021;188(11):384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05011-9.
Zhong YP, Xue FF, Wei P, Li RH, Cao CY, Yi T. Water-soluble MoS2 quantum dots for facile and sensitive fluorescence sensing of alkaline phosphatase activity in serum and live cells based on the inner filter effect. Nanoscale. 2018;10(45):21298–306. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr05549a.
Xu JH, Zhang H, Zhang W, Li P, Zhang W, Wang H, Tang B. Fluorescent nanosensor for in situ detection of phosphate and alkaline phosphatase in mice with parathyroid dysfunction. Chem Commun. 2020;56(16):2431–4. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc08828h.
Liu L, Wu DH, Zhen S, Lu KQ, Yi XY, Sun ZF. Electrochemical detection of telomerase in cancer cells based on the in-situ formation of streptavidin-biotin-DNA-biotin networks for signal amplification. Sensor Actuat B-Chem. 2021;334:129659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129659.
Sun J, Hu T, Xu XL, Wang L, Yang XR. A fluorescent ELISA based on the enzyme-triggered synthesis of poly (thymine)-templated copper nanoparticles. Nanoscale. 2016;8(38):16846–50. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr06446a.
Xing KY, Peng J, Shan S, Liu DF, Huang YN, Lai WH. Green enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on the single-stranded binding protein-assisted aptamer for the detection of mycotoxin. Anal Chem. 2020;92(12):8422–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01073.
Ma LY, Zhang XP, Peng Y, Chen W, Xiao Y, Fang HJ, Yang HL, Zhou Y. Based on intervening PCR for detection of alkaline phosphatase and zearalenone. Microchem J. 2023;186:108314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.108314.
Wang YA, Wang XF, Wang SY, Fotina HN, Wang ZL. Development of a highly sensitive and specific monoclonal antibody based on indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of zearalenone in food and feed Samples. Toxins. 2022;14(3):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030220.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82260644) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20212BAB215041) and Pilot Demonstration Project of Ceilings in Funding for Provincial Science and Technology Program of Jiangxi Academy of Sciences (2021YSBG22023 and 2023YJC2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xudong Jing: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Writing—original draft, Writing – review & editing. Sha Yu: Investigation, Software. Ganggang Zhang: Investigation, Software, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. Yanyan Tang: Investigation, Software. Jiaqi Yin: Investigation, Software. Juan Peng: Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation. Weihua Lai: Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, X., Yu, S., Zhang, G. et al. Sensitive fluorescence ELISA for the detection of zearalenone based on self-assembly DNA nanocomposites and copper nanoclusters. Anal Bioanal Chem 416, 983–992 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05088-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05088-6