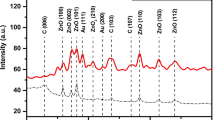
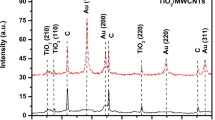
Abstract
In present work, the enzyme cholesterol oxidase (ChOx) was immobilized by Nafion® (Naf) on Pt,Ru–C nanocomposite and an ionic liquid (IL)–modified carbon paste electrode (CPE) in order to create cholesterol biosensor (Naf/ChOx/Pt,Ru–C/IL-CPE). The prepared working electrodes were characterized using scanning electron microscopy–energy-dispersive spectrometry, while their electrochemical performance was evaluated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopic, cyclic voltammetric, and amperometric techniques. Excellent synergism between IL 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide ([AMIM][DCA]), Pt,Ru–C, and ChOx, as modifiers of CPE, offers the most pronounced analytical performance for improved cholesterol amperometric determination in phosphate buffer solution pH 7.50 at a working potential of 0.60 V. Under optimized experimental conditions, a linear relationship between oxidation current and cholesterol concentration was found for the range from 0.31 to 2.46 µM, with an estimated detection limit of 0.13 µM and relative standard deviation (RSD) below 5.5%. The optimized amperometric method in combination with the developed Naf/ChOx/Pt,Ru–C/IL-CPE biosensor showed good repeatability and high selectivity towards cholesterol biosensing. The proposed biosensor was successfully applied to determine free cholesterol in a human blood serum sample via its enzymatic reaction product hydrogen peroxide despite the presence of possible interferences. The percentage recovery ranged from 99.08 to 102.81%, while RSD was below 2.0% for the unspiked as well as the spiked human blood serum sample. The obtained results indicated excellent accuracy and precision of the method, concluding that the developed biosensor can be a promising alternative to existing commercial cholesterol tests used in medical practice.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajaram R, Mathiyarasu J. The design and fabrication of disposable sensors: an overview. In: Pandikumar A, Shalini Devi KS, editors. Disposable electrochemical sensors for healthcare monitoring: material properties and design. The Royal Society of Chemistry: Croydon, United Kingdom; 2021; pp. 3, 13. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781839163364.
Kaariz DGA, Darabi E, Mohammad ES. Fabrication of Au/ZnO/MWCNTs electrode and its characterization for electrochemical cholesterol biosensor. J Theor Appl Phys. 2020;14:339–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40094-020-00390-5.
Li L-H, Dutkiewicz EP, Huang Y-C, Zhou H-B, Hsu C-C. Analytical methods for cholesterol quantification. J Food Drug Anal. 2019;27:375–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2018.09.001.
Thakur N, Gupta D, Mandal D, Nagaiah TC. Ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensors for dopamine and cholesterol: recent advances, challenges and strategies. Chem Commun. 2021;57:13084. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC05271C.
Shrestha R, Chen Z, Gao Z, Chen Y, Okada E, Ukawa S, Nakagawa T, Nakamura K, Tamakoshi A, Chiba H, Hui S-P. HPLC with spectrophotometric or mass spectrometric detection for quantifying very-long chain fatty acids in human plasma and its association with cardiac risk factors. Ann Clin Biochem. 2021;58:400–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/00045632211007.
Olisov D, Lee K, Jun S-H, Song SH, Kim JH, Lee YA, Shin CH, Song J. Measurement of serum steroid profiles by HPLC-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2019;1117:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.04.001.
Tran HV, Nguyen TV, Nguyen LTN, Hoang HS, Huynh CD. Silver nanoparticles as a bifunctional probe for label-free and reagentless colorimetric hydrogen peroxide chemosensor and cholesterol biosensor. J Sci-Adv Mater Dev. 2020;5:385–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2020.06.001.
Xu X, Zhao Y, Tan H, Ma Y, Li Y. In situ encapsulation of horseradish peroxidase in zeolitic imidazolate framework–8 enables catalyzing luminol reaction under near-neutral conditions for sensitive chemiluminescence determination of cholesterol. Microchim Acta. 2020;187:346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04313-8.
Amiri M, Arshi S. An overview on electrochemical determination of cholesterol. Electroanalysis. 2020;32:1391–407. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201900669.
Chokkareddy R, Niranjan T, Redhi GG. Ionic liquid based electrochemical sensors and their applications. In: Green sustainable process for chemical and environmental engineering and science. Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; 2020. pp. 367–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-817386-2.00013-5.
Okwundu OS, Aniekwe EU, Nwanno CE. Unlimited potentials of carbon: different structures and uses (a Review). Metall Mater Eng. 2018;24:145–71. https://doi.org/10.30544/388.
Tigari G, Manjunatha JG, Nagarajappa H, Prinith NS. Research developments in carbon materials based sensors for determination of hormones. J Electrochem Sci Eng. 2022;12:3–23. https://doi.org/10.5599/jese.1094.
Unal DN, Sadak S, Uslu B. A review on electrochemical and optical sensing platform based on ionic liquids for different molecules determination. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2021;10:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2021.1978055.
Ghorbanizamani F, Timur S. Ionic liquids from biocompatibility and electrochemical aspects toward applying in biosensing devices. Anal Chem. 2018;90:640–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03596.
Kalambate PK, Rao Z, Dhanjai, Wu J, Shen Y, Boddula R, Huang Y. Electrochemical (bio) sensors go green. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;163:112270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112270.
Shamshina JL, Berton P. Use of ionic liquids in chitin biorefinery: a systematic review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00011.
Wang X, Hao J. Recent advances in ionic liquid-based electrochemical biosensors. Sci Bull. 2016;61:1281–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1151-6.
Yavir K, Marcinkowski Ł, Marcinkowska R, Namieśnik J, Kloskowski A. Analytical applications and physicochemical properties of ionic liquid based hybrid materials: a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1054:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.10.061.
Bankole OE, Verma DK, Chávez González ML, Guzmán Ceferino J, Sandoval-Cortés J, Aguilar CN. Recent trends and technical advancements in biosensors and their emerging applications in food and bioscience. Food Biosci. 2022;47:101695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101695.
Maduraiveeran G, Sasidharan M, Ganesan V. Electrochemical sensor and biosensor platforms based on advanced nanomaterials for biological and biomedical applications. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;103:113–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.12.031.
Naresh V, Lee N. A review on biosensors and recent development of nanostructured materials-enabled biosensors. Sensors. 2021;21:1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041109.
Nemiwal M, Zhang TC, Kumar D. Enzyme immobilized nanomaterials as electrochemical biosensors for detection of biomolecules. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2022;156:110006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2022.110006.
Rajapaksha RDAA, Hashim U, Gopinath SCB, Parmin NA, Fernando CAN. Nanoparticles in electrochemical bioanalytical analysis. In: Nanoparticles in analytical and medical devices. Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; 2021. pp 83–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821163-2.00006-6.
Saxena U, Das AB. Nanomaterials towards fabrication of cholesterol biosensors: key roles and design approaches. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;75:196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.08.042.
Stephanie R, Kim MW, Kim SH, Kim J-K, Park CY, Park TJ. Recent advances of bimetallic nanomaterials and its nanocomposites for biosensing applications. Trend Anal Chem. 2021;135:116159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116159.
Kaya SI, Yıldırım S, Cetinkaya A, Erkmen C, Uslu B, Ozkan SA. Nanomaterial-based electroanalytical sensors for the selected prohibited anabolic agents, hormones and metabolic modulators and their sensitive assays. Trend Anal Chem. 2021;145:116457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116457.
Canbay E, Yaşa İ, Akyilmaz E. Development an amperometric microbial-enzyme hybrid cholesterol biosensor based on ionic liquid MWCNT carbon paste electrode. Electroanalysis. 2021;33:2381–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202100251.
Karimi S, Ghourchian H, Rahimi P, Rafiee-Pour H-A. A nanocomposite based biosensor for cholesterol determination. Anal Methods. 2012;4:3225–31. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AY25826A.
Wolny A, Chrobok A. Ionic liquids for development of heterogeneous catalysts based on nanomaterials for biocatalysis. Nanomaterials. 2021;11:2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082030.
Rzelewska-Piekut M, Regel-Rosocka M. Separation of Pt(IV), Pd(II), Ru(III) and Rh(III) from model chloride solutions by liquid-liquid extraction with phosphonium ionic liquids. Sep Purif Technol. 2019;212:791–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.11.091.
Alagappan M, Immanuel S, Sivasubramanian R, Kandaswamy A. Development of cholesterol biosensor using Au nanoparticles decorated f-MWCNT covered with polypyrrole network. Arab J Chem. 2020;13:2001–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.02.018.
Devi S, Kanwar SS. Cholesterol oxidase: source, properties and applications. Insights Enzyme Res. 2017;1:1. https://doi.org/10.21767/2573-4466.100005.
Li G, Zeng J, Zhao L, Wang Z, Dong C, Liang J, Zhou Z, Huang Y. Amperometric cholesterol biosensor based on reduction graphene oxide-chitosan-ferrocene/platinum nanoparticles modified screen-printed electrode. J Nanopar Res. 2019;21:162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4602-6.
Rodrigues F, Devi S, Meenakshi S, Pandian K, Perumal P. Carbon nanotube based amperometric biosensor for the quantitative detection of cholesterol. IOSR J Biotechnol Biochem. 2017;3:10–20. https://doi.org/10.9790/264X-03021020.
Salazar P, Martín M, González-Mora JL. In situ electrodeposition of cholesterol oxidase-modified polydopamine thin film on nanostructured screen printed electrodes for free cholesterol determination. J Electroanal Chem. 2019;837:191–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.02.032.
Zheng Y, Xuan X, Wang J, Fan M. The enhanced dissolution of β-cyclodextrin in some hydrophilic ionic liquids. J Phys Chem A. 2010;114:3926–31. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp907333v.
Yu X, Sun Y, Xue L, Huang X, Qu Y. Strategies for improving the catalytic performance of an enzyme in ionic liquids. Top Catal. 2014;57:923–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-014-0253-0.
Švancara I, Metelka R, Vytřas K. Piston-driven carbon paste electrode holders for electrochemical measurements. In: Vytřas K, Kalcher K, editors. Sensing in electroanalysis: University of Pardubice, Pardubice; 2005. p. 7.
Ravisankar P, Naga Navya Ch, Pravallika D, Navya SD. A review on step-by-step analytical method validation. IOSR J Pharm. 2015;5:7–19.
Anojčić J, Guzsvány V, Vajdle O, Kónya Z, Kalcher K. Rapid amperometric determination of H2O2 by a Pt nanoparticle/Vulcan XC72 composite-coated carbon paste electrode in disinfection and contact lens solutions. Monatsh Chem. 2018;149:1727–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-018-2253-4.
Anojčić J, Kullawanichaiyanan K, Mutić S, Guzsvány V, Leesakul N, Mimica Dukić N. Self-assembled iridium(III) complex microspheres on the carbon paste electrode surface for signal enhanced amperometric determination of H2O2 in color cream developers. J Electroanal Chem. 2022;904:115873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115873.
Ghosh S, Ahmad R, Kumar KS. Immobilization of cholesterol oxidase: an overview. Open Biotechnol J. 2018;12:176–88. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874070701812010176.
KaliyarajSelva Kumar A, Zhang Y, Li D, Compton RG. A mini-review: how reliable is the drop casting technique? Electrochem Commun. 2020;121:10686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2020.106867.
García-Miranda Ferrari A, Foster CW, Kelly PJ, Brownson DAC, Banks CE. Determination of the electrochemical area of screen-printed electrochemical sensing platforms. Biosensors. 2018;8:53. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020053.
Figueiredo-Filho LCS, Brownson DAC, Gómez-Mingot M, Iniesta J, Fatibello-Filho O, Banks CE. Exploring the electrochemical performance of graphitic paste electrodes: graphene vs. graphite. Analyst. 2013;138:6354. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN00950E.
Vicentini FC, Ravaninia AE, Figueiredo-Filho LCS, Iniesta J, Banks CE, Fatibello-Filho O. Imparting improvements in electrochemical sensors: evaluation of different carbon blacks that give rise to significant improvement in the performance of electroanalytical sensing platforms. Electrochim Acta. 2014;157:125–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.204.
Švancara I, Kalcher K, Walcarius A, Vytras K. Electroanalysis with carbon paste electrodes. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2012.
Zarrougui R, Hachicha R, Rjab R, Ghodbane O. 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids employed as suitable electrolytes for high energy density supercapacitors based on graphene nanosheets electrodes. J Mol Liq. 2018;249:795–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.078.
Pérez-Rodríguez S, Pastor E, Lázaro MJ. Electrochemical behavior of the carbon black Vulcan XC-72R: influence of the surface chemistry. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2018;43:7911–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.03.040.
Siller-Ceniceros AA, Sánchez-Castro ME, Morales-Acosta D, Torres-Lubian JR, Martínez GE, Rodríguez-Varela FJ. Innovative functionalization of Vulcan XC-72 with Ru organometallic complex: significant enhancement in catalytic Activity of Pt/C Electrocatalyst for the methanol oxidation reaction (MOR). App Catal B: Environ. 2017;209:455–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.023.
Yang G, Sun Y, Lv P, Zhen F, Cao X, Chen X, Wang Z, Yuan Z, Kong X. Preparation of Pt–Ru/C as an oxygen-reduction electrocatalyst in microbial fuel cells for wastewater treatment. Catalysts. 2016;6:150. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6100150.
Yu X, Zhang Q, Ling Y, Yang Z, Cheng H. Promoted stability and electrocatalytic activity of PtRu electrocatalyst derived from coating by cerium oxide with high oxygen storage capacity. App Surf Sci. 2018;455:815–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.058.
Kung C-C, Lin P-Y, Buse FJ, Xue Y, Yu X, Dai L, Liu C-C. Preparation and characterization of three dimensional graphene foam supported platinum–ruthenium bimetallic nanocatalysts for hydrogen peroxide based electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;52:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.08.025.
Liu T-Z, Hu R, Liu Y, Zhang K-L, Bai R-Y, Yang Y-H. Amperometric immunosensor based on covalent organic frameworks and Pt/Ru/C nanoparticles for the quantification of C-reactive protein. Microchim Acta. 2020;187:320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04286-8.
Stasyuk N, Gayda G, Zakalskiy A, Zakalska O, Serkiz R, Gonchar M. Amperometric biosensors based on oxidases and PtRu nanoparticles as artificial peroxidase. Food Chem. 2019;285:213–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.117.
Kumari L, Kanwar SS. Cholesterol oxidase and its applications. Adv Microbiol. 2012;2:49–65. https://doi.org/10.4236/aim.2012.22007.
John RAB, Kumar AR. A critical review on recent advancements and crucial aspects of enzymatic and non-enzymatic cholesterol biosensors. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci. 2021;7:12–40. https://doi.org/10.26479/2021.0704.02.
Kalaivani GJ, Suja SK. Cholesterol oxidase immobilized inulin based nanocomposite as the sensing material for cholesterol in biological and food samples. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2020;140:109631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2020.109631.
Narwal V, Deswal R, Batra B, Kalra V, Hooda R, Sharma M, Rana JS. Cholesterol biosensors: a review. Steroids. 2019;143:6–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2018.12.003.
Dervisevic M, Çevik E, Şenel M, Nergiz C, Abasiyanik MF. Amperometric cholesterol biosensor based on reconstituted cholesterol oxidase on boronic acid functional conducting polymers. J Electroanal Chem. 2016;776:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.06.033.
Kim MW, Kim YH, Bal J, Stephanie R, Baek SH, Lee SK, Park CY, Park TJ. Rational design of bienzyme nanoparticles-based total cholesterol electrochemical sensors and the construction of cholesterol oxidase expression system. Sens Actuators: B Chem. 2021;349:130742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130742.
Jang H-S, Kim D, Lee C, Yan B, Qin X, Piao Y. Nafion coated Au nanoparticle-graphene quantum dot nanocomposite modified working electrode for voltammetric determination of dopamine. Inorg Chem Commun. 2019;105:174–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2019.05.009.
Zheng D, Ye J, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Yu C. Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid on ordered mesoporous carbon/Nafion composite film. J Electroanal Chem. 2009;625:82–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2008.10.012.
Kumar S, Vicente-Beckett V. Glassy carbon electrodes modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the determination of ascorbic acid by square-wave voltammetry. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2012;3:388–96. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.3.45.
Acknowledgements
This paper is dedicated to the memory of our wonderful colleague and Professor Dr. Valéria Guzsvány in remembrance of her great effort and conceptualization of this work.
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia (Grant No. 451–03-47/2023–01/200125) and CEEPUSIII (CZ-0212–16-2223) network.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The studies have been approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Sciences, University of Novi Sad (No. of decision 0601–117/23–15-2), and the studies have been performed in accordance with ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mutić, S., Stanković, D., Kónya, Z. et al. Facile immobilization of cholesterol oxidase on Pt,Ru–C nanocomposite and ionic liquid–modified carbon paste electrode for an efficient amperometric free cholesterol biosensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 5709–5722 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04847-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04847-9