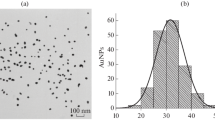
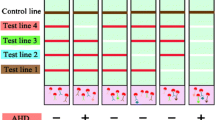
Abstract
Aquatic toxins are a group of toxic compounds produced by several types of freshwater and marine algae and cyanobacteria and transported through the food chains of water bodies. Potential contamination of aquaculture products (raw and processed fish and seafood) with aquatic toxins requires the use of efficient screening methods for their control. In this study, a multiplex immunochromatographic test system for the simultaneous detection of three aquatic toxins—phycotoxins domoic acid (DA) and okadaic acid (OA), and cyanotoxin microcystin-LR (MC-LR)—is for the first time developed. For this, a competitive indirect immunochromatographic analysis (ICA) based on gold-labeled secondary antibodies was carried out. The LODs/cutoffs/working ranges of the ICA were 0.05/0.3/0.07–0.29, 1.3/100/3.2–58.2, and 0.1/2.0/0.2–1.1 ng/mL for MC-LR, DA, and OA, respectively. The assay duration was 18 min. The developed test system was used to analyze water samples from natural sources (salt and fresh water) and fish samples. For sample preparation of water, simple dilution with a buffer was proposed; for fish samples, methanol–water extraction was utilized. It was demonstrated that the triple LFIA specifically detected target aquatic toxins with recoveries of 85.0–121.5%. The developed multiplex LFIA can be considered a promising analytical solution for the rapid, easy, and sensitive control of water and food safety.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louzao MC, Vilariño N, Vale C, Costas C, Cao A, Raposo-Garcia S, Vieytes MR, Botana L. Current trends and new challenges in marine phycotoxins. Mar Drugs. 2022;20198. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20030198.
Botana LM. Toxicological perspective on climate change: aquatic toxins. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016;29:619–25. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00020.
Daguer H, Hoff RB, Molognoni L, Kleemann CR, Felizardo LV. Outbreaks, toxicology, and analytical methods of marine toxins in seafood. Curr Opin Food Sci. 2018;24:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2018.10.006.
Vilarino N, Louzao MC, Abal P, Cagide E, Carrera C, Vieytes MR, Botana LM. Human poisoning from marine toxins: unknowns for optimal consumer protection. Toxins. 2018;10(8):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10080324.
Murk AJ, Nicolas J, Smulders FJM, Burk C, Gerssen A. Marine biotoxins: types of poisoning, underlying mechanisms of action and risk management programmes Food safety assurance and veterinary public health. Chem Haz Foods Animal Origin. 2019;7:207–39. https://doi.org/10.3920/978-90-8686-877-3_09.
Farabegoli F, Blanco L, Rodriguez LP, Vieites JM, Cabado AG. Phycotoxins in marine shellfish: origin, occurrence and effects on humans. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(6):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060188.
Christensen VG, Khan E. Freshwater neurotoxins and concerns for human, animal, and ecosystem health: a review of anatoxin-a and saxitoxin. Sci Total Environ. 2020;736: 139515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139515.
Petroff R, Hendrix A, Shum S, Grant KS, Lefebvre KA, Burbacher TM. Public health risks associated with chronic, low-level domoic acid exposure: a review of the evidence. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;227: 107865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107865.
Lefebvre KA, Robertson A. Domoic acid and human exposure risks: a review. Toxicon. 2010;56(2):218–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.05.034.
Fu LL, Zhao XY, Ji LD, Xu J. Okadaic acid (OA): Toxicity, detection and detoxification. Toxicon. 2019;160:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2018.12.007.
Arman T, Clarke JD. Microcystin toxicokinetics, molecular toxicology, and pathophysiology in preclinical rodent models and humans. Toxins. 2021;13(8):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080537.
Fessard V, Le Hegarat L. A strategy to study genotoxicity: application to aquatic toxins, limits and solutions. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010;397(5):1715–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3699-3.
EFSA. Marine biotoxins in shellfish – summary on regulated marine biotoxins Scientific opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food chain in feed and food. EFSA J. 2009;1306:1–23. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1306.
Guidelines for drinking-water quality. fourth edition incorporating the first and second addenda. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022.
World Health Organization. Cyanobacterial toxins: microcystins. Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality and Guidelines for safe recreational water environments. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020 (WHO/HEP/ECH/WSH/2020.6). https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/338066/WHO-HEP-ECH-WSH-2020.6-eng.pdf.
Rasmussen SA, Andersen AJC, Andersen NG, Nielsen KF, Hansen PJ, Larsen TO. Chemical diversity, origin, and analysis of phycotoxins. J Natur Prod. 2016;79(3):662–73. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b01066.
Liang Y, Li A, Chen J, Tan Z, Tong M, Liu Z, Qiu J, Yu R. Progress on the investigation and monitoring of marine phycotoxins in China. Harmful Algae. 2022;111: 102152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2021.102152.
D’Amore T, Lo Magro S, Vita V, Di Taranto A. Optimization and validation of a high throughput UHPLC-MS/MS method for determination of the EU regulated lipophilic marine toxins and occurrence in fresh and processed shellfish. Mar Drugs. 2022;20(3):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20030173.
Dubois M, Demoulin L, Charlier C, Singh G, Godefroy SB, Campbell K. Development of ELISAs for detecting domoic acid, okadaic acid, and saxitoxin and their applicability for the detection of marine toxins in samples collected in Belgium. Food Additiv Contam: Part A. 2010;27:859–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440041003662881.
Dzantiev BB, Byzova NA, Urusov AE, Zherdev AV. Immunochromatographic methods in food analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2014;5:81–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2013.11.007.
Mahmoudi T, de la Guardia M, Shirdel B, Mokhtarzadeh A, Baradarn B. Recent advancements in structural improvements of lateral flow assays towards point-of-care testing TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2019;116:13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.04.016.
Dillon M, Zaczek-Moczydlowska MA, Edwards C, Turner AD, Miller PI, Moore H, McKinney A, Lawton L, Campbell K. Current trends and challenges for rapid smart diagnostics at point-of-site testing for marine toxins. Sensors. 2021;21(7):2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072499.
Zhang K, Wu J, Li Y, Wu Y, Huang T, Tang D. Hollow nanogold microsphere-signalized lateral flow immunodipstick for the sensitive determination of the neurotoxin brevetoxin B. Microchim Acta. 2014;181(11–12):1447–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1291-9.
Hendrickson OD, Zvereva EA, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. Ultrasensitive lateral flow immunoassay of phycotoxin microcystin-LR in seafood based on magnetic particles and peroxidase signal amplification. Food Control. 2022;133: 108655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108655.
Li Y, Xu X, Liu L, Kuang H, Xu L, Xu C. A gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of tetrodotoxin. Analyst. 2020;145:2143–51. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0an00170h.
Akter S, Vehniäinen M, Kankaanpää HT, Lamminmäki U. Rapid and highly sensitive non-competitive immunoassay for specific detection of nodularin. Microorganisms. 2017;5(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms5030058.
Liu B-H, Hung C-T, Lu C-C, Chou H-N, Yu F-Y. Production of monoclonal antibody for okadaic acid and its utilization in an ultrasensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and one-step immunochromatographic strip. J Agric Food Chem. 2014;62:1254–60. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404827s.
Hu L, Liu J, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Jia R, Cai C, Wu W, Chen S-F. Development of an immunochromatographic strip test for the rapid detection of okadaic acid in shellfish sample. J Appl Phycol. 2013;25:1091–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9949-3.
Lu S-Y, Lin C, Li Y-S, Zhou Y, Meng X-M, Yu S-Y, Li Z-H, Li L, Ren H-L, Liu Z-S. A screening lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for on-site detection of okadaic acid in shellfish products. Anal Biochem. 2012;422:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2011.12.039.
Wang R, Zeng L, Yang H, Zhong Y, Wang J, Ling S, Farhan Saeed A, Yuan J, Wang S. Detection of okadaic acid (OA) using ELISA and colloidal gold immunoassay based on monoclonal antibody. J Hazard Mater. 2017;339:154–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.06.030.
Tsao Z-J, Liao Y-C, Liu B-H, Su C-C, Yu F-Y. Development of a monoclonal antibody against domoic acid and its application in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and colloidal gold immunostrip. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55(13):4921–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0708140.
Jawaid W, Meneely J, Campbell K, Hooper M, Melville K, Holmes S, Rice J, Elliott C. Development and validation of the first high performance-lateral flow immunoassay (HP-LFIA) for the rapid screening of domoic acid from shellfish extracts. Talanta. 2013;116:663–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.07.027.
Xing C, Liu L, Song S, Feng M, Kuang H, Xu C. Ultrasensitive immunochromatographic assay for the simultaneous detection of five chemicals in drinking water. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;66:445–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.12.004.
Melnik S, Neumann AC, Karongo R, Dirndorfer S, Stubler M, Ibl V, Niessner R, Knopp D, Stoger E. Cloning and plant-based production of antibody MC10E7 for a lateral flow immunoassay to detect [4-arginine]microcystin in freshwater. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018;16:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12746.
Boobphahom S, Ly MN, Soum V, Pyun N, Kwon OS, Rodthongkum N, Shin K. Recent advances in microfluidic paper-based analytical devices toward high-throughput screening. Molecules. 2020;25(13):2970. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25132970.
Guan T, Liu D, Li X, Shu B, Li M, Liu Y, Xu Z, Shen Y, Sun Y, Lei H, Shen X. Magnet-actuated droplet microfluidic immunosensor coupled with gel imager for detection of microcystin-LR in aquatic products. Talanta. 2020;219: 121329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121329.
Ling S, Li X, Zhang D, Wang K, Zhao W, Zhao Q, Wang R, Yuan J, Xin S, Wang S. Detection of okadaic acid (OA) and tetrodotoxin (TTX) simultaneously in seafood samples using colloidal gold immunoassay. Toxicon. 2019;165:103–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2019.04.011.
Zhang H, Luo J, Beloglazova N, Yang S, De Saeger S, Mujtaba Mari G, Zhang S, Shen J, Wang Z, Yu X. Portable multiplex immunochromatographic assay for quantitation of two typical algae toxins based on dual-color fluorescence microspheres. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67:6041–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00011.
Zvereva EA, Byzova NA, Sveshnikov PG, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. Cut-off on demand: adjustment of the threshold level of an immunochromatographic assay for chloramphenicol. Anal Methods. 2015;7:6378–84. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AY00835B.
Bartosh AV, Sotnikov DV, Hendrickson OD, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. Design of multiplex lateral flow tests: a case study for simultaneous detection of three antibiotics. Biosensors. 2020;10:17. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10030017.
Finlay WJJ, Shaw I, Reilly JP, Kane M. Generation of high-affinity chicken single-chain Fv antibody fragments for measurement of the Pseudonitzschia pungens toxin domoic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72(5):3343–9. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.5.3343-3349.2006.
Köhler G, Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975;256:495–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/256495a0.
Frens G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat Phys Sci. 1973;241:20–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/physci241020a0.
Hendrickson OD, Zvereva EA, Shanin IA, Zherdev AV, Tarannum N, Dzantiev BB. Highly sensitive immunochromatographic detection of antibiotic ciprofloxacin in milk. Appl Biochem Microbiol. 2018;54(6):670–6. https://doi.org/10.1134/S000368381806008X.
TotalLab 1D v14.1 manual. TotalLab Ltd. 2015. https://irp-cdn.multiscreensite.com/20593b6f/files/uploaded/userguide.pdf. Accessed 9 Sept 2022.
Uhrovcik J. Strategy for determination of LOD and LOQ values–some basic aspects. Talanta. 2014;119:178–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.10.061.
Huang X, Aguilar ZP, Xu H, Lai W, Xiong Y. Membrane-based lateral flow immunochromatographic strip with nanoparticles as reporters for detection: a review. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;75:166–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.08.032.
Hermanson GT. Bioconjugate Techniques. 3rd ed. Pierce Biotechnology, Thermo Fisher Scientific: Rockford, IL, USA; 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2009-0-64240-9.
Urusov AE, Petrakova AV, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. “Multistage in one touch” design with a universal labelling conjugate for high-sensitive lateral flow immunoassays. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;86(57):5–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.027.
Hendrickson OD, Zvereva EA, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. Cascade-enhanced lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of okadaic acid in seawater, fish, and seafood. Foods. 2022;11:1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121691.
Urusov AE, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. Use of gold nanoparticle-labeled secondary antibodies to improve the sensitivity of an immunochromatographic assay for aflatoxin B1. Microchim Acta. 2014;181(15–16):1939–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1288-4.
Byzova NA, Urusov AE, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. Multiplex highly sensitive immunochromatographic assay based on the use of nonprocessed antisera. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(7):1903–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-0853-9.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to S.M. Pridvorova for TEM studies and D.S. Popravko for the design of Fig. 3.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation (grant number 20–43-07001; development and validation of the test system) and by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (consideration of registration and processing tools for the tests).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Elena A. Zvereva: Methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft. Olga D. Hendrickson: Investigation; data curation; writing, original draft; writing, review and editing. Olga N. Solopova: Investigation, data curation. Anatoly V. Zherdev: Conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Peter G. Sveshnikov: Conceptualization, supervision. Boris B. Dzantiev: Supervision, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Studies in animals were performed following the EU Directive 2010/63/EU for animal experiments and authorized by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Research Center of Biotechnology (protocol code N22-D February 12, 2020).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zvereva, E.A., Hendrickson, O.D., Solopova, O.N. et al. Triple immunochromatographic test system for detection of priority aquatic toxins in water and fish. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 7553–7563 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04298-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04298-8