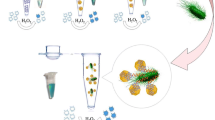
Abstract
We developed an effective and specific colorimetric strategy to detect Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) based on hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB)-induced supramolecular assembly of β-cyclodextrin-capped gold nanoparticles (β-CD-AuNPs). In this study, ssDNA aptamer of S. typhimurium could combine with CTAB to form the supramolecular ssDNA-CTAB composite, so the ssDNA aptamer was applied to control the concentration of CTAB. In the presence of S. typhimurium, ssDNA aptamers selectively bound to S. typhimurium but not to CTAB, leading to the host–guest chemistry reaction of CTAB and β-CD resulting in β-CD-AuNP supramolecular assembly aggregation with an obvious color change. The ratio of absorption at 650 and 520 nm (A650nm/A520nm) has a linear correlation to the log scale of the concentration of the bacteria (1 × 102–1 × 107 CFU/mL) with a low limit of detection (LOD) of 13 CFU/mL. In addition, this optical sensor has good selectivity and practicability. In milk samples, the recovery was 93.55–111.32%, which suggested its potential application in real samples.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Kirk MD, Pires SM, Black RE, Caipo M, Crump JA, Devleesschauwer B, Döpfer D, Fazil A, Fischer-Walker CL, Hald T, Hall AJ, Keddy KH, Lake RJ, Lanata CF, Torgerson PR, Havelaar AH, Angulo FJ. World Health Organization estimates of the global and regional disease burden of 22 foodborne bacterial, protozoal, and viral diseases, 2010: a data synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015;12(12):e1001921. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001921.
Zhang L, Huang R, Liu W, Liu H, Zhou X, Xing D. Rapid and visual detection of Listeria monocytogenes based on nanoparticle cluster catalyzed signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;86:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.05.100.
Newell DG, Koopmans M, Verhoef L, Duizer E, Aidara-Kane A, Sprong H, Opsteegh M, Langelaar M, Threfall J, Scheutz F, van der Giessen J, Kruse H. Food-borne diseases—the challenges of 20 years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010;139(Suppl 1):S3-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.01.021.
Narvaez-Bravo C, Rodas-Gonzalez A, Fuenmayor Y, Flores-Rondon C, Carruyo G, Moreno M, Perozo-Mena A, Hoet AE. Salmonella on feces, hides and carcasses in beef slaughter facilities in Venezuela. Int J Food Microbiol. 2013;166(2):226–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.07.009.
Lee K-M, Runyon M, Herrman TJ, Phillips R, Hsieh J. Review of Salmonella detection and identification methods: aspects of rapid emergency response and food safety. Food Control. 2015;47:264–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.07.011.
Singer RS, Cooke CL, Maddox CW, Isaacson RE, Wallace RL. Use of pooled samples for the detection of Salmonella in feces by polymerase chain reaction. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2006;18(4):319–25. https://doi.org/10.1177/104063870601800401.
Yao S, Li J, Pang B, Wang X, Shi Y, Song X, Xu K, Wang J, Zhao C. Colorimetric immunoassay for rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on etching-enhanced peroxidase-like catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles. Mikrochim Acta. 2020;187(9):504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04473-7.
Chen S, Zong X, Zheng J, Zhang J, Zhou M, Chen Q, Man C, Jiang Y. A colorimetric strategy based on aptamer-catalyzed hairpin assembly for the on-site detection of Salmonella typhimurium in milk. Foods. 2021;10(11):2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112539.
Wang S, Zheng L, Cai G, Liu N, Liao M, Li Y, Zhang X, Lin J. A microfluidic biosensor for online and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using fluorescence labeling and smartphone video processing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;140: 111333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111333.
Zhu W, Chen Y, He Y, Fang W, Ying Y, Li Y, Fu Y. Cooperation mode of outer surface and inner space of nanochannel: separation-detection system based on integrated nanochannel electrode for rapid and facile detection of Salmonella. Anal Chem. 2020;92(2):1818–25. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03644.
Bhandari D, Chen FC, Bridgman RC. Detection of salmonella typhimurium in romaine lettuce using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Biosensors (Basel). 2019;9(3):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030094.
Ma X, Lin X, Xu X, Wang Z. Fabrication of gold/silver nanodimer SERS probes for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Microchim Acta. 2021;188(6):202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04791-4.
Farka Z, Juřík T, Pastucha M, Skládal P. Enzymatic precipitation enhanced surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for the detection of Salmonella in powdered milk. Anal Chem. 2016;88(23):11830–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03511.
Zhang Y, Tian J, Li K, Tian H, Xu W. Label-free visual biosensor based on cascade amplification for the detection of Salmonella. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1075:144–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.05.020.
Du G, Wang L, Zhang D, Ni X, Zhou X, Xu H, Xu L, Wu S, Zhang T, Wang W. Colorimetric aptasensor for progesterone detection based on surfactant-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Anal Biochem. 2016;514:2–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.09.006.
Tarokh A, Pebdeni AB, Othman HO, Salehnia F, Hosseini M. Sensitive colorimetric aptasensor based on g-C(3)N(4)@Cu(2)O composites for detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food and water. Mikrochim Acta. 2021;188(3):87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04745-w.
Yi J, Wu P, Li G, Xiao W, Li L, He Y, He Y, Ding P, Chen C. A composite prepared from carboxymethyl chitosan and aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric determination of Salmonella typhimurium. Mikrochim Acta. 2019;186(11):711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3827-5.
Wu W-h, Li M, Wang Y, Ouyang H-x, Wang L, Li C-x, Cao Y-c, Meng Q-h, Lu J-x. Aptasensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2012;7(1):658. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-658.
Lehn J-M. Supramolecular chemistry—scope and perspectives molecules, supermolecules, and molecular devices (nobel lecture). Angew Chem Int Ed in Engl. 1988;27(1):89–112. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.198800891.
Yang L, Tan X, Wang Z, Zhang X. Supramolecular polymers: historical development, preparation, characterization, and functions. Chem Rev. 2015;115(15):7196–239. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500633b.
Ma X, Zhao Y. Biomedical applications of supramolecular systems based on host-guest interactions. Chem Rev. 2015;115(15):7794–839. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500392w.
Palanisamy S, Sakthinathan S, Chen SM, Thirumalraj B, Wu TH, Lou BS, Liu X. Preparation of β-cyclodextrin entrapped graphite composite for sensitive detection of dopamine. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;135:267–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.008.
Connors KA. The stability of cyclodextrin complexes in solution. Chem Rev. 1997;97(5):1325–58. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr960371r.
Lai W-F, Rogach AL, Wong W-T. Chemistry and engineering of cyclodextrins for molecular imaging. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(20):6379–419. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00040E.
Geng WC, Sessler JL, Guo DS. Supramolecular prodrugs based on host-guest interactions. Chem Soc Rev. 2020;49(8):2303–15. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cs00622b.
Wang T, Cheng Y, Zhang Y, Zha J, Ye J, Chu Q, Cheng G. β-cyclodextrin modified quantum dots as pseudo-stationary phase for direct enantioseparation based on capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Talanta. 2020;210:120629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120629.
Ban R, Abdel-Halim ES, Zhang J, Zhu JJ. β-Cyclodextrin functionalised gold nanoclusters as luminescence probes for the ultrasensitive detection of dopamine. Analyst. 2015;140(4):1046–53. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4an02161d.
Cabaleiro-Lago C, Nilsson M, Söderman O. Self-diffusion NMR studies of the host−guest interaction between β-cyclodextrin and alkyltrimethylammonium bromide surfactants. Langmuir. 2005;21(25):11637–44. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0516835.
Oh T, Takahashi T, Kim S, Heller MJ. CTAB enhancement of FRET in DNA structures. J Biophotonics. 2016;9(1–2):49–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbio.201500221.
Bi S, Wang Y, Pang B, Yan L, Wang T. An investigation on the interaction of DNA with hesperetin/apigenin in the presence of CTAB by resonance Rayleigh light scattering technique and its analytical application. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2012;90:158–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.01.037.
Joshi R, Janagama H, Dwivedi HP, Senthil Kumar TM, Jaykus LA, Schefers J, Sreevatsan S. Selection, characterization, and application of DNA aptamers for the capture and detection of Salmonella enterica serovars. Mol Cell Probes. 2009;23(1):20–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2008.10.006.
Liu Y, Male KB, Bouvrette P, Luong JHT. Control of the size and distribution of gold nanoparticles by unmodified cyclodextrins. Chem Mater. 2003;15(22):4172–80. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0342041.
Hollamby MJ, Eastoe J, Chemelli A, Glatter O, Rogers S, Heenan RK, Grillo I. Separation and purification of nanoparticles in a single step. Langmuir. 2010;26(10):6989–94. https://doi.org/10.1021/la904225k.
Wen D, Liu W, Haubold D, Zhu C, Oschatz M, Holzschuh M, Wolf A, Simon F, Kaskel S, Eychmüller A. Gold aerogels: three-dimensional assembly of nanoparticles and their use as electrocatalytic interfaces. ACS Nano. 2016;10(2):2559–67. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b07505.
Bao L, Liu C, Zhang Z-L, Pang D-W. Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv Mater. 2015;27(10):1663–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201405070.
Mel’nikov SM, Sergeyev VG, Yoshikawa K. Discrete coil-globule transition of large DNA induced by cationic surfactant. J Am Chem Soc. 1995;117(9):2401–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00114a004.
Dias RS, Innerlohinger J, Glatter O, Miguel MG, Lindman B. Coil-globule transition of DNA molecules induced by cationic surfactants: a dynamic light scattering study. J Phys Chem B. 2005;109(20):10458–63. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0444464.
Wu Y, Liu L, Zhan S, Wang F, Zhou P. Ultrasensitive aptamer biosensor for arsenic(III) detection in aqueous solution based on surfactant-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Analyst. 2012;137(18):4171–8. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an35711a.
Hu J, Tang F, Jiang YZ, Liu C. Rapid screening and quantitative detection of Salmonella using a quantum dot nanobead-based biosensor. Analyst. 2020;145(6):2184–90. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0an00035c.
Xu M, Wang R, Li Y. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium in foods using an electrochemical immunosensor based on screen-printed interdigitated microelectrode and immunomagnetic separation. Talanta. 2016;148:200–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.10.082.
Luo F, Li Z, Dai G, Lu Y, He P, Wang Q. Simultaneous detection of different bacteria by microchip electrophoresis combined with universal primer-duplex polymerase chain reaction. J Chromatogr A. 2020;1615:460734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460734.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82073557), Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan Item (Grant No. 20200602010ZP), and Interdisciplinary Research Funding Program for Doctoral Postgraduates of Jilin University (Grant No. 101832020DJX082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, S., Wang, X., Wang, F. et al. Colorimetric detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide-induced supramolecular assembly of β-cyclodextrin-capped gold nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 6069–6076 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04166-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04166-5