Abstract
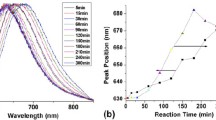
Chemical sensing for the sensitive and reliable detection of mercury(II) ions (Hg2+) is of great importance in environmental protection, food safety, and biomedical applications. Due to the bio-enrichment property of Hg2+ in organisms, it is particularly meaningful to develop an effective tool that can in situ and rapidly monitor the level of Hg2+ in living organisms. In this work, we report ligand functionalized gold-silver bimetallic nanoclusters with bright red fluorescence as intracellular probes for imaging Hg2+ in living cells and zebrafish. The bimetallic nanoclusters of DTT-GSH@Au/AgNCs (DG-Au/AgNCs) with strong fluorescence that benefited from the synergistic effect of Au and Ag atoms were obtained through a one-pot synthesis method, incorporating glutathione (GSH) and dithiothreitol (DTT) as the reducers and functionalized ligands. Attractively, the bright red fluorescence of DG-Au/AgNCs could be rapidly and selectively quenched by Hg2+ within 1 min with a very low detection limit of 1.01 nM. Additionally, DG-Au/AgNCs had a great advantage in the detection of Hg2+ in living cells and zebrafish owing to its notably strong red fluorescence at 665 nm, which could avoid effectively auto-fluorescence interference from the organism. Such easily prepared bimetallic fluorescent nanoclusters would be expected to provide a noninvasive and sensitive approach in the detection of heavy metals in situ for environmental protection.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang LY, Zhang W, Ren MY, Cao FF, Chen FF, Zhang YT, Shang LH. Mercury distribution in a typical shallow lake in northern China and its reemission from sediment. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe. 2020;192:110316.
Kim KH, Kabir E, Jahan SA. A review on the distribution of Hg in the environment and its human health impacts. J Hazard Mater. 2016;306:376–85.
Kim HN, Ren WX, Kim JS, Yoon J. Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for detection of lead, cadmium, and mercury ions. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41:3210–44.
Li Z, Wei Q, Yuan R, Zhou X, Liu H, Shan H, Song Q. A new room temperature ionic liquid l-butyl-3-trimethylsilylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate as a solvent for extraction and preconcentration of mercury with determination by cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta. 2007;71:68–72.
Shi JB, Ji XM, Wu Q, Liu HW, Qu GB, Yin YG, Hu LG, Jiang GB. Tracking mercury in individual tetrahymena using a capillary single cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry online system. Anal Chem. 2020;92:622–7.
Zhu Zh, Chan G, Ray S, Zhang X, Hieftje G. Use of a solution cathode glow discharge for cold vapor generation of mercury with determination by ICP atomic emission spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2008;80:7043–50.
Oskolok KV, Monogarova OV, Alov NV. Determination of mercury (II) in drinking water by total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and liquid-liquid microextraction. Anal Lett. 2018;51:2457–67.
Carter KP, Young AM, Palmer AE. Fluorescent sensors for measuring metal ions in living systems. Chem Rev. 2014;114:4564–601.
Li Y, Xie JF, Chang CC, Wang CM, Tu HL. Highly sensitive detection of mercury ions using zincophosphite framework nanoparticle–polyaniline composites. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2020;10:9724–30.
Egan JG, Hynes AJ, Fruehwald HM, Ebralidze II, King SD, Esfahani RAM, Naumkin FY, Easton EB, Zenkina OV. A novel material for the detection and removal of mercury (II) based on a 2, 6-bis (2-thienyl) pyridine receptor. J Mater Chem C. 2019;33:10187–95.
Das S, Sarkar A, Rakshit A, Datta A. A sensitive water-soluble reversible optical probe for Hg2+ detection. Inorg Chem. 2018;57:5273–81.
Lim JW, Kim TY, Woo MA. Trends in sensor development toward next-generation point-of-care testing for mercury. Biosensors Bioelectron. 2021;183:113228.
Gill R, Zayats M, Willner I. Semiconductor quantum dots for bioanalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47:7602–25.
Zhang LB, Wang EK. Metal nanoclusters: new fluorescent probes for sensors and bioimaging. Nano Today. 2014;9:132–57.
Xu JQ, Zhu XM, Zhou X, Khusbu FY, Ma CB. Recent advances in the bioanalytical and biomedical applications of DNA templated silver nanoclusters. Trac Trend Anal Chem. 2020;124:115786.
Bai XL, Xu SY, Wang LY. Full range pH stable Au-clusters in nanogel for confinement enhanced emission and improved sulfide sensing in living cells. Anal Chem. 2018;90:3270–5.
Sun HH, Qing TP, He XX, Shangguan JF, Jia RC, Bu HC, Huang J, Wang KM. Rapid synthesis of Au/Ag bimetallic nanoclusters with highly biochemical stability and its applications for temperature and ratiometric pH sensing. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1070:88–96.
Xie Y, Xianyu Y, Wang NX, Yan ZY, Liu Y, Zhu K, Hatzakis NS, Jiang XY. Functionalized gold nanoclusters identify highly reactive oxygen species in living organisms. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1702026.
Xu HF, Yu LS, Zhang SQ, Xu XY, Chen TT, Ye HZ, Zhu X. Signal on fluorescence assay for pyrophosphate ions based on DNA stabilized silver nanoclusters. Luminescence. 2019;34:774–8.
Jia MN, Mi WY, Guo SS, Yang QZ, Jin Y, Shao N. Peptide-capped functionalized Ag/Au bimetal nanoclusters with enhanced red fluorescence for lysosome targeted imaging of hypochlorite in living cells. Talanta. 2020;216:120926.
Song CX, Xu JY, Chen Y, Zhang LL, Lu Y, Qing ZH. DNA templated fluorescent nanoclusters for metal ions detection. Molecules. 2019;24:4189.
Babaee E, Barati A, Gholivand MB, Taherpour AA, Zolfaghar N, Shamsipu M. Determination of Hg2+ and Cu2+ ions by dual emissive Ag/Au nanocluster/carbon dots nanohybrids: switching the selectivity by pH adjustment. J Hazard Mater. 2019;367:437–46.
Liu R, Duan S, Bao L, Wu Z, Zhou J, Yu R. Photonic crystal enhanced gold-silver nanoclusters fluorescent sensor for Hg2+ ion. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1114:50–7.
Liu JJ, Geng YJ, Li DW, Yao H, Huo ZP, Li YF, Zhang K, Zhu SJ, Wei HT, Xu WQ, Jiang JL, Yang B. Deep red emissive carbonized polymer dots with unprecedented narrow full width at half maximum. Adv Mater. 2020;32:1906641.
Chu SY, Wang HQ, Du YX, Yang F, Yang L, Jiang CL. Portable smartphone platform integrated with a nanoprobe based fluorescent paper strip: visual monitoring of glutathione in human serum for health prognosis. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2020;8:8175–83.
Gupta A, Chaudhary A, Mehta P, Dwivedi C, Khan S, Verma NC, Nandi CK. Nitrogen doped, thiol-functionalized carbon dots for ultrasensitive Hg (II) detection. Chem Commun. 2015;51:10750–3.
Yang Z, Xu M, Liu Y, He F, Gao F, Su Y, Wei H, Zhang Y. Nitrogen doped, carbon rich, highly photoluminescent carbon dots from ammonium citrate. Nanoscale. 2014;6:1890–5.
Jiang K, Wang Y, Gao X, Cai C, Lin H. Facile, quick and gram scale synthesis of ultralong lifetime room temperature phosphorescent carbon dots by microwave irradiation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018;57:6216–20.
Tao S, Lu S, Geng Y, Zhu S, Redfern SAT, Song Y, Feng T, Xu W, Yang B. Design of metal free polymer carbon dots: a new class of room temperature phosphorescent materials. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018;57:2393–8.
Luo ZT, Yuan X, Yu Y, Zhang QB, Leong DT, Lee JY, Xie JP. From aggregation induced emission of Au (I)-thiolate complexes to ultrabright Au (0) @ Au (I)-thiolate core-shell nanoclusters. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:16662–70.
Li JZ, Zhang SM, Yu Y, Wang YM, Zhang L, Lin BX, Guo ML, Cao YJ. A novel universal nanoplatform for ratiometric fluorescence biosensing based on silver nanoclusters beacon. Chem Eng J. 2020;391:123526.
Zang J, Li C, Zhou K, Dong H, Chen B, Wang F, Zhao G. Nanomolar Hg2+ detection using β-lactoglobulin stabilized fluorescent gold nanoclusters in beverage and biological media. Anal Chem. 2018;88:10275–83.
Qi YX, Zhang M, Zhu A, Shi G. Terbium (III)/gold nanocluster conjugates: the development of a novel ratiometric fluorescent probe for mercury (II) and a paper-based visual sensor. Analyst. 2015;140:5656–61.
Liu W, Wang X, Wang Y, Li J, Shen D, Kang Q, Chen L. Ratiometric fluorescence sensor based on dithiothreitol modified carbon dots-gold nanoclusters for the sensitive detection of mercury ions in water samples. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;262:810–7.
Hu X, Wang W, Huang Y. Copper nanocluster based fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ in water and food stuff. Talanta. 2016;154:409–15.
Peng J, Ling J, Zhang XQ, Bai HP, Zheng L, Cao QE, Ding ZT. Sensitive detection of mercury and copper ions by fluorescent DNA/Ag nanoclusters in guanine rich DNA hybridization. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2015;137:1250–7.
Zuo X, Zhang H, Zhu Q, Wang W, Feng J, Chen X. A dual color fluorescent biosensing platform based on WS2 nanosheet for detection of Hg2+ and Ag+. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;85:464–70.
Gu W, Pei XY, Cheng YX, Zhang CL, Zhang JD, Yan YH, Ding CP, Xian YZ. Black phosphorus quantum dots as the ratiometric fluorescence probe for trace mercury ion detection based on inner filter effect. ACS Sensors. 2017;2:576–82.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support from Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (2020C02024, 2021C02061), the Public Projects of Zhejiang Province (LGC20C200004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21806168), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2008085QB69), and Scientific Research Foundation for High-Level Talents of West Anhui University (WGKQ2021001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.P.W. and W.W. contributed equally. The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All experiments in situ were carried out in accordance with the Ethical Committee Approval of China. The study protocol was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of China Jiliang University. We took great efforts to reduce the number of animals used in these studies and to reduce animal suffering from pain and discomfort.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary data to this article can be found on the website.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, W., Yang, L. et al. Surface engineered bimetallic gold/silver nanoclusters for in situ imaging of mercury ions in living organisms. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 4235–4244 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04076-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04076-6