Abstract
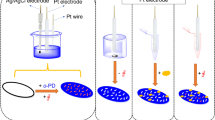
In this study, a porous molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor was successfully fabricated for the selective assay of bisphenol S (BPS) by introducing N-methacryloyl-l tyrosine functional monomer. The molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)–based sensor (MA-Tyr@MIP/GCE) was prepared via photopolymerization on the glassy carbon electrode and subsequently characterized by using cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The analytical performance of the sensor was evaluated via CV and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) measurements. Under the optimized conditions, the rebinding experiment demonstrated that the peak current of the porous MIP-based sensor obviously decreased with the increase of BPS concentration in the concentration range of 1–10 fM. Therefore, the detection limit was determined as 0.171 fM. It should be underlined that MA-Tyr@MIP/GCE exhibited high sensitivity and excellent selectivity because MA-TyrMA-Tyr@MIP/GCE sensor has a higher imprinting factor (IF) toward BPS in respect to competitive analogs, i.e., bisphenol A, bisphenol B, and bisphenol F. The practical application of the sensor also showed good reproducibility and stability for the detection of BPS in human serum and water samples. These results showed MA-Tyr@MIP/GCE successfully applied for the selective recognition of BPS in biological and water samples with high sensitivity and excellent selectivity.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frankowski R, Płatkiewicz J, Stanisz E, Grześkowiak T, Zgoła-Grześkowiak A. Biodegradation and photo-Fenton degradation of bisphenol A, bisphenol S and fluconazole in water. Environ Pollut. 2021;289.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117947.
Liu D, Wu P, Zhao N, Nie S, Cui J, Zhao M, Jin H. Differences of bisphenol analogue concentrations in indoor dust between rural and urban areas. Chemosphere. 2021;276:130016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130016.
Zhang Y, Lei Y, Lu H, Shi L, Wang P, Ali Z, Li J. Electrochemical detection of bisphenols in food: a review. Food Chem. 2021;346:128895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128895.
Lestido-Cardama A, Sánchez BM, Sendón R, Rodríguez-Bernaldo de Quirós A, Barbosa-Pereira L. Study on the chemical behaviour of Bisphenol S during the in vitro gastrointestinal digestion and its bioaccessibility. Food Chem. 2022;367.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130758.
Reina-Pérez I, Olivas-Martínez A, Mustieles V, Ruiz-Ojeda FJ, Molina-Molina JM, Olea N, Fernández MF. Bisphenol F and bisphenol S promote lipid accumulation and adipogenesis in human adipose-derived stem cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021;152.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112216.
Gély CA, Huesca A, Picard-Hagen N, Toutain PL, Berrebi A, Gauderat G, Gayrard V, Lacroix MZ. A new LC/MS method for specific determination of human systemic exposure to bisphenol A, F and S through their metabolites: application to cord blood samples. Environ Int. 2021;151.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106429.
Dualde P, Pardo O, Fernández SF, Pastor A, Yusà V. Determination of four parabens and bisphenols A, F and S in human breast milk using QuEChERS and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019;1114–1115:154–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.03.004.
Deceuninck Y, Bichon E, Gény T, Veyrand B, Grandin F, Viguié C, Marchand P, Le Bizec B. Quantitative method for conjugated metabolites of bisphenol A and bisphenol S determination in food of animal origin by ultra high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2019;1601:232–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.05.001.
Kaya SI, Cetinkaya A, Ozkan SA. Latest advances in determination of bisphenols with nanomaterials, molecularly imprinted polymers and aptamer based electrochemical sensors. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2020;0:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2020.1864719.
Huang YY, Pang YH, Shen XF, Jiang R, Wang YY. Covalent organic framework DQTP modified pencil graphite electrode for simultaneous determination of bisphenol A and bisphenol S. Talanta. 2022;236:122859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122859.
Freitas JM, Wachter N, Rocha-Filho RC. Determination of bisphenol S, simultaneously to bisphenol A in different water matrices or solely in electrolyzed solutions, using a cathodically pretreated boron-doped diamond electrode. Talanta. 2020;217:121041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121041.
Chen K, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Huang L, Wang R, Yue X, Zhu W, Zhang D, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wang J. Label-free fluorescence aptasensor for sensitive determination of bisphenol S by the salt-adjusted FRET between CQDs and MoS2. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;259:717–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.116.
Bernardo RA, Sousa JCP, Gallimberti M, Junior FB, Vaz BG, Chaves AR. A fast and direct determination of bisphenol S in thermal paper samples using paper spray ionization mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2021;28:57288–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14603-0.
Crapnell RD, Dempsey-Hibbert NC, Peeters M, Tridente A, Banks CE. Molecularly imprinted polymer based electrochemical biosensors: overcoming the challenges of detecting vital biomarkers and speeding up diagnosis. Talanta Open. 2020;2:100018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talo.2020.100018.
Cui B, Liu P, Liu X, Liu S, Zhang Z. Molecularly imprinted polymers for electrochemical detection and analysis: progress and perspectives. J Mater Res Technol. 2020;9:12568–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.08.052.
Özgür E, Parlak O, Beni V, Turner APF, Uzun L. Bioinspired design of a polymer-based biohybrid sensor interface. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;251:674–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.030.
Zuo KH, Zeng YP, Jiang D. Effect of polyvinyl alcohol additive on the pore structure and morphology of the freeze-cast hydroxyapatite ceramics. Mater Sci Eng C. 2010;30:283–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2009.11.003.
Hur D, Ekti SF, Say R. N-Acylbenzotriazole mediated synthesis of some methacrylamido amino acids. Lett Org Chem. 2007;4:585–7. https://doi.org/10.2174/157017807782795556.
Uzun L, Say R, Ünal S, Denizli A. Production of surface plasmon resonance based assay kit for hepatitis diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron. 2009;24:2878–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.02.021.
Ozkan SA, Kauffmann J-M, Zuman P. Electroanalysis in biomedical and pharmaceutical sciences. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2015.
Pang YH, Huang YY, Wang L, Shen XF, Wang YY. Determination of bisphenol A and bisphenol S by a covalent organic framework electrochemical sensor. Environ Pollut. 2020;263:114616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114616.
Rao H, Zhao X, Liu X, Zhong J, Zhang Z, Zou P, Jiang Y, Wang X, Wang Y. A novel molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on graphene quantum dots coated on hollow nickel nanospheres with high sensitivity and selectivity for the rapid determination of bisphenol S. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;100:341–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.09.016.
Yao J, Chen M, Li N, Liu C, Yang M. Experimental and theoretical studies of a novel electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and B, N, F-CQDs/AgNPs for enhanced specific identification and dual signal amplification in highly selective and ultra-trace bisphenol S determi. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1066:36–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.03.051.
Viter R, Kunene K, Genys P, Jevdokimovs D, Erts D, Sutka A, Bisetty K, Viksna A, Ramanaviciene A, Ramanavicius A. Photoelectrochemical bisphenol S sensor based on ZnO-nanoroads modified by molecularly imprinted polypyrrole. Macromol Chem Phys. 2020;221:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.201900232.
Acknowledgements
This work was produced as a part of S. Irem Kaya’s Ph.D. thesis. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Ankara University Scientific Research Project Foundation (Project No: 21L0237002), Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No human or animal subjects were used in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaya, S.I., Corman, M.E., Uzun, L. et al. A porous molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for specific determination of bisphenol S from human serum and bottled water samples in femtomolar level. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 2775–2785 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03928-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03928-5