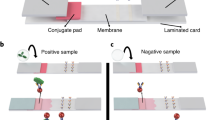
Abstract
Nanoparticle (NP)-based lateral flow assay (LFA) technology has outstanding characteristics that make it ideal for point-of-care bioanalytical applications. However, LFAs still have important limitations, especially related to sensitivity, which is in general worse than that of other well-established bioassays such as ELISA or PCR. Many efforts have been made for enhancing the sensitivity of LFAs, mainly actuating on the nanoparticle labels and on alternative optical detection modes. However, strip pads modification for such a purpose is an incipient vast field of research. This article gives a brief overview on the recent advances proposed for signal amplification actuating on different pads and the general architecture of the LFA strips. Such strategies offer universal tools that can be adapted to any LFA, independently of the kind of sample, analyte, and label. The principles of the different strategies developed to achieve novel signal amplification and sensitive detection are discussed, and some examples of relevant approaches are highlighted, together with future prospects and challenges.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kasetsirikul S, Shiddiky MJA, Nguyen NT. Challenges and perspectives in the development of paper-based lateral flow assays. Microfluid Nanofluid. 2020;24:17.
Huang Y, Xu T, Wang W, Wen Y, Li K, Qian L, et al. Lateral flow biosensors based on the use of micro and nanomaterials: a review on recent developments. Microchim Acta. 2020;187:70.
Tang RH, Liu LN, Zhang SF, He XC, Li XJ, Xu F, et al. A review on advances in methods for modification of paper supports for use in point-of-care testing. Microchim Acta. 2019;186:521.
Li F, You M, Li S, Hu J, Liu C, Gong Y, et al. Paper-based point-of-care immunoassays: recent advances and emerging trends. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;39:107442.
Soh JH, Chan HM, Ying JY. Strategies for developing sensitive and specific nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays as point-of-care diagnostic device. Nano Today. 2020;30:100831.
Zhou Y, Ding L, Wu Y, Huang X, Lai W, Xiong Y. Emerging strategies to develop sensitive AuNP-based ICTS nanosensors. Trends Anal Chem. 2019;112:147–60.
Huang X, Aguilar ZP, Xu H, Lai W, Xiong Y. Membrane-based lateral flow immunochromatographic strip with nanoparticles as reporters for detection: a review. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;75:166–80.
Liu L, Yang D, Liu G. Signal amplification strategies for paper-based analytical devices. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;136:60–75.
Hsieh HV, Dantzler JL, Weigl BH. Analytical tools to improve optimization procedures for lateral flow assays. Diagnostics. 2017;7:29.
Liu Y, Zhan L, Qin Z, Sackrison J, Bischof JC. Ultrasensitive and highly specific lateral flow assays for point-of-care diagnosis. ACS Nano. 2021;15:3593–611.
Ishii M, Preechakasedkit P, Yamada K, Chailapakul O, Suzuki K, Citterio D. Wax-assisted one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay on lateral flow test devices. Anal Sci. 2018;34:51–6.
Zhong Y, Chen Y, Yao L, Zhao D, Zheng L, Liu G, et al. Gold nanoparticles based lateral flow immunoassay with largely amplified sensitivity for rapid melamine screening. Microchim Acta. 2016;183:1989–94.
Rivas L, de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Serrano L, Altet L, Francino O, Sánchez A, et al. Triple lines gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow assay for enhanced and simultaneous detection of Leishmania DNA and endogenous control. Nano Res. 2015;8:3704–14.
Lu Z, Rey E, Vemulapati S, Srinivasan B, Mehta S, Erickson D. High-yield paper-based quantitative blood separation system. Lab Chip. 2018;18:3865–71.
Shen Y, Shen G. Signal-enhanced lateral flow immunoassay with dual gold nanoparticle conjugates for the detection of hepatitis B surface antigen. ACS Omega. 2019;4:5083–7.
Chen M, Yu Z, Liu D, Peng T, Liu K, Wang S, et al. Dual gold nanoparticle lateflow immunoassay for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;876:71–6.
Rivas L, Medina-Sánchez M, de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Merkoçi A. Improving sensitivity of gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays by using wax-printed pillars as delay barriers of microfluidics. Lab Chip. 2014;14:4406–14.
Zhang SF, Liu LN, Tang RH, Liu Z, He XC, Qu ZG, et al. Sensitivity enhancement of lateral flow assay by embedding cotton threads in paper. Cellulose. 2019;26:8087–99.
Tsai TT, Huang TH, Chen CA, Ho NYJ, Chou YJ, Chen CF. Development a stacking pad design for enhancing the sensitivity of lateral flow immunoassay. Sci Rep. 2018;8:17319.
Kim K, Joung HA, Han GR, Kim MG. An immunochromatographic biosensor combined with a water-swellable polymer for automatic signal generation or amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;85:422–8.
Panraksa Y, Apilux A, Jampasa, Puthong S, Henry CS, Rengpipatf S, et al. A facile one-step gold nanoparticles enhancement based on sequential patterned lateral flow immunoassay device for C-reactive protein detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2021;329:129241.
Preechakasedkit P, Siangproh W, Khongchareonporn N, Ngamrojanavanich N, Chailapakul O. Development of an automated wax-printed paper-based lateral flow device for alpha-fetoprotein enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;102:27–32.
He X, Liu Z, Yang Y, Li L, Wang L, Li A, et al. Sensitivity enhancement of nucleic acid lateral flow assays through a physical−chemical coupling method: dissoluble saline barriers. ACS Sensors. 2019;4:1691–700.
Bikkarolla SK, McNamee SE, McGregor S, Vance P, McGhee H, Marlow EL, et al. A lateral flow immunoassay with self-sufficient microfluidic system for enhanced detection of thyroid-stimulating hormone. AIP Adv. 2020;10:125316.
Credou J, Volland H, Danob J, Berthelot T. A one-step and biocompatible cellulose functionalization for covalent antibody immobilization on immunoassay membranes. J Mater Chem B. 2013;1:3277–86.
Yew CHT, Azari P, Choi JR, Muhamad F, Pingguan-Murphy B. Electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers as a reaction membrane for lateral flow assay. Polymers. 2018;10:1387.
Zhang LX, Jiang L, Willett DR, Marcus RK. Parallel, open-channel lateral flow (immuno) assay substrate based on capillary-channeled polymer films. Analyst. 2016;141:807–14.
Quesada-González D, Stefani C, González I, de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Domingo N, Mutjé P, et al. Signal enhancement on gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow tests using cellulose nanofibers. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;141:111407.
Zhang Y, Liu X, Wang L, Yang H, Zhang X, Zhu C, et al. Improvement in detection limit for lateral flow assay of biomacromolecules by test-zone pre-enrichment. Sci Rep. 2020;10:9604.
Parolo C, Medina-Sánchez M, de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Merkoçi A. Simple paper architecture modifications lead to enhanced sensitivity in nanoparticle based lateral flow immunoassay. Lab Chip. 2013;13:386–90.
Nunes-Pauli GE, de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Parolo C, Helmuth-Bechtold I, Merkoçi A. Lab-in-a-syringe using gold nanoparticles for rapid immunosensing of protein biomarkers. Lab Chip. 2015;15:399–405.
Zadehkafi A, Siavashi M, Asiaei S, Bidgoli MR. Simple geometrical modifications for substantial color intensity and detection limit enhancements in lateral-flow immunochromatographic assays. J Chromatogr B 2019;1110–1111:1–8.
Eltzov E, Marks RA. Colorimetric stack pad immunoassay for bacterial identification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;87:572–8.
Afriat R, Chalupowicz D, Eltzov E. Development of a point-of-care technology for bacterial identification in milk. Talanta. 2020;219:121223.
Acknowledgements
The financial support of the FC-GRUPIN-ID/2018/000166 project from the Asturias Regional Government and the CTQ2017-86994-R project from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (MINECO) is gratefully acknowledged. A. de la Escosura-Muñiz also acknowledges the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (MICINN) for the “Ramón y Cajal” Research Fellow (RyC-2016-20299).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz-González, M., de la Escosura-Muñiz, A. Strip modification and alternative architectures for signal amplification in nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 4111–4117 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03421-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03421-5