Abstract
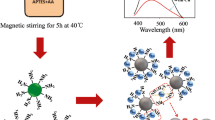
We present a new “off-on” fluorescence probe for detecting hypochlorite (ClO−) based on silicon quantum dots coupled with silver nanoparticles (SiQDs/AgNPs) as nanocomplexes. Via introducing N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]ethylenediamine and catechol as initial reactants, silicon quantum dots (SiQDs) with excellent properties were synthesized through a simple hydrothermal method. Transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were used to characterize the morphology and structure of quantum dots. The fluorescence of SiQDs could be quenched by the silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) by surface plasmon-enhanced energy transfer (SPEET) from SiQDs (donor) to AgNPs (acceptor). The AgNPs could be etched by adding ClO−, thus freeing the SiQDs from the AgNP surfaces and restoring the SiQDs’ fluorescence. The sensing system exhibits many advantages, such as wide linear response range, high sensitivity, and excellent selectivity. Under optimized conditions, wide linear ranges (from 0.1 to 100.0 μM) and low detection limits (0.08 μM) were obtained for ClO−.

Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu T, Zhang L, Sun M, Deng D, Su Y, Yi L. Amino-functionalized metal-organic frameworks nanoplates-based energy transfer probe for highly selective fluorescence detection of free chlorine. Anal Chem. 2016;88(6):3413.
Rook JJ. Formation of haloforms during chlorination of natural water. Acta Polytech Hung. 2002;42(2):234–43.
Bellar TA, Lichtenberg JJ, Kroner RC. The occurrence of organohalides in chlorinated drinking waters. J Am Water Works Assoc. 1974;66(12):703–6.
Hanson SJ, Punzalan RC, Greenup RA, Liu H, Sato TT, Havens PL. Incidence and risk factors for venous thromboembolism in critically ill children after trauma. J Pediatr Surg. 2010;45(9):1920–1.
Hinckley AF, Bachand AM, Reif JS. Late pregnancy exposures to disinfection by-products and growth-related birth outcomes. Environ Health Perspect. 2005;113(12):1808–13.
Emmanuel E, Keck G, Blanchard JM, Vermande P, Perrodin Y. Toxicological effects of disinfections using sodium hypochlorite on aquatic organisms and its contribution to AOX formation in hospital wastewater. Environ Int. 2004;30(7):891–900.
Manish M, Rizwan SM, Khiem T, RS P, MA B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;20(7):1126–67.
Goiffon RJ, Martinez SC, Piwnicaworms D. A rapid bioluminescence assay for measuring myeloperoxidase activity in human plasma. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6271.
Sugiyama S, Okada Y, Sukhova GK, Virmani R, Heinecke JW, Libby P. Macrophage myeloperoxidase regulation by granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human atherosclerosis and implications in acute coronary syndromes. Am J Pathol. 2001;158(3):879–91.
Daugherty A, Dunn JL, Rateri DL, Heinecke JW. Myeloperoxidase, a catalyst for lipoprotein oxidation, is expressed in human atherosclerotic lesions. J Clin Invest. 1994;94(1):437–44.
Pan S, Deen MJ, Ghosh R. Low-cost graphite-based free chlorine sensor. Anal Chem. 2015;87(21):10734–7.
Tang Y, Su Y, Yang N, Zhang L, Lv Y. Carbon nitride quantum dots: a novel chemiluminescence system for selective detection of free chlorine in water. Anal Chem. 2014;86(9):4528.
Wang Y, Zhang P, Lu Q, Wang Y, Fu W, Tan Q, et al. Water-soluble MoS2 quantum dots are a viable fluorescent probe for hypochlorite. Mikrochim Acta. 2018;185(4):233.
Walekar LS, Pawar SP, Gore AH, Suryawanshi VD, Undare SS, Anbhule PV, et al. Surfactant stabilized AgNPs as a colorimetric probe for simple and selective detection of hypochlorite anion (ClO−) in aqueous solution: environmental sample analysis. Colloid Surface A. 2016;491:78–85.
Li K, Hou JT, Yang J, Yu XQ. A tumor-specific and mitochondria-targeted fluorescent probe for real-time sensing of hypochlorite in living cells. Chem Commun. 2017;53(40):5539–41.
Yan L, Hu C, Li J. A fluorescence turn-on probe for rapid monitoring of hypochlorite based on coumarin Schiff base. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410:7457.
Hosseini MS, Hashemipour Z, Hosseini N. Synthesis of l-tyrosine-capped ZnSe quantum dots and its application to hypochlorite determination in water. Int J Environ Anal Chem. 2016;96(10):1–14.
Park S, Choi S, Yu J. DNA-encapsulated silver nanodots as ratiometric luminescent probes for hypochlorite detection. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014;9(1):129.
Zhan Y, Luo F, Guo L, Qiu B, Lin Y, Li J, et al. Preparation of an efficient ratiometric fluorescent nanoprobe (m-CDs@[Ru(bpy)3](2+)) for visual and specific detection of hypochlorite on site and in living cells. ACS Sens. 2017;2(11):1684–91.
Zhang J, Yu SH. Highly photoluminescent silicon nanocrystals for rapid, label-free and recyclable detection of mercuric ions. Nanoscale. 2014;6(8):4096–101.
Zhang XD, Chen XK, Yang JJ, Jia HR, Li YH, Chen Z, et al. Quaternized silicon nanoparticles with polarity-sensitive fluorescence for selectively imaging and killing gram-positive bacteria. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26(33):5958–70.
Zhong Y, Peng F, Bao F, Wang S, Ji X, Yang L, et al. Large-scale aqueous synthesis of fluorescent and biocompatible silicon nanoparticles and their use as highly photostable biological probes. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(22):8350–6.
Zhong Y, Sun X, Wang S, Peng F, Bao F, Su Y, et al. Facile, large-quantity synthesis of stable, tunable-color silicon nanoparticles and their application for long-term cellular imaging. ACS Nano. 2015;9(6):5958–67.
Yan Y, Zhang K, Yu H, Zhu H, Sun M, Hayat T, et al. Sensitive detection of sulfide based on the self-assembly of fluorescent silver nanoclusters on the surface of silica nanospheres. Talanta. 2017;174:387–93.
Qu F, Xia W, Xia L, You J, Han W. A ratiometric detection of heparin with high sensitivity based on aggregation-enhanced emission of gold nanoclusters triggered by silicon nanoparticles. Talanta. 2019;193:37–43.
Zhang Y, Ning X, Mao G, Ji X, He Z. Fluorescence turn-on detection of target sequence DNA based on silicon nanodot-mediated quenching. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(13):3209–16.
Ma SD, Chen YL, Feng J, Liu JJ, Zuo XW, Chen XG. One-step synthesis of water-dispersible and biocompatible silicon nanoparticles for selective heparin sensing and cell imaging. Anal Chem. 2016;88(21):10474–81.
Zhang X, Chen X, Kai S, Wang HY, Yang J, Wu FG, et al. Highly sensitive and selective detection of dopamine using one-pot synthesized highly photoluminescent silicon nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2015;87(6):3360–5.
Yi Y, Deng J, Zhang Y, Li H, Yao S. Label-free Si quantum dots as photoluminescence probes for glucose detection. Chem Commun. 2013;49(6):612–4.
Yi Y, Zhu G, Liu C, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Li H, et al. A label-free silicon quantum dots-based photoluminescence sensor for ultrasensitive detection of pesticides. Anal Chem. 2013;85(23):11464–70.
Chen S, Quan Y, Yu Y-L, Wang J-H. Graphene quantum dot/silver nanoparticle hybrids with oxidase activities for antibacterial application. ACS Biomater-Sci Eng. 2017;3(3):313–21.
Ma JL, Yin BC, Wu X, Ye BC. Simple and cost-effective glucose detection based on carbon nanodots supported on silver nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2017;89(2):1323–8.
Li J, Li Y, Shahzad SA, Chen J, Chen Y, Wang Y, et al. Fluorescence turn-on detection of glucose via the Ag nanoparticle mediated release of a perylene probe. Chem Commun. 2015;51(29):6354–6.
Sasikumar T, Ilanchelian M. Colorimetric detection of hypochlorite based on the morphological changes of silver nanoprisms to spherical nanoparticles. Anal Methods. 2017;9(21):3151–8.
Han Y, Chen Y, Feng J, Liu J, Ma S, Chen X. One-pot synthesis of fluorescent silicon nanoparticles for sensitive and selective determination of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol in aqueous solution. Anal Chem. 2017;89(5):3001–8.
Feng J, Chen Y, Han Y, Liu J, Ren C, Chen X. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles: a low-temperature trypsin-assisted preparation and Fe(3+) sensing. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;926:107–17.
Ou S-H, Pan L-S, Jow J-J, Chen H-R, Ling T-R. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor, formed on Ag screen-printed electrodes, for the enantioselective recognition of D and L phenylalanine. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;105:143–50.
Liu X, Yan Z, Sun Y, Ren J, Qu X. A label-free ratiometric electrochemical DNA sensor for monitoring intracellular redox homeostasis. Chem Commun. 2017;53(46):6215–8.
Zhu X, Zhao T, Nie Z, Liu Y, Yao S. Non-redox modulated fluorescence strategy for sensitive and selective ascorbic acid detection with highly photoluminescent nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles via solid-state synthesis. Anal Chem. 2015;87(16):8524–30.
Yu Y, Tao Y, Yang B, Wu D, Qin Y, Kong Y. Smart chiral sensing platform with alterable enantioselectivity. Anal Chem. 2017;89(23):12930–7.
Dong Y, Li G, Zhou N, Wang R, Chi Y, Chen G. Graphene quantum dot as a green and facile sensor for free chlorine in drinking water. Anal Chem. 2012;84(19):8378–82.
Hu Y, Yang J, Jia L, Yu J-S. Ethanol in aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution: hydrothermal synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon dots as multifunctional nanosensors. Carbon. 2015;93:999–1007.
Tang Q, Yang T, Huang Y. Copper nanocluster-based fluorescent probe for hypochlorite. Microchim Acta. 2015;182(13–14):2337–43.
Huang Y, Zhang P, Gao M, Zeng F, Qin A, Wu S, et al. Ratiometric detection and imaging of endogenous hypochlorite in live cells and in vivo achieved by using an aggregation induced emission (AIE)-based nanoprobe. Chem Commun. 2016;52(45):7288–91.
Xue M, Zhang L, Zou M, Lan C, Zhan Z, Zhao S. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots: a facile and green fluorescence probe for free chlorine. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015;219:50–6.
Funding
This study received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21607061), the Opening Project of State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics of Hunan University (2016017), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, the Collaborative Innovation Center of Technology and Material of Water Treatment, and the Program of Young Backbone Teachers in Jiangsu University (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1552 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Zhu, G., Zeng, W. et al. Highly sensitive and selective “off-on” fluorescent sensing platform for ClO− in water based on silicon quantum dots coupled with nanosilver. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 1561–1568 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01597-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01597-5