Abstract
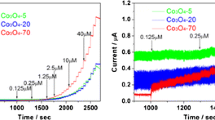
In this work, high-performance non-enzymatic catalysts based on 3D hierarchical hollow porous Co3O4 nanododecahedras in situ decorated on carbon nanotubes (3D Co3O4-HPND/CNTs) were successfully prepared via direct carbonizing metal-organic framework-67 in situ grown on carbon nanotubes. The morphology, microstructure, and composite of 3D Co3O4-HPND/CNTs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, micropore and chemisorption analyzer, and X-ray diffraction. The electrochemical characterizations indicated that 3D Co3O4-HPND/CNTs present considerably catalytic activity toward glucose oxidation and could be promising for constructing high-performance electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors and glucose/O2 biofuel cell. When used for non-enzymatic glucose detection, the 3D Co3O4-HPND/CNTs modified glassy carbon electrode (3D Co3O4-HPND/CNTs/GCE) exhibited excellent analytical performance with high sensitivity (22.21 mA mM−1 cm−2), low detection limit of 0.35 μM (S/N = 3), fast response (less than 5 s) and good stability. On the other hand, when the 3D Co3O4-HPND/CNTs/GCE worked as an anode of a biofuel cell, a maximum power density of 210 μW cm−2 at 0.15 V could be obtained, and the open circuit potential was 0.68 V. The attractive 3D hierarchical porous structural features, the large surface area, and the excellent conductivity based on the continuous and effective electron transport network in 3D Co3O4-HPND/CNTs endow 3D Co3O4-HPND/CNTs with the enhanced electrochemical performance and promising applications in electrochemical sensing, biofuel cell, and other energy storage and conversion devices such as supercapacitor.

High-performance non-enzymatic catalysts for enzymeless glucose sensing and biofuel cell based on 3D hierarchical hollow porous Co3O4 nanododecahedras anchored on carbon nanotubes were successfully prepared via direct carbonizing metal-organic framework-67 in situ grown on carbon nanotubes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galant AL, Kaufman RC, Wilson JD. Glucose: detection and analysis. Food Chem. 2015;188:149–60.
Hao T, Wei X, Nie Y, Xu Y, Lu K, Yan Y, et al. Surface modification and ratiometric fluorescence dual function enhancement for visual and fluorescent detection of glucose based on dual-emission quantum dots hybrid. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;230:70–6.
Riegel AL, Borzenkova N, Haas V, Scharfer P, Schabel W. Activity determination of FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase immobilized in PEDOT: PSS-PVA composite films for biosensor applications. Eng Life Sci. 2016;6:577–85.
Mu Y, Jia D, He Y, Miao Y, Wu HL. Nano nickel oxide modified non-enzymatic glucose sensors with enhanced sensitivity through an electrochemical process strategy at high potential. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011;26:2948–52.
Tan XC, Tian Y, Cai P, Zou XY. Glucose biosensor based on glucose oxidase immobilized in sol-gel chitosan/silica hybrid composite film on Prussian blue modified glass carbon electrode. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005;381:500–7.
Sun L, Ma Y, Zhang P, Chao L, Huang T, Xie Q, et al. An amperometric enzyme electrode and its biofuel cell based on a glucose oxidase-poly (3-anilineboronic acid)-Pd nanoparticles bionanocomposite for glucose biosensing. Talanta. 2015;138:100–7.
Song Y, Su D, Shen Y, Liu H, Wang L. Design and preparation of open circuit potential biosensor for in vitro and in vivo glucose monitoring. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409:161–8.
Heller A, Feldman B. Electrochemical glucose sensors and their applications in diabetes management. Chem Rev. 2008;108:2482–505.
Zhan B, Liu C, Chen H, Shi H, Wang L, Chen P, et al. Free-standing electrochemical electrode based on Ni(OH)2/3D graphene foam for nonenzymatic glucose detection. Nano. 2014;6:7424–9.
Huang TK, Lin KW, Tung SP, Cheng TM, Chang IC, Hsieh YZ, et al. Glucose sensing by electrochemically grown copper nanobelt electrode. Electroanal Chem. 2009;123:123–7.
Xing Y, Gao G, Zhu G, Gao J, Ge Z, Yang H. A nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on Ni(OH)2-CNT-PVDF composite and its application in measuring serum glucose. Electrochem Soc. 2014;161:B106–10.
Dhara K, Stanley J, Ramachandran T, Nair BG, TGS B. Cupric oxide modified screen printed electrode for the nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016;16:8772–8.
Wang G, Lu X, Zhai T, Ling Y, Wang H, Tong Y, et al. Free-standing nickel oxide nanoflake arrays: synthesis and application for highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Nano. 2012;4:3123–7.
Morteza NS. Novel magnetic nanocomposites comprising reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4/gelatin utilized in ultrasensitive non-enzymatic biosensing. Int J Electrochim Sci. 2016;11:10256–69.
Zheng M, Li L, Gu P, Lin Z, Xue H, Pang H. A glassy carbon electrode modified with ordered nanoporous Co3O4 for non-enzymatic sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta. 2017;184:1–7.
Prasad R, Bhat BR. Self-assembly synthesis of Co3O4/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites: an efficient enzyme-free glucose sensor. New J Chem. 2015;39:9735–42.
Lee KK, Loh PY, Sow CH, Chin WS. CoOOH nanosheets on cobalt substrate as a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electroanal Chem. 2012;20:128–32.
Ding Y, Wang Y, Su L, Bellagamba M, Zhang H, Lei Y. Electrospun Co3O4 nanofibers for sensitive and selective glucose detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;26:542–8.
Yang M, Jeong JM, Lee KG, Kim DH, Lee SJ, Choi BG. Hierarchical porous microspheres of the Co3O4@graphene with enhanced electrocatalytic performance for electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;89:612–9.
Li S-J, Du J-M, Chen J, Mao N-N, Zhang M-J, Pang H. Electrodeposition of cobalt oxide nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide: a two-dimensional hybrid for enzyme-free glucose sensing. J Solid State Electrochem. 2013;18:1049–56.
Guan C, Zhao W, Hu YT, Lai ZC, Li X, Sun S, et al. Cobalt oxide and N-doped carbon nanosheets derived from a single two-dimensional metal-organic framework precursor and their application in flexible asymmetric supercapacitors. Nanoscale Horiz. 2017;2:99–105.
Guan C, Liu X, Ren W, Li X, Cheng C, Wang J. Rational design of metal-organic framework derived hollow NiCo2O4 arrays for flexible supercapacitor and electrocatalysis. Adv Energy Mater. 2017;7:1602391.
Liu S, Xiang Z, Hu Z, Zheng X, Cao D. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 as a luminescent material for the sensing of metal ions and small molecules. J Mater Chem. 2011;21:6649.
Yi X, Dong W, Zhang X, Xie J, Huang Y. MIL-53(Fe) MOF-mediated catalytic chemiluminescence for sensitive detection of glucose. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:8805–12.
Guan C, Sumboja A, Wu H, Ren W, Liu X, Zhang H, et al. Hollow Co3O4 nanosphere embedded in carbon arrays for stable and flexible solid-state zinc-air batteries. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1704117.
Guan C, Liu X, Elshahawy AM, Zhang H, Wu H, Pennycook SJ, et al. Metal-organic framework derived hollow CoS2 nanotube arrays: an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Nanoscale Horiz. 2017;2:342–8.
Zhang E, Xie Y, Ci S, Jia J, Porous WZ. Co3O4 hollow nanododecahedra for nonenzymatic glucose biosensor and biofuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;81:46–53.
Yang J, Zhang WD, Gunasekaran S. An amperometric non-enzymatic glucose sensor by electrodepositing copper nanocubes onto vertically well-aligned multi-walled carbon nanotube arrays. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;26:279–84.
Rana U, Chakrabarti K, Malik S. In situ preparation of fluorescent polyaniline nanotubes doped with perylene tetracarboxylic acids. J Mater Chem A. 2011;21:11098.
Wu ZS, Yang S, Sun Y, Parvez K, Feng X, Mullen K. 3D nitrogen-doped graphene aerogel-supported Fe3O4 nanoparticles as efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;22:9082–5.
Meng S, Wu M, Wang Q, Dai Z, Si W, Huang W, et al. Cobalt oxide nanosheets wrapped onto nickel foam for non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Nanotechnology. 2016;27:344001.
Wu B, Hu D, Kuang Y, Yu Y, Zhang X, Chen J. High dispersion of platinum-ruthenium nanoparticles on the 3,4,9,10-perylene tetracarboxylic acid-functionalized carbon nanotubes for methanol electro-oxidation. Chem Commun. 2011;47:5253–5.
Zhu G, Lee H. Electrochemical sandwich-type biosensors for α-1 antitrypsin with carbon nanotubes and alkaline phosphatase labeled antibody-silver nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;89:959–63.
Yu L, Yang J, Lou XW. Formation of CoS2 nanobubble hollow prisms for highly reversible lithium storage. Angew Chem. 2016;55:13422–6.
Liu Y, Hu W, Li X, Dong B, Shang X, Han G, et al. Facile one-pot synthesis of CoS2-MoS2/CNTs as efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl Surf Sci. 2016;384:51–7.
Ma Y, Wu X, Feng XJ, Tan HQ, Yan LK, Liu Y, et al. Highly efficient hydrogen evolution from seawater by a low-cost and stable CoMoP@C electrocatalyst superior to Pt/C. Energy Environ Sci. 2017;10:788–98.
Li Y, Liu J, Chen C, Zhang X, Chen J. Preparation of NiCoP hollow quasi-polyhedra and their electrocatalytic properties for hydrogen evolution in alkaline solution. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:5982–91.
Dong XC, Xu H, Wang XW, Huang YX, Chan-Park MB, Zhang H, et al. 3D graphene-cobalt oxide electrode for high-performance supercapacitor and enzymeless glucose detection. ACS Nano. 2012;6:3206–13.
Li M, Han C, Zhang Y, Bo X, Guo L. Facile synthesis of ultrafine Co3O4 nanocrystals embedded carbon matrices with specific skeletal structures as efficient non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;861:25–35.
Cao F, Guo S, Ma H, Shan D, Yang S, Gong J. Nickel oxide microfibers immobilized onto electrode by electrospinning and calcination for nonenzymatic glucose sensor and effect of calcination temperature on the performance. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011;26:2756–60.
Li C, Su Y, Zhang S, Lv X, Xia H, Wang Y. An improved sensitivity nonenzymatic glucose biosensor based on a CuxO modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;26:903–7.
Liu M, Liu R, Chen W. Graphene wrapped Cu2O nanocubes: non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors for the detection of glucose and hydrogen peroxide with enhanced stability. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;45:206–12.
Park S, Chung TD, Kim HC. Nonenzymatic glucose detection using mesoporous platinum. Anal Chem. 2003;75:3046–9.
Kang L, He D, Bie L, Jiang P. Nanoporous cobalt oxide nanowires for non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015;220:888–94.
Liu Y, Cao X, Kong R, Du G, Asiri AM, Lu Q, et al. Cobalt phosphide nanowire array as an effective electrocatalyst for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5:1901–4.
Yang J, Cho M, Lee Y. Synthesis of hierarchical NiCo2O4 hollow nanorods via sacrificial-template accelerate hydrolysis for electrochemical glucose oxidation. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;75:15–22.
Trifonov A, Herkendell K, Tel-Vered R, Yehezkeli O, Woerner M, Willner I. Enzyme-capped relay-functionalized mesoporous carbon nanoparticles: effective bioelectrocatalytic matrices for sensing and biofuel cell applications. ACS Nano. 2013;7:11358–68.
Scherbahn V, Putze MT, Dietzel B, Heinlein T, Schneider JJ, Lisdat F. Biofuel cells based on direct enzyme–electrode contacts using PQQ-dependent glucose dehydrogenase/bilirubin oxidase and modified carbon nanotube materials. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;61:631–8.
Slaughter G, Kulkarni T. Fabrication of palladium nanowire array electrode for biofuel cell application. Microelectron Eng. 2016;149:92–6.
Yang L, Zhang Y, Chu M, Deng W, Tan Y, Ma M, et al. Facile fabrication of network film electrodes with ultrathin Au nanowires for nonenzymatic glucose sensing and glucose/O2 fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;52:105–10.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by NSFC (21475035, 21235002, 21275041), the Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of NSFC (21521063), and PCSIRT (IRT1238).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hunan University and performed in accordance with their ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2.59 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Zhang, X., Huang, J. et al. High-performance non-enzymatic catalysts based on 3D hierarchical hollow porous Co3O4 nanododecahedras in situ decorated on carbon nanotubes for glucose detection and biofuel cell application. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 2019–2029 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-0875-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-0875-3