Abstract
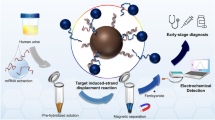
A new homogeneous electrochemical sensing system was developed for sensitive detection of microRNA-21 (miRNA-21) based on target-induced glucose release from propylamine-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN) with glucometer readout. Glucose molecules (as the signal tracers) were initially gated into the pores through the interaction of the negatively charged anchor DNA with the aminated MSN. Upon addition of target miRNA, the analyte competitively hybridized with anchor DNA to form the RNA-DNA duplex, thus resulting in detachment of anchor DNA from the MSN accompanying the pore opening. The loaded glucose molecules released out from the pores because of concentration gradients, which could be detected by using a portable personal glucometer (PGM). Experimental results indicated that the PGM signal increased with the increasing miRNA level, and exhibited a good linear dependence on the miRNA-21 concentration from 50 pM to 5.0 nM with a detection limit of 19 pM under optimum conditions. Additionally, multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles also showed good stability and favorable selectivity, and satisfactory accuracy for the miRNA detection in cell lysates with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Such good analytical performance endows it as a promising scheme for the efficient and convenient detection of miRNA in clinical diagnosis and therapy.

An electrochemical sensing system is designed for detection of microRNA-21 based on target-induced glucose release from propylamine-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticle with glucometer readout.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Cramb S, Mengersen K, Turrell G, Baade P. Spatial inequalities in colorectal and breast cancer survival: premature deaths and associated factors. Health Place. 2012;18:1412–21.
De Vega R, Sanchez M, Eiro N, Vizoso F, Sperling M, Karst U, et al. Multimodal laser ablation/desorption imaging analysis of Zn and MMP-11 in breast tissues. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0537-x.
Kenny L, Orsi F, Adam A. Interventional radiology in breast cancer. Breast. 2017;35:98–103.
Fan L, Strasser-Wippl K, Li J, Louis J, Finkelstein D, Yu K, et al. Breast cancer in China. Lancet. 2014;15:e279–89.
Hasanzadeh M, Shadjou N, de la Guardia M. Early stage screening of breast cancer using electrochemical biomarker detection. TrAC-Anal Chem. 2017;91:67–76.
Falagan-Lotsch P, Grzincic E, Murphy C. New advances in nanotechnology-based diagnosis and therapeutics for breast cancer: an assessment of active-targeting inorganic nanoplatforms. Bioconjug Chem. 2017;28:135–52.
Petrovic N, Davidovic R, Bajic V, Obradovic M, Isenovic R. MiroRNA in breast cancer: the association with BRCA1/2. Cancer Biomark. 2017;19:119–28.
Hu B, Guo J, Xu Y, Wei H, Zhao G, Guan Y. A sensitive colorimetric assay for nucleic acid detection based on isothermal signal amplification technology. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409:4819–25.
Rupaimoole R, Slack F. MiroRNA therapeutics: toward a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:203–21.
Clancy E, Burke M, Arabkari V, Barry T, Kelly H, Dwyer R, et al. Amplification-free detection of microRNAs via a rapid microarray-based sandwich assay. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409:3497–505.
Matin F, Jeet V, Clements J, Yousef G, Batra J. MiroRNA theranostics in prostate cancer precision medicine. Clin Chem. 2016;62:1318–33.
Tian L, Qian K, Qi L, Liu Q, Yao C, Song W, et al. Gold nanoparticles superlattices assembly for electrochemical biosensor detection of microRNA-21. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;99:564–70.
Li Q, Wang Q, Yang X, Wang K, Zhang H, Nie W. High sensitivity surface plasmon resonance biosensor for detection of microRNA and small molecule based on graphene oxide-gold nanoparticle composites. Talanta. 2017;174:521–6.
Yang F, Zhang T, Li S, Song P, Zhang K, Guan Q, et al. Endogenous microRNA-triggered and real-time monitored drug release via cascaded energy transfer payloads. Anal Chem. 2017;89:10239–47.
Yan H, Xu Y, Lu Y, Xing W. Reduced graphene oxide-based solid-phase extraction for the enrichment and detection of microRNA. Anal Chem. 2017;89:10137–40.
Hou L, Zhu C, Wu X, Chen G, Tang D. Bioresponsive controlled release from mesoporous silica nanocontainers with glucometer readout. Chem Commun. 2014;50:1441–3.
Gao Z, Tang D, Xu M, Chen G, Yang H. Nanoparticle-based pseudo hapten for target-responsive cargo release from a magnetic mesoporous silica nanocontainers. Chem Commun. 2014;50:6256–8.
Qiu Z, Shu J, Jin G, Xu M, Wei Q, Chen G, et al. Invertase-labeling gold-dendrimer for in situ amplified detection of mercury(II) with glucometer readout and thymine-Hg2+-thymine coordination chemistry. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;77:681–6.
Tang D, Lin Y, Zhou Q, Lin Y, Li P, Niessner R, et al. Low-cost and highly sensitive immunosensing platform for aflatoxins using one-step competitive displacement reaction mode and portable glucometer-based detection. Anal Chem. 2014;86:11451–8.
Gai P, Gu C, Li H, Sun X, Li F. Ultrasensitive ratiometric homogenous electrochemical microRNA biosensing via target-triggered Ru(III) release and redox recycling. Anal Chem. 2017; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03268.
Zhang Z, Balogh D, Wang F, Willner I. Smart mesoporous SiO2 nanoparticles for the DNAzyme-induced multiplexed release of substrates. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:1934–40.
Yan F, Zhang T, Li S, Song P, Zhang K, Guan Q, et al. Endogenous microRNA-triggered and real-time monitored drug release via cascaded energy transfer payloads. Anal Chem. 2017;89:10239–47.
Kaplan M, Kilic T, Guler G, Mandli J, Amine A, Ozsoz M. A novel method for sensitive microRNA detection: electropolymerization based doping. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;92:770–8.
Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhao L, Bao T, Wen W, Zhang X, et al. Integrated amplified aptasensor with in-situ precise preparation of copper nanoclusters for ultransensitive electrochemical detection of microRNA-21. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;98:386–91.
Yuan Y, Wu Y, Chi B, Wen S, Liang R, Qiu J. Simultaneously electrochemical detection of microRNAs based on multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles probe coupling with hybridization chain reaction. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;97:325–31.
Su S, Cao W, Liu W, Lu Z, Zhu D, Chao J, et al. Dual-mode electrochemical analysis of microRNA-21 using gold nanoparticle-decorated MoS2 nanosheets. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;94:552–9.
Zhang J, Zhao Q, Wu Y, Zhang B, Peng W, Piao J, et al. The construction of a novel nucleic acids detection microplatform based on the NSET for one-step detecting TK1-DNA and microRNA-21. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;97:26–33.
Yin H, Li B, Zhou Y, Wang H, Wang M, Ai S. Signal-on fluorescence biosensor for microRNA-21 detection based on DNA strand displacement reaction and Mg2+-dependent DNAzyme cleavage. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;96:106–12.
Li S, He K, Liao R, Chen C, Chen X, Cai C. An interference-free and label-free sandwich-type magnetic silicon microsphere-rGO-based probe for fluorescence detection of microRNA. Talanta. 2017;174:679–83.
Zhen S, Xiao X, Li C, Huang C. An enzyme-free DNA circuit-assisted graphene oxide enhanced fluoresence anisotropy assay for microRNA detection with improved sensitivity and selectivity. Anal Chem. 2017;89:8766–71.
Killc T, Topkaya S, Ozkan Ariksoysal D, Ozsoz M, Ballar P, Erac Y, et al. Electrochemical based detection of microRNA, mir21 in breast cancer cells. Biosens Bioelectron. 2012;38:195–201.
Qian R, Ding L, Ju H. Switchable fluorescent imaging of intracellular telomerase activity using telomerase-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:13282–5.
Liang X, Wang L, Wang D, Zeng L, Fang Z. Portable and quantitative monitoring of mercury ions using DNA-gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles using a glucometer readout. Chem Commun. 2016;52:2192–4.
Livak K, Schmittgen T. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔC T method. Methods. 2011;25:402–8.
Lerbret A, Lelong G, Mason P, Saboungi M, Brady J. Molecular dynamics and neutron scatting study of glucose solutions confined in MCM-41. J Phys Chem B. 2011;115:910–8.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no.: 81302696), Chongqing Health and Family Planning Commission Medical Research Project (Grant no.: 2017ZDXM031), and the National Basic research Program of China (program 973) (Grant no.: 2015CB755400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, K., Zhang, Y. & Tong, X. Sensitive electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 based on propylamine-functionalized mesoporous silica with glucometer readout. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 1863–1871 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-0859-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-0859-3