Abstract
As an essential enzyme highly associated with various human diseases, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) plays an important role in human tissues. Developing new materials and strategies for monitoring ALP is thus important. We have developed a novel label-free fluorescent sensing system for ALP activity that is based on the “turn-on” fluorescence of VS2 quantum dots. The fluorescence of VS2 quantum dots quenched by Fe3+ can be restored by ascorbic acid, which is generated by hydrolysis of l-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate catalyzed by ALP. Rapid, convenient, and sensitive detection of ALP is achieved in the range from 3 to 1000 U/L (R 2 =0.9985), with a detection limit of 0.27 U/L. The proposed sensor exhibits excellent selectivity for ALP compared with other enzymes and proteins, such as glucose oxidase, lysozyme, trypsin, human serum albumin, and bovine serum albumin. The reliability for ALP determination in human serum plasma has been demonstrated with satisfactory recovery, revealing promising application in clinical diagnosis and biomedical research.

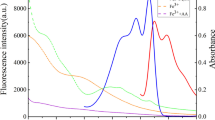
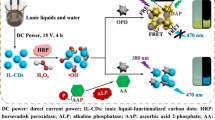
Hydrothermally synthesized VS2 quantum dots serving as a novel turn-on fluorescent probe for detection of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity. AA l-ascorbic acid, AAP l-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate, NAC N-acetyl-l-cysteine








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu JM, Cui ML, Wang XX, Lin LP, Jiao L, Zhang LH, et al. A highly selective affinity adsorption imprinting phosphorescence sensor for determination of trace alkaline phosphatase and prediction of human diseases. Sens Actuators B. 2013;186:521–7.
Wu NJ, Lan JB, Yan LP, You JS. A sensitive colorimetric and fluorescent sensor based on imidazolium-functionalized squaraines for the detection of GTP and alkaline phosphatase in aqueous solution. Chem Commun. 2014;50:4438–41.
Hu ZZ, Chen J, Li YX, Wang Y, Zhang QF, Hussain E, et al. Nucleic acid-controlled quantum dots aggregation: a label-free fluorescence turn-on strategy for alkaline phosphatase detection. Talanta. 2017;169:64–9.
Qu FL, Pei HM, Kong RM, Zhu SY, Xia L. Novel turn-on fluorescent detection of alkaline phosphatase based on green synthesized carbon dots and MnO2 nanosheets. Talanta. 2017;165:136–42.
Lorente JA, Valenzuela H, Morote J, Gelabert A. Serum bone alkaline phosphatase levels enhance the clinical utility of prostate specific antigen in the staging of newly diagnosed prostate cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med. 1999;26:625–32.
Dong L, Miao QQ, Hai ZJ, Yuan Y, Liang GL. Enzymatic hydrogelation-induced fluorescence turn-off for sensing alkaline phosphatase in vitro and in living cells. Anal Chem. 2015;87:6475–8.
Ooi K, Shiraki K, Morishita Y, Nobori T. High-molecular intestinal alkaline phosphatase in chronic liver diseases. J Clin Lab Anal. 2007;21:133–9.
Diaz AN, Sanchez FG, Ramos MC, Torijas MC. Horseradish peroxidase sol-gel immobilized for chemiluminescence measurements of alkaline-phosphatase activity. Sens Actuators B. 2002;82:176–9.
Miao P, Ning LM, Li XX, Shu YQ, Li GX. An electrochemical alkaline phosphatase biosensor fabricated with two DNA probes coupled with lambda exonuclease. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011;27:178–82.
Choi Y, Ho NH, Tung CH. Sensing phosphatase activity by using gold nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46:707–9.
Song ZG, Kwok RTK, Zhao EG, He ZK, Hong YN, Lam JWY, et al. A ratiometric fluorescent probe based on ESIPT and AIE processes for alkaline phosphatase activity assay and visualization in living cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6:17245–54.
Zhang LL, Zhao JJ, Duan M, Zhang H, Jiang JH, Yu RQ. Inhibition of dsDNA-templated copper nanoparticles by pyrophosphate as a label-free fluorescent strategy for alkaline phosphatase assay. Anal Chem. 2013;85:3797–801.
Chen L, Yang GC, Wu P, Cai CX. Real-time fluorescence assay of alkaline phosphatase in living cells using boron-doped graphene quantum dots as fluorophores. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;96:294–9.
Xiang X, Zhang Z, Han L, Huang FH, Zheng MM, Tang H, et al. Fluorescence switching sensor for sensitive detection of sinapine using carbon quantum dots. Sens Actuators B. 2017;241:482–8.
Xu Q, Wei HP, Hu XY. Glutathione detection based on ZnS quantum-dot-based off-on fluorescent probe. Chin J Anal Chem. 2013;41(7):1102–6.
Liu XL, Jiang H, Ye J, Zhao CQ, Gao SP, Wu CY, et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot stabilized magnetic iron oxide nanoprobe for fluorescence, magnetic resonance, and computed tomography triple-modal in vivo bioimaging. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26:8694–706.
Akshath US, Shubha LR, Bhatt P, Thakur MS. Quantum dots as optical labels for ultrasensitive detection of polyphenols. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;57:317–23.
Xiang X, Shi JB, Huang FH, Zheng MM, Deng QC. Quantum dots-based label-free fluorescence sensor for sensitive and non-enzymatic detection of caffeic acid. Talanta. 2015;141:182–7.
Fu X, Ilanchezhiyan P, Kumar GM, Cho HD, Zhang L, Chan AS, et al. Tunable UV-visible absorption of SnS2 layered quantum dots produced by liquid phase exfoliation. Nanoscale. 2017;9:1820–6.
Jiang H. Electronic band structures of molybdenum and tungsten dichalcogenides by the GW approach. J Phys Chem C. 2012;116:7664–71.
Kalantar-zadeh K, Ou JZ, Daeneke T, Strano MS, Pumera M, Gras SL. Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides in biosystems. Adv Funct Mater. 2015;25:5086–99.
Raza F, Park JH, Lee HR, Kim HI, Jeon SJ, Kim JH. Visible-light-driven oxidative coupling reactions of amines by photoactive WS2 nanosheets. ACS Catal. 2016;6:2754–9.
Mahler B, Hoepfner V, Liao K, Ozin GA. Colloidal synthesis of 1T-WS2 and 2H-WS2 nanosheets: applications for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:14121–7.
Chhowalla M, Shin HS, Eda G, Li LJ, Loh KP, Zhang H. The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat Chem. 2013;5:263–75.
Lin LX, Xu YX, Zhang SW, Ross IM, Ong ACM, Allwood DA. Fabrication of luminescent monolayered tungsten dichalcogenides quantum dots with giant spin-valley coupling. ACS Nano. 2013;7:8214–23.
Huang H, Du CC, Shi HY, Feng X, Li J, Tan YL, et al. Water-soluble monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots with upconversion fluorescence. Part Part Syst Charact. 2015;32:72–9.
Lee C, Wei XD, Kysar JW, Hone J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science. 2008;321:385–8.
Feng J, Sun X, Wu CZ, Peng LL, Lin CW, Hu SL, et al. Metallic few-layered VS2 ultrathin nanosheets: high two-dimensional conductivity for in-plane supercapacitors. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:17832–8.
Liao JY, Manthiram A. High-performance Na2Ti2O5 nanowire arrays coated with VS2 nanosheets for sodium-ion storage. Nano Energy. 2015;18:20–7.
Fang WY, Zhao HB, Xie YP, Fang JH, Xu JQ, Chen ZW. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of VS2/graphene nanocomposites with superior high-rate capability as lithium-ion battery cathodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:13044–52.
Du CC, Shang AQ, Shang MX, Ma XH. Water-soluble VS2 quantum dots with unusual fluorescence for biosensing. Sens Actuators B. 2017; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.070.
Yan YH, Zhang CL, Gu W, Ding CP, Li XC, Xian YZ. Facile synthesis of water-soluble WS2 quantum dots for turn-on fluorescent measurement of lipoic acid. J Phys Chem C. 2016;120:12170–7.
Gao Z, Wang LB, Su RX, Huang RL, Qi W, He ZM. A carbon dot-based “off-on” fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of phytic acid. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;70:232–8.
Xu Q, Pu P, Zhao JG, Dong CB, Gao C, Chen YS, et al. Preparation of highly photoluminescent sulfur-doped carbon dots for Fe(III) detection. J Mater Chem A. 2015;3:542–6.
Hu Q, He MH, Mei YQ, Feng WJ, Jing S, Kong JM, et al. Sensitive and selective colorimetric assay of alkaline phosphatase activity with Cu(II)-phenanthroline complex. Talanta. 2017;163:146–52.
Liu YQ, Xiong EH, Li XY, Li JJ, Zhang XH, Chen JH. Sensitive electrochemical assay of alkaline phosphatase activity based on TdT-mediated hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzyme nanowires for signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;87:970–5.
Ma JL, Yin BC, Wu X, Ye BC. Copper-mediated DNA-scaffolded silver nanocluster on-off switch for detection of pyrophosphate and alkaline phosphates. Anal Chem. 2016;88:9219–25.
Tang C, Qian ZS, Huang YY, Xu JM, Ao H, Zhao MZ, et al. A fluorometric assay for alkaline phosphatase activity based on β-cyclodextrin-modified carbon quantum dots through host-guest recognition. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;83:274–80.
Hu YL, Geng X, Zhang L, Huang ZM, Ge J, Li ZH. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots mediated fluorescent on-off assay for rapid and highly sensitive pyrophosphate and alkaline phosphatase detection. Sci Rep. 2017;7:5849. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41598-017-06356-Z.
Zhang YY, Li YX, Zhang CY, Zhang QF, Huang XA, Yang MD, et al. Fluorescence turn-on detection of alkaline phosphatase activity based on controlled release of PEI-capped Cu nanoclusters from MnO2 nanosheets. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409(20):4771–8.
Liu JJ, Tang DS, Chen ZT, Yan XM, Zhong Z, Kang LT, et al. Chemical redox modulated fluorescence of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for probing the activity of alkaline phosphatase. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;94:271–7.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21475051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and was approved by the Ethical Committee of the First Hospital of Jilin University. All blood samples were from healthy persons with their informed consent.
Human and animal rights
No violation of human or animal rights occurred during this investigation.
Compliance with ethical standards
ESM 1
(PDF 167 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Du, C., Shang, M. et al. VS2 quantum dot label-free fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of ALP. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 1417–1426 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0778-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0778-8