Abstract
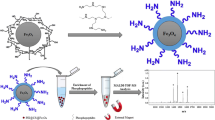
As one of the most important posttranslational modifications, protein phosphorylation plays an important role in vital movement. However, an efficiency enrichment treatment prior to MS detection is still a crucial step to protein phosphorylation analysis. In this work, a novel hybrid microsphere for efficient phosphopeptide enrichment was prepared by reverse-phase suspension polymerization of cellulose derivative and chitosan. The microspheres bore different kinds of amine groups and the main enrichment mechanism was based on anion exchange. This approach exhibited high selectivity for phosphopeptides from β-casein, α-casein, and non-fat milk. Three phosphopeptides could still be detected when the amount of β-casein was as low as 10 fmol. This study demonstrated a new attractive solid-phase support for phosphopeptide enrichment to meet the increasing need of phosphoproteomics analysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Larsen MR. Analytical strategies for phosphoproteomics. Proteomics. 2009;9(6):1451–68.
Li XS, Wu JH, Zhao Y, Zhang WP, Gao Q, Guo L, et al. Preparation of magnetic polymer material with phosphate group and its application to the enrichment of phosphopeptides. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218(25):3845–53.
Batalha IL, Roque AC. Phosphopeptide enrichment using various magnetic nanocomposites: an overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1355:193–209.
Leitner A. Enrichment strategies in phosphoproteomics. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1355:105–21.
Wang ZG, Lv N, Bi WZ, Zhang JL, Ni JZ. Development of the affinity materials for phosphorylated proteins/peptides enrichment in phosphoproteomics analysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(16):8377–92.
Andersson L, Porath J. Isolation of phosphoproteins by immobilized metal (Fe3+) affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1986;154(1):250–4.
Posewitz MC, Tempst P. Immobilized gallium(III) affinity chromatography of phosphopeptides. Anal Chem. 1999;71(14):2883–92.
Yu Z, Han G, Sun S, Jiang X, Chen R, Wang F, et al. Preparation of monodisperse immobilized Ti(4+) affinity chromatography microspheres for specific enrichment of phosphopeptides. Anal Chim Acta. 2009;636(1):34–41.
Zhao PX, Zhao Y, Guo XF, Wang H, Zhang HS. Isolation of phosphopeptides using zirconium-chlorophosphonazo chelate-modified silica nanoparticles. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218(18):2528–39.
Larsen MR, Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P, Jorgensen TJ. Highly selective enrichment of phosphorylated peptides from peptide mixtures using titanium dioxide microcolumns. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005;4(7):873–86.
Kweon HK, Hakansson K. Selective zirconium dioxide-based enrichment of phosphorylated peptides for mass spectrometric analysis. Anal Chem. 2006;78(6):1743–9.
Han L, Shan Z, Chen D, Yu X, Yang P, Tu B, et al. Mesoporous Fe2O3 microspheres: rapid and effective enrichment of phosphopeptides for MALDI-TOF MS analysis. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2008;318(2):315–21.
Li Y, Liu Y, Tang J, Lin H, Yao N, Shen X, et al. Fe3O4@Al2O3 magnetic core-shell microspheres for rapid and highly specific capture of phosphopeptides with mass spectrometry analysis. J Chromatogr A. 2007;1172(1):57–71.
Li Y, Qi D, Deng C, Yang P, Zhang X. Cerium ion-chelated magnetic silica microspheres for enrichment and direct determination of phosphopeptides by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 2008;7(4):1767–77.
Wang ZG, Cheng G, Liu YL, Zhang JL, Sun DH, Ni JZ. Novel core-shell cerium(IV)-immobilized magnetic polymeric microspheres for selective enrichment and rapid separation of phosphopeptides. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;417:217–26.
Jabeen F, Hussain D, Fatima B, Musharraf SG, Huck CW, Bonn GK, et al. Silica-lanthanum oxide: pioneer composite of rare-Earth metal oxide in selective phosphopeptides enrichment. Anal Chem. 2012;84(23):10180–5.
Cheng G, Zhang JL, Liu YL, Sun DH, Ni JZ. Monodisperse REPO4 (RE = Yb, Gd, Y) hollow microspheres covered with nanothorns as affinity probes for selectively capturing and labeling phosphopeptides. Chemistry. 2012;18(7):2014–20.
Wang F, Shi Z, Hu F, Xia Z, Wang L. Tuning of Ti-doped mesoporous silica for highly efficient enrichment of phosphopeptides in human placenta mitochondria. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013;405(5):1683–93.
Zhao M, Deng C, Zhang X. The design and synthesis of a hydrophilic core-shell-shell structured magnetic metal-organic framework as a novel immobilized metal ion affinity platform for phosphoproteome research. Chem Commun (Camb). 2014;50(47):6228–31.
Xu S, Whitin JC, Yu TT, Zhou H, Sun D, Sue HJ, et al. Capture of phosphopeptides using alpha-zirconium phosphate nanoplatelets. Anal Chem. 2008;80(14):5542–9.
Atakay M, Celikbicak O, Salih B. Amine-functionalized sol–gel-based lab-in-a-pipet-tip approach for the fast enrichment and specific purification of phosphopeptides in MALDI-MS applications. Anal Chem. 2012;84(6):2713–20.
Chen CT, Wang LY, Ho YP. Use of polyethylenimine-modified magnetic nanoparticles for highly specific enrichment of phosphopeptides for mass spectrometric analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;399(8):2795–806.
Hargrove AE, Nieto S, Zhang T, Sessler JL, Anslyn EV. Artificial receptors for the recognition of phosphorylated molecules. Chem Rev. 2011;111(11):6603–782.
Fischnaller M, Bakry R, Vallant RM, Huber LA, Bonn GK. C60-fullerene bound silica for the preconcentration and the fractionation of multiphosphorylated peptides. Anal Chim Acta. 2013;761:92–101.
Dong M, Wu M, Wang F, Qin H, Han G, Dong J, et al. Coupling strong anion-exchange monolithic capillary with MALDI-TOF MS for sensitive detection of phosphopeptides in protein digest. Anal Chem. 2010;82(7):2907–15.
Huang D, Yang Q, Jin S, Deng Q, Zhou P. Determination of global DNA methylation level by capillary electrophoresis using octyl-modified quaternized cellulose as an electrolyte additive. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406(12):2771–7.
Shen F, Hu Y, Guan P, Ren X. Facile preparation of titanium phosphate-modified chitosan for selective capture of phosphopeptides. J Sep Sci. 2013;36(3):540–7.
Wang ZG, Zhang JL, Sun DH, Ni JZ. Novel Ti4+-chelated magnetic nanostructured affinity microspheres containing N-methylene phosphonic chitosan for highly selective enrichment and rapid separation of phosphopeptides. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(39):6886–92.
Shen F, Hu Y, Guan P, Ren X. Ti(4+)-phosphate functionalized cellulose for phosphopeptides enrichment and its application in rice phosphoproteome analysis. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012;902:108–15.
Duan J, He X, Zhang L. Magnetic cellulose-TiO2 nanocomposite microspheres for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem Commun (Camb). 2015;51(2):338–41.
Zhou J, Chang C, Zhang R, Zhang L. Hydrogels prepared from unsubstituted cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Macromol Biosci. 2007;7(6):804–9.
Huang D, Yang Q, Jin S, Deng Q, Zhou P. Self-assembly of cellulose nanoparticles as electrolyte additive for capillary electrophoresis separation. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1367:148–53.
Kjellstrom S, Jensen ON. Phosphoric acid as a matrix additive for MALDI MS analysis of phosphopeptides and phosphoproteins. Anal Chem. 2004;76(17):5109–17.
Feng S, Ye M, Zhou H, Jiang X, Jiang X, Zou H, et al. Immobilized zirconium ion affinity chromatography for specific enrichment of phosphopeptides in phosphoproteome analysis. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6(9):1656–65.
Wu T, Shi J, Zhang C, Zhang L, Du Y. Highly specific phosphopeptide enrichment by titanium(IV) cross-linked chitosan composite. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016;1008:234–9.
Yan Y, Zheng Z, Deng C, Zhang X, Yang P. Facile synthesis of Ti(4+)-immobilized Fe3O4@polydopamine core-shell microspheres for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem Commun (Camb). 2013;49(44):5055–7.
Li XS, Pan YN, Zhao Y, Yuan BF, Guo L, Feng YQ. Preparation of titanium-grafted magnetic mesoporous silica for the enrichment of endogenous serum phosphopeptides. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1315:61–9.
Xu LN, Li LP, Jin L, Bai Y, Liu HW. Guanidyl-functionalized graphene as a bifunctional adsorbent for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem Commun (Camb). 2014;50(75):10963–6.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China (no. 214CFB179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 539 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, L., Jin, S., Fan, M. et al. Preparation of quaternized cellulose/chitosan microspheres for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 3309–3317 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0273-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0273-2