Abstract
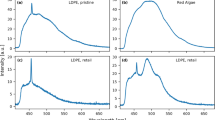
Classification of plastics is of great importance in the recycling industry as the littering of plastic wastes increases day by day as a result of its extensive use. In this paper, we demonstrate the efficacy of a combined laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)–Raman system for the rapid identification and classification of post-consumer plastics. The atomic information and molecular information of polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene were studied using plasma emission spectra and scattered signal obtained in the LIBS and Raman technique, respectively. The collected spectral features of the samples were analyzed using statistical tools (principal component analysis, Mahalanobis distance) to categorize the plastics. The analyses of the data clearly show that elemental information and molecular information obtained from these techniques are efficient for classification of plastics. In addition, the molecular information collected via Raman spectroscopy exhibits clearly distinct features for the transparent plastics (100% discrimination), whereas the LIBS technique shows better spectral feature differences for the colored samples. The study shows that the information obtained from these complementary techniques allows the complete classification of the plastic samples, irrespective of the color or additives. This work further throws some light on the fact that the potential limitations of any of these techniques for sample identification can be overcome by the complementarity of these two techniques.

ᅟ







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grégoire S, Boudinet M, Pelascini F, Surma F, Detalle V, Holl Y. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for polymer identification. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;400(10):3331–40.
Padmini Devi G, Chaitanya Kumari Bindu Madhavi MS. Adverse effects of plastics on environment and humanbeings. J Chem Pharm Sci. 2014;3:56–8.
Gondal MA, Siddiqui MN. Identification of different kinds of plastics using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for waste management. J Environ Sci Health Part A. 2007;42(13):1989–97.
Huth-Fehre T, Feldhoff R, Kantimm T, et al. NIR-remote sensing and artificial neural networks for rapid identification of post consumer plastics. J Mol Struct. 1995;348:143–6.
Andrady AL. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull. 2011;62(8):1596–605.
Shashoua Y. Conservation of plastics (materials science, degradation and preservation). Oxford: Butterworth–Heinemann; 2008.
Kupper L, Gulmine JV, Janissek PR, Heise HM. Attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy for micro-domain analysis of polyethylene samples after accelerated ageing within weathering chambers. Vib Spectrosc. 2004;34(1):63–72.
AnavoHandheldAnalyzer, Anavo™ Handheld Analyzer http://www.axsuncom/products/anavo-handheld-analyzerphp. 2012.
Van Den Broek W, Derks E, Van De Ven EW, Wienke D, Geladi P, Buydens LMC. Plastic identification by remote sensing spectroscopic NIR imaging using kernel partial least squares (KPLS). Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 1996;35(2):187–97.
Van Den Broek W, Wienke D, Melssen WJ, Buydens LMC. Plastic material identification with spectroscopic near infrared imaging and artificial neural networks. Anal Chim Acta. 1998;361(1):161–76.
Yu Y, Guo L, Hao Z, et al. Accuracy improvement on polymer identification using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with adjusting spectral weightings. Opt Express. 2014;22(4):3895–901.
Allen V, Kalivas JH, Rodriguez RG. Post-consumer plastic identification using Raman spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc. 1999;53(6):672–81.
Serrano J, Moros J, Laserna JJ. Molecular signatures in femtosecond laser-induced organic plasmas: comparison with nanosecond laser ablation. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2016;18:2398–408.
Guirado S, Fortes FJ, Laserna JJ. Multi-pulse excitation for underwater analysis of copper-based alloys using a novel remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system. Appl Spectrosc. 2016;70(4):618–26.
Gangopadhyay D, Singh SK, Sharma P, et al. Spectroscopic and structural study of the newly synthesized heteroligand complex of copper with creatinine and urea. Spectrochim Acta A. 2016;154:200–6.
Devangad P, Unnikrishnan VK, Nayak R, et al. Performance evaluation of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for quantitative analysis of rare earth elements in phosphate glasses. Opt Mater. 2016;52:32–7.
Sharma S, Misra A, Lucey P, Wiens R, Clegg S. Combined remote LIBS and Raman spectroscopy at 8.6 m of sulfur-containing minerals, and minerals coated with hematite or covered with basaltic dust. Spectrochim Acta A. 2007;68(4):1036–45.
Clegg S, Wiens R, Sharma S, Lucey P, Misra A, Barefield J. LIBS-Raman spectroscopy of minerals using remote surface modification techniques. In: 37th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 2006. p. 13–17.
Sattmann R, Monch I, Krause H, et al. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for polymer identification. Appl Spectrosc. 1998;52(3):456–61.
Fink H, Panne U, Niessner R. Process analysis of recycled thermoplasts from consumer electronics by laser-induced plasma spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2002;74(17):4334–42.
Unnikrishnan VK, Choudhari KS, Kulkarni SD, Nayak R, Kartha VB, Santhosh C. Analytical predictive capabilities of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) with principal component analysis (PCA) for plastic classification. RSC Adv. 2013;3(48):25872–80.
Jasik J, Heitz J, Pedarnig JD, Veis P. Vacuum ultraviolet laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis of polymers. Spectrochim Acta B. 2009;64(10):1128–34.
Anzano J, Casanova M-E, Bermúdez M-S, Lasheras R-J. Rapid characterization of plastics using laser-induced plasma spectroscopy (LIPS). Polym Test. 2006;25(5):623–7.
Hoehse M, Paul A, Gornushkin I, Panne U. Multivariate classification of pigments and inks using combined Raman spectroscopy and LIBS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;402(4):1443–50.
Bazalgette Courrèges-Lacoste G, Ahlers B, Pérez FR. Combined Raman spectrometer/laser-induced breakdown spectrometer for the next ESA mission to Mars. Spectrochim Acta A. 2007;68(4):1023–8.
Moros J, Lorenzo JA, Lucena P, Miguel Tobaria L, Laserna JJ. Simultaneous Raman spectroscopy–laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for instant standoff analysis of explosives using a mobile integrated sensor platform. Anal Chem. 2010;82(4):1389–400.
Matroodi F, Tavassoli SH. Simultaneous Raman and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy by a single setup. Appl Phys B. 2014;117(4):1081–9.
Choi S-J, Choi J-J, Yoh JJ. Advancing the experimental design for simultaneous acquisition of laser induced plasma and Raman signals using a single pulse. Spectrochim Acta B. 2016;123:1–5.
Burgio L, Melessanaki K, Doulgeridis M, Clark RJH, Anglos D. Pigment identification in paintings employing laser induced breakdown spectroscopy and Raman microscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2001;56(6):905–13.
Bruder R, Detalle V, Coupry C. An example of the complementarity of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and Raman microscopy for wall painting pigments analysis. J Raman Spectrosc. 2007;38(7):909–15.
Matroodi F, Tavassoli SH. Experimental investigation on concurrent laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy Raman spectroscopy. Appl Opt. 2015;54(3):400–7.
Rios LM, Jones PR, Moore C, Narayan UV. Quantitation of persistent organic pollutants adsorbed on plastic debris from the Northern Pacific Gyre's eastern garbage patch. J Environ Monit. 2010;12(12):2226–36.
Karemore G, Nielsen M, Mascarenhas KK, Choudhari KS, Patil A, Unnikrishnan VK, Prabhu V, Chowla A, Santhosh C. Classification of laser induced fluorescence spectra from normal and malignant tissues using learning vector quantization neural network in bladder cancer diagnosis. In: BioInformatics and BioEngineering, 2008. BIBE 2008. 8th IEEE International Conference on, 2008. IEEE, p. 1–6.
Patil A, Choudhari KS, Prabhu V, Unnikrishnan VK, Bhat S, Pai KM, Kartha VB, Santhosh C. Highly sensitive high performance liquid chromatography-laser induced fluorescence for proteomics applications. ISRN Spectrosc. 2012;2012.
Patil A, Prabhu V, Choudhari KS, et al. Evaluation of high-performance liquid chromatography laser-induced fluorescence for serum protein profiling for early diagnosis of oral cancer. J Biomed Opt. 2010;15(6):067007.
Unnikrishnan VK, Choudhari KS, D Kulkarni S, et al. Biomedical and environmental applications of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Pramana. 2014;82(2):397–401.
Devangad P, Unnikrishnan VK, Tamboli MM, et al. Quantification of Mn in glass matrices using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) combined with chemometric approaches. Anal Methods. 2016;8(39):7177–84.
Sato H, Shimoyama M, Kamiya T, et al. Raman spectra of high density, low density, and linear lowdensity polyethylene pellets and prediction of their physical properties by multivariate data analysis. J Appl Polym Sci. 2002;86(2):443–8.
Andreassen E. Infrared and Raman spectroscopy of polypropylene. In: Karger-Kocsis J, editor. Polypropylene: an A–Z reference. Kluwer: Dordrecht; 1999. p. 320–8.
Do Rego AMB, Vilar MR, da Silva JL. Mechanisms of vibrational and electronic excitations of polystyrene films in high resolution electron energy loss spectroscopy. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom. 1997;85(1):81–91.
Bower DI, Maddams WF. The vibrational spectroscopy of polymers. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1992.
Bahl SK, Cornell DD, Boerio FJ, McGraw GE. Interpretation of the vibrational spectra of poly (ethylene terephthalate). J Polym Sci Part C: Polym Lett. 1974;12(1):13–9.
Anzano J, Bonilla B, Montull-Ibor B, Casas-Gonzalez J. Plastic identification and comparison by multivariate techniques with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J Appl Polym Sci. 2011;121(5):2710–6.
Scheirs J, Long TE. Modern polyesters: chemistry and technology of polyesters and copolyesters. New York: Wiley; 2003.
Galan-Freyle NJ, Figueroa-Navedo AM, Pacheco-Londoño YC, Ortiz-Rivera W, Pacheco-Londoño LC, Hernández-Rivera SP. Chemometrics-enhanced fiber optic Raman detection, discrimination and quantification of chemical agents simulants concealed in commercial bottles. Anal Chem Res. 2014;2:15–22.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to BRNS, DAE for the financial support under the research grant with Ref. No. 34/14/04/2014-BRNS. Muhammed Shameem thanks Manipal University for providing research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
K. M. Muhammed Shameem and K. S. Choudhari contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 575 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shameem, K.M.M., Choudhari, K.S., Bankapur, A. et al. A hybrid LIBS–Raman system combined with chemometrics: an efficient tool for plastic identification and sorting. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 3299–3308 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0268-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0268-z