Abstract
AFM tips are modified with silver nanoparticles using an AC electrical field. The used technique works with sub-micron precision and also does not require chemical modification of the tip. Based on the electrical parameters applied in the process, particle density and particle position on the apex of the tip can be adjusted. The feasibility of the method is proven by subsequent tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) measurements using the fabricated tips as a measurement probe. Since this modification process itself does not require any lithographic processing, the technique can be easily adapted to modify AFM tips with a variety of nanostructures with pre-defined properties, while being parallelizable for a potential commercial application.

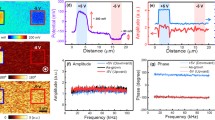
Silver nanoparticles attached to AFM tips using dielectrophoresis. Comparing nanoparticles attached using 1 kHz (left) to 1 MHz (right), SEM and optical (inset) images









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giessibl FJ. Advances in atomic force microscopy. Rev Mod Phys. 2003;75:949–83. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.75.949.
Colton RJ. Procedures in scanning probe microscopies. Chichester : Wiley; 1998.
Gan Y. Invited Review Article: a review of techniques for attaching micro- and nanoparticles to a probe’s tip for surface force and near-field optical measurements. Rev Sci Instrum. 2007;78:081101. doi:10.1063/1.2754076.
Pethig R. Dielectrophoresis: Status of the theory, technology, and applications. Biomicrofluidics. 2010;4:022811. doi:10.1063/1.3456626.
Gascoyne PRC, Vykoukal J. Particle separation by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2002;23:1973–83. doi:10.1002/1522-2683(200207)23:13<1973::AID-ELPS1973>3.0.CO;2-1.
Hermanson KD. Dielectrophoretic assembly of electrically functional microwires from nanoparticle suspensions. Science. 2001;294:1082–6. doi:10.1126/science.1063821.
Barsotti RJ, Vahey MD, Wartena R, Chiang Y-M, Voldman J, Stellacci F. Assembly of metal nanoparticles into nanogaps. Small. 2007;3:488–99. doi:10.1002/smll.200600334.
Gierhart BC, Howitt DG, Chen SJ, Smith RL, Collins SD. Frequency dependence of gold nanoparticle superassembly by dielectrophoresis. Langmuir. 2007;23:12450–6. doi:10.1021/la701472y.
Kretschmer R, Fritzsche W. Pearl chain formation of nanoparticles in microelectrode gaps by dielectrophoresis. Langmuir. 2004;20:11797–801. doi:10.1021/la0482352.
Raychaudhuri S, Dayeh SA, Wang D, Yu ET. Precise semiconductor nanowire placement through dielectrophoresis. Nano Lett. 2009;9:2260–6. doi:10.1021/nl900423g.
Leiterer C, Broenstrup G, Jahr N, Urban M, Arnold C, Christiansen S, et al. Applying contact to individual silicon nanowires using a dielectrophoresis (DEP)-based technique. J Nanoparticle Res. 2013;15:1–7. doi:10.1007/s11051-013-1628-z.
Liu Y, Chung J-H, Liu WK, Ruoff RS. Dielectrophoretic assembly of nanowires. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110:14098–106. doi:10.1021/jp061367e.
Hong SH, Kang MG, Cha H-Y, Son MH, Hwang JS, Lee HJ, et al. Fabrication of one-dimensional devices by a combination of AC dielectrophoresis and electrochemical deposition. Nanotechnology. 2008;19:105305. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/19/10/105305.
Suehiro J. Fabrication and characterization of nanomaterial-based sensors using dielectrophoresis. Biomicrofluidics. 2010;4:022804. doi:10.1063/1.3430535.
Wei Y, Wei W, Liu L, Fan S. Mounting multi-walled carbon nanotubes on probes by dielectrophoresis. Diam Relat Mater. 2008;17:1877–80. doi:10.1016/j.diamond.2008.04.001.
Lucci M, Regoliosi P, Reale A, Di Carlo A, Orlanducci S, Tamburri E, et al. Gas sensing using single wall carbon nanotubes ordered with dielectrophoresis. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2005;111–112:181–6. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2005.06.033.
Li J, Zhang Q, Yang D, Tian J. Fabrication of carbon nanotube field effect transistors by AC dielectrophoresis method. Carbon. 2004;42:2263–7. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2004.05.002.
Vijayaraghavan A, Blatt S, Weissenberger D, Oron-Carl M, Hennrich F, Gerthsen D, et al. Ultra-large-scale directed assembly of single-walled carbon nanotube devices. Nano Lett. 2007;7:1556–60. doi:10.1021/nl0703727.
Krupke R, Hennrich F, Weber HB, Kappes MM, Löhneysen HV. Simultaneous deposition of metallic bundles of single-walled carbon nanotubes using Ac-dielectrophoresis. Nano Lett. 2003;3:1019–23. doi:10.1021/nl0342343.
Washizu M, Suzuki S, Kurosawa O, Nishizaka T, Shinohara T. Molecular dielectrophoresis of biopolymers. IEEE Trans Ind Appl. 1994;30:835–43.
Wolff A, Leiterer C, Csaki A, Fritzsche W. Dielectrophoretic manipulation of DNA in microelectrode gaps for single-molecule constructs. Front Biosci. 2008;13:6834–40.
Wu M-D, Shih W-P, Tsai Y-C, Chen Y-J, Chang S-H, Chang P-Z. Rapid dielectrophoresis assembly of a single carbon nanocoil on AFM Tip apex. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol. 2012;11:328–35. doi:10.1109/TNANO.2011.2174253.
Lee HW, Kim SH, Kwak YK, Han CS. Nanoscale fabrication of a single multiwalled carbon nanotube attached atomic force microscope tip using an electric field. Rev Sci Instrum. 2005;76:046108. doi:10.1063/1.1891445.
Kim J-E, Park J-K, Han C-S. Use of dielectrophoresis in the fabrication of an atomic force microscope tip with a carbon nanotube: experimental investigation. Nanotechnology. 2006;17:2937–41. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/17/12/019.
Kim J-E, Han C-S. Use of dielectrophoresis in the fabrication of an atomic force microscope tip with a carbon nanotube: a numerical analysis. Nanotechnology. 2005;16:2245–50. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/046.
You Y, Purnawirman NA, Hu H, Kasim J, Yang H, Du C, et al. Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using single-crystalline Ag nanowire as tip. J Raman Spectrosc. 2010;41:1156–62. doi:10.1002/jrs.2559.
Jose J, Kress S, Barik A, Otto LM, Shaver J, Johnson TW, et al. Individual template-stripped conductive gold pyramids for tip-enhanced dielectrophoresis. ACS Photonics. 2014;1:464–70. doi:10.1021/ph500091h.
Leiterer C, Deckert-Gaudig T, Singh P, Wirth J, Deckert V, Fritzsche W. Dielectrophoretic positioning of single nanoparticles on atomic force microscope tips for tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: nanoanalysis. Electrophoresis. 2015;36:1142–8. doi:10.1002/elps.201400530.
Rasmussen A, Deckert V. Surface- and tip-enhanced Raman scattering of DNA components. J Raman Spectrosc. 2006;37:311–7. doi:10.1002/jrs.1480.
Deckert-Gaudig T, Deckert V. Ultraflat transparent gold nanoplates-ideal substrates for tip-enhanced raman scattering experiments. Small. 2009;5:432–6. doi:10.1002/smll.200801237.
van Schrojenstein Lantman EM, Deckert-Gaudig T, Mank AJG, Deckert V, Weckhuysen BM. Catalytic processes monitored at the nanoscale with tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nat Nanotechnol. 2012;7:583–6. doi:10.1038/nnano.2012.131.
Leiterer C, Berg S, Eskelinen A-P, Csaki A, Urban M, Törmä P, et al. Assembling gold nanoparticle chains using an AC electrical field: Electrical detection of organic thiols. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2013;176:368–73. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2012.09.088.
Böhme R, Mkandawire M, Krause-Buchholz U, Rösch P, Rödel G, Popp J, et al. Characterizing cytochrome c states—TERS studies of whole mitochondria. Chem Commun. 2011;47:11453. doi:10.1039/c1cc15246g.
Yang Z, Aizpurua J, Xu H. Electromagnetic field enhancement in TERS configurations. J Raman Spectrosc. 2009;40:1343–8. doi:10.1002/jrs.2429.
Deckert-Gaudig T, Richter M, Knebel D, Jähnke T, Jankowski T, Stock E, et al. A modified transmission tip-enhanced Raman scattering (TERS) setup provides access to opaque samples. Appl Spectrosc. 2014;68:916–9. doi:10.1366/13-07419.
Singh P, Deckert-Gaudig T, Schneidewind H, Kirsch K, van Schrojenstein Lantman EM, Weckhuysen BM, et al. Differences in single and aggregated nanoparticle plasmon spectroscopy. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015;17:2991–5. doi:10.1039/C4CP04850D.
Acknowledgments
We thank Franka Jahn for SEM and TEM imaging.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Funding sources
Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany (BMBF) and the German Reseach Foundation (DFG) for financial support of the project NAWION (FKZ: 16SV5386K, V4MNI014) and DEP4TERS (FKZ: FR 1348/19-1).
Additional information
Christian Leiterer and Erik Wünsche contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 283 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leiterer, C., Wünsche, E., Singh, P. et al. High precision attachment of silver nanoparticles on AFM tips by dielectrophoresis. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 3625–3631 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9447-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9447-6