Abstract
While metabolomics is increasingly used to investigate the food metabolome and identify new markers of food exposure, limited attention has been given to the validation of such markers. The main objectives of the present study were to (1) discover potential food exposure markers (PEMs) for a range of plant foods in a study setting with a mixed dietary background and (2) validate PEMs found in a previous meal study. Three-day weighed dietary records and 24-h urine samples were collected three times during a 6-month parallel intervention study from 107 subjects randomized to two distinct dietary patterns. An untargeted UPLC-qTOF-MS metabolomics analysis was performed on the urine samples, and all features detected underwent strict data analyses, including an iterative paired t test and sensitivity and specificity analyses for foods. A total of 22 unique PEMs were identified that covered 7 out of 40 investigated food groups (strawberry, cabbages, beetroot, walnut, citrus, green beans and chocolate). The PEMs reflected foods with a distinct composition rather than foods eaten more frequently or in larger amounts. We found that 23 % of the PEMs found in a previous meal study were also valid in the present intervention study. The study demonstrates that it is possible to discover and validate PEMs for several foods and food classes in an intervention study with a mixed dietary background, despite the large variability in such a dataset. Final validation of PEMs for intake of foods should be performed by quantitative analysis.

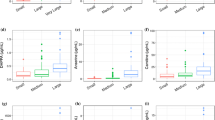
Examples of two urinary exposure markers for cabbage (left) and beetroot (right) found in the study from an untargeted LC‐MS metabolomics analysis of urine samples and self‐reported food intake data


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Favé G, Beckmann ME, Draper JH, Mathers JC (2009) Measurement of dietary exposure: a challenging problem which may be overcome thanks to metabolomics? Genes Nutr 4:135–141
Bingham SA (2002) Biomarkers in nutritional epidemiology. Public Health Nutr 5:821–827
Primrose S, Draper J, Elsom R, Kirkpatrick V, Mathers JC, Seal C, Beckmann M, Haldar S, Beattie JH, Lodge JK, Jenab M, Keun H, Scalbert A (2011) Metabolomics and human nutrition. Br J Nutr 105:1277–1283
Llorach R, Garcia-Aloy M, Tulipani S, Vazquez-Fresno R, Andres-Lacueva C (2012) Nutrimetabolomic strategies to develop new biomarkers of intake and health effects. J Agric Food Chem 60:8797–8808
Penn L, Boeing H, Boushey CJ, Dragsted LO, Kaput J, Scalbert A, Welch A, Mathers J (2010) Assessment of dietary intake: NuGO symposium report. Genes Nutr 5:205–213
Llorach R, Urpi-Sarda M, Jáuregui O, Monagas M, Andres-Lacueva C (2009) An LC-MS- based metabolomics approach for exploring urinary metabolome modifications after cocoa consumption. J Proteome Res 8:5060–5068
Tulipani S, Llorach R, Jáuregui O, López-Uriarte P, Garcia-Aloy M, Bullo M, Salas-Salvadó J, Andrés-Lacueva C (2011) Metabolomics unveils urinary changes in subjects with metabolic syndrome following 12-week nut consumption. J Proteome Res 10:5047–5058
Lodge JK (2010) Symposium 2: Modern approaches to nutritional research challenges: targeted and non-targeted approaches for metabolite profiling in nutritional research. Proc Nutr Soc 69:95–102
Spencer JPE, Abd El Mohsen MM, Minihane A, Mathers JC (2008) Biomarkers of the intake of dietary polyphenols: strengths, limitations and application in nutrition research. Br J Nutr 99:12–22
Andersen MS, Reinbach HC, Rinnan Å, Barri T, Mithril C, Dragsted LO (2013) Discovery of exposure markers in urine for Brassica-containing meals served with different protein sources by UPLC-qTOF-MS untargeted metabolomics. Metabolomics 9:984–997
Mithril C, Dragsted LO, Meyer C, Tetens I, Biltoft-Jensen A, Astrup A (2013) Dietary composition and nutrient content of the New Nordic Diet. Public Health Nutr 16:777–785
Poulsen SP, Due A, Jordy AB, Stark KD, Stender S, Holst C, Astrup A, Larsen TM (2013) Health effect of the New Nordic Diet in adults with increased waist circumference: a 6-mo randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.069393
Barri T, Holmer-Jensen J, Hermansen K, Dragsted LO (2012) Metabolic fingerprinting of high-fat plasma samples processed by centrifugation- and filtration-based protein precipitation delineates significant differences in metabolite information coverage. Anal Chim Acta 718:47–57
Pluskal T, Castillo S, Villar-Briones A, Orešič M (2010) MZmine 2: modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinforma 11:395–404
Bijlsma S, Bobeldijk I, Verheij ER, Ramaker R, Kochhar S, Macdonald IA, van Ommen B, Smilde AK (2006) Large-scale human metabolomics studies: a strategy for data (pre-) processing and validation. Anal Chem 78:567–574
Storey JD (2002) A direct approach to false discovery rates. J R Stat Soc B 64:479–498
Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Eisner R, Young N, Gautam B, Hau DD, Psychogios N, Dong E, Bouatra S, Mandal R, Sinelnikov I, Xia J, Jia L, Cruz JA, Lim E, Sobsey CA, Shrivastava S, Huang P, Liu P, Fang L, Peng J, Fradette R, Cheng D, Tzur D, Clements M, Lewis A, De Souza A, Zuniga A, Dawe M, Xiong Y, Clive D, Greiner R, Nazyrova A, Shaykhutdinov R, Li L, Vogel HJ, Forsythe I (2009) HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D603–D610
Smith CA, O'Maille G, Want EJ, Qin C, Trauger SA, Brandon TR, Custodio DE, Abagyan R, Siuzdak G (2005) METLIN: a metabolite mass spectral database. Ther Drug Monit 27:747–751
Gerlich M, Neumann S (2013) MetFusion: integration of compound identification strategies. J Mass Spectrom 48:291–298
Neveu V, Perez-Jiménez J, Vos F, Crespy V, du Chaffaut L, Mennen L, Knox C, Eisner R, Cruz J, Wishart D, Scalbert A (2010) Phenol-Explorer: an online comprehensive database on polyphenol contents in foods. Database (Oxford). doi:10.1093/database/bap024
Afendi FM, Okada T, Yamazaki M, Hirai-Morita A, Nakamura Y, Nakamura K, Ikeda S, Takahashi H, Altaf-Ul-Amin M, Darusman LK, Saito K, Kanaya S (2012) KNApSAcK family databases: integrated metabolite–plant species databases for multifaceted plant research. Plant Cell Physiol 53:e1–e12
Sumner L, Amberg A, Barrett D, Beale M, Beger R, Daykin C, Fan T, Fiehn O, Goodacre R, Griffin J, Hankemeier T, Hardy N, Harnly J, Higashi R, Kopka J, Lane A, Lindon J, Marriott P, Nicholls A, Reily M, Thaden J, Viant M (2007) Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 3:211–221
Rago D, Mette K, Gürdeniz G, Marini F, Poulsen M, Dragsted LO (2013) A LC-MS metabolomics approach to investigate the effect of raw apple intake in the rat plasma metabolome. Metabolomics. doi:10.1007/s11306-013-0534-9
Nelson AC, Huang W, Moody DE (2001) Variables in human liver microsome preparation: impact on the kinetics of l-alpha-acetylmethadol (LAAM) n-demethylation and dextromethorphan O-demethylation. Drug Metab Dispos 29:319–325
Wein M, Lavid N, Lunkenbein S, Lewinsohn E, Schwab W, Kaldenhoff R (2002) Isolation, cloning and expression of a multifunctional O-methyltransferase capable of forming 2,5-dimethyl-4-methoxy-3(2H)-furanone, one of the key aroma compounds in strawberry fruits. Plant J 31:755–765
Gonthier M, Cheynier V, Donovan JL, Manach C, Morand C, Mila I, Lapierre C, Rémésy C, Scalbert A (2003) Microbial aromatic acid metabolites formed in the gut account for a major fraction of the polyphenols excreted in urine of rats fed red wine polyphenols. J Nutr 133:461–467
Bianchi F, Careri M, Musci M, Mangia A (2007) Fish and food safety: determination of formaldehyde in 12 fish species by SPME extraction and GC–MS analysis. Food Chem 100:1049–1053
Bingham SA, Cassidy A, Cole TJ, Welch A, Runswick SA, Black AE, Thurnham D, Bates C, Khaw KT, Key TJA (1995) Validation of weighed records and other methods of dietary assessment using the 24 h urine nitrogen technique and other biological markers. Br J Nutr 73:531–550
González-Molina E, Domínguez-Perles R, Moreno DA, García-Viguera C (2010) Natural bioactive compounds of Citrus limon for food and health. J Pharm Biomed Anal 51:327–345
Vermeulen M, Van Den Berg R, Freidig AP, Van Bladeren PJ, Vaes WHJ (2006) Association between consumption of cruciferous vegetables and condiments and excretion in urine of isothiocyanate mercapturic acids. J Agric Food Chem 54:5350–5358
Lloyd AJ, Beckmann M, Haldar S, Seal C, Brandt K, Draper J (2013) Data-driven strategy for the discovery of potential urinary biomarkers of habitual dietary exposure. Am J Clin Nutr 97:377–389
González-Barrio R, Edwards CA, Crozier A (2011) Colonic catabolism of ellagitannins, ellagic acid, and raspberry anthocyanins: in vivo and in vitro studies. Drug Metab Dispos 39:1680–1688
Heinzmann SS, Brown IJ, Chan Q, Bictash M, Dumas M, Kochhar S, Stamler J, Holmes E, Elliott P, Nicholson JK (2010) Metabolic profiling strategy for discovery of nutritional biomarkers: proline betaine as a marker of citrus consumption. Am J Clin Nutr 92:436–443
Favé G, Beckmann M, Lloyd A, Zhou S, Harold G, Lin W, Tailliart K, Xie L, Draper J, Mathers J (2011) Development and validation of a standardized protocol to monitor human dietary exposure by metabolite fingerprinting of urine samples. Metabolomics 7:469–484
Lloyd AJ, Beckmann M, Favé G, Mathers JC, Draper J (2011) Proline betaine and its biotransformation products in fasting urine samples are potential biomarkers of habitual citrus fruit consumption. Br J Nutr 106:812–824
Pujos-Guillot E, Hubert J, Martin J, Lyan B, Quintana M, Claude S, Chabanas B, Rothwell JA, Bennetau-Pelissero C, Scalbert A, Comte B, Hercberg S, Morand C, Galan P, Manach C (2013) Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics for the discovery of biomarkers of fruit and vegetable intake: citrus fruit as a case study. J Proteome Res 12:1645–1659
Feldman JM, Lee EM (1985) Serotonin content of foods: effect on urinary excretion of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. Am J Clin Nutr 42:639–643
Shively CA, Tarka SM Jr (1984) Methylxanthine composition and consumption patterns of cocoa and chocolate products. Prog Clin Biol Res 158:149–178
Rodopoulos N, Höjvall L, Norman A (1996) Elimination of theobromine metabolites in healthy adults. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 56:373–383
Cornish HH, Christman AA (1957) A study of the metabolism of theobromine, theophylline, and caffeine in man. J Biol Chem 228:315–323
Farag MA, Motaal AA (2010) Sulforaphane composition, cytotoxic and antioxidant activity of crucifer vegetables. J Adv Res 1:65–70
Edmands WMB, Beckonert OP, Stella C, Campbell A, Lake BG, Lindon JC, Holmes E, Gooderham NJ (2011) Identification of human urinary biomarkers of cruciferous vegetable consumption by metabonomic profiling. J Proteome Res 10:4513–4521
Rechner AR, Smith MA, Kuhnle G, Gibson GR, Debnam ES, Srai SKS, Moore KP, Rice-Evans CA (2004) Colonic metabolism of dietary polyphenols: influence of structure on microbial fermentation products. Free Radic Biol Med 36:212–225
Podsędek A, Sosnowska D, Redzynia M, Anders B (2006) Antioxidant capacity and content of Brassica oleracea dietary antioxidants. Int J Food Sci Technol 41:49–58
Frank T, Stintzing FC, Carle R, Bitsch I, Quaas D, Straẞ G, Bitsch R, Netzel M (2005) Urinary pharmacokinetics of betalains following consumption of red beet juice in healthy humans. Pharmacol Res 52:290–297
Walsh MC, Brennan L, Malthouse JPG, Roche HM, Gibney MJ (2006) Effect of acute dietary standardization on the urinary, plasma, and salivary metabolomic profiles of healthy humans. Am J Clin Nutr 84:531–539
Rasmussen LG, Savorani F, Larsen TM, Dragsted LO, Astrup A, Engelsen SB (2011) Standardization of factors that influence human urine metabolomics. Metabolomics 2011(7):71–83
Koulman A, Volmer DA (2008) Perspectives for metabolomics in human nutrition: an overview. Nutr Bull 33:324–330
Acknowledgments
The intervention study was conducted as part of the OPUS project. OPUS is an acronym of the Danish title of the project 'Optimal well-being, development and health for Danish children through a healthy New Nordic Diet' and is supported by a grant from the Nordea Foundation, Denmark. The authors would like thank Majbritt Hybholt for providing the food intake data and Daniela Rago, Ümmühan Celik and Bernard Lyan for their contribution to the laboratory work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 204 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andersen, MB.S., Kristensen, M., Manach, C. et al. Discovery and validation of urinary exposure markers for different plant foods by untargeted metabolomics. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 1829–1844 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7498-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7498-5