Abstract
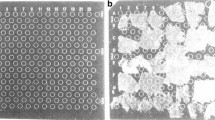
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI/IMS) is a useful tool for measuring drug distributions. To obtain reproducible analytical results with MALDI/IMS, it is essential to apply a homogeneous matrix coating onto sample surfaces. A simple and inexpensive automatic matrix spraying system (AMSS) with good reproducibility was developed in this study. In addition, drug distributions in organs were measured by MALDI/IMS using the AMSS for forensic toxicology applications. The AMSS was constructed from simple components, including an air brush, a turntable, and a microscope. Organ slices placed onto conductive sheets were attached to the turntable. The trigger of the air brush was held with a clamp to ensure that it sprayed continuously onto a defined area of the table. Periodic spraying of the matrix solution and evaporation of solvent were performed by rotating the turntable. The droplets and crystals on the sample surfaces were observed under a microscope attached to the turntable. The droplet size, rotation rate of the turntable, and the formulation of the matrix solution were optimized. The homogeneity of the matrix coating was evaluated using the coefficients of variation (CV) obtained by quantifying the color density of the sheet surface. The AMSS enabled more homogeneous matrix coating (intersheet CV = 5.4 %) than manual spraying (intersheet CV = 16.7 %) when 10 mL of 0.5 % aqueous trifluoroacetic acid/acetonitrile (1:3, v/v) containing 10 mg/mL α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid were sprayed as droplets less than 50 μm in diameter onto a turntable rotating at 30 rpm. The distributions of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and its main metabolites in the brain, liver, and kidney of a mouse that died from an MDMA overdose (58 mg/kg i.p.) were visualized by MALDI/IMS using the AMSS. The ion intensities of MDMA obtained from the same regions on three sequential kidney slices showed acceptable variations (CV = 2.9–8.8 % for five different regions), implying repeatable measurements with MALDI/IMS using the AMSS. It was revealed that MDMA was particularly concentrated around the brain stem and the major calix of the kidney. The AMSS would be suitable for preparing samples for measuring the distributions of drugs in organs at toxic dose levels in forensic toxicological applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalant H (2001) CMAJ 165:917–928
Lyles J, Cadet JL (2003) Brain Res Brain Res Rev 42:155–168
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (2010) World drug report 2010. United Nations, New York
National Police Agency of Japan (2010) White paper on police 2009. National Police Agency of Japan, Tokyo
Fineschi V, Masti A (1996) Int J Legal Med 108:272–275
Skopp G (2010) Forensic Sci Med Pathol 6:314–325
Teotia AK, Pal R (2009) J Forensic Med Toxicol 26:49–53
Zhu BL, Ishikawa T, Michiue T, Li DR, Zhao D, Quan L, Oritani S, Bessho Y, Maeda H (2007) Forensic Sci Int 173:122–129
Takayasu T, Ishida Y, Kimura A, Kawaguchi M, Kondo T (2008) Forensic Toxicol 26:80–84
Klys M, Rojek S, Woźniak K, Rzepecka-Woźniak E (2007) Leg Med 9:185–191
Miki A, Katagi M, Shima N, Kamata H, Tatsuno M, Nakanishi T, Tsuchihashi H, Takubo T, Suzuki K (2011) Forensic Toxicol 29:111–116
Khatib-Shahidi S, Andersson M, Herman JL, Gillespie TA, Caprioli RM (2006) Anal Chem 78:6448–6456
Trim PJ, Henson CM, Avery JL, McEwen A, Snel MF, Claude E, Marshall PS, West A, Princivalle AP, Clench MR (2008) Anal Chem 80:8628–8634
Hopfgartner G, Varesio E, Stoeckli M (2009) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:733–736
Kuwayama K, Tsujikawa K, Miyaguchi H, Kanamori T, Iwata YT, Inoue H (2011) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 25:2397–2406
Holcomb A, Owens KG (2010) Anal Chim Acta 658:49–55
Chen Y, Allegood J, Liu Y, Wang E, Cachón-González B, Cox TM, Merrill AH Jr, Sullards MC (2008) Anal Chem 80:2780–2788
Erb WJ, Owens KG (2008) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:1168–1174
Baluya DL, Garrett TJ, Yost RA (2007) Anal Chem 79:6862–6867
Trimpin S, Herath TN, Inutan ED, Wager-Miller J, Kowalski P, Claude E, Michael Walker J, Mackie K (2010) Anal Chem 82:359–367
Bouschen W, Schulz O, Eikely D, Spengler B (2010) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24:355–364
Aerni HR, Cornett DS, Caprioli RM (2006) Anal Chem 78:827–834
Schuerenberg M, Luebbert C, Deininger SO, Ketterlinus R, Suckau D (2007) Nat Methods 4:iii–iv
Tanaka K, Inoue T, Ohki H (1988) Rep Natl Res Inst Police Sci 41:114–119
Agency EM (2011) Guideline on bioanalytical method validation. European Medicines Agency, London
US FDA (2001) Guidance for industry bioanalytical method validation. US FDA, Rockville
Milroy CM (2011) Forensic Sci Med Pathol 7:248–252
García-Repetto R, Moreno E, Soriano T, Jurado C, Giménez MP, Menéndez M (2003) Forensic Sci Int 135:110–114
Scheidweiler KB, Ladenheim B, Barnes AJ, Cadet JL, Huestis MA (2011) J Anal Toxicol 35:470–480
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) (21790616) from The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuwayama, K., Tsujikawa, K., Miyaguchi, H. et al. Distribution measurements of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine and its metabolites in organs by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry using an automatic matrix spraying system with an air brush and a turntable. Anal Bioanal Chem 404, 1823–1830 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6279-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6279-x