Abstract
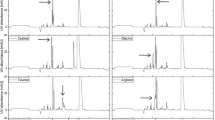
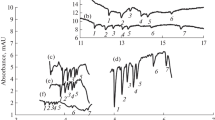
The methodology for separations of saccharides in standard electrophoretic systems has been transferred to the short-capillary electrophoresis format. The laboratory-designed apparatus used employs a quartz capillary with an internal diameter of 10 μm, a total length of 10 cm, and an effective length of 4 cm, in combination with contactless conductivity detection. It has been applied to separations of neutral mono- and disaccharides. The saccharides are separated in the anionic form, in solutions of alkali hydroxides, namely, KOH, NaOH, and LiOH. The separation of a model mixture of five saccharides (sucrose, lactose, glucose, fructose, and ribose) takes less than 1 min, the LOD equaling 15, 35, 19, 17, and 24 mg L−1 and the LOQ equaling 52, 117, 63, 53, and 79 mg L−1 for sucrose, lactose, glucose, fructose, and ribose, respectively. The technique developed has been used to determine sucrose, glucose and fructose in high-energy drinks. The separation is finished within less than 50 s; the saccharide contents determined are identical with the declared values within the reliability interval in most cases, the RSD value being mostly less than 2 %. In general, the separation system developed is very convenient for rapid analyses of large sets of similar samples, e.g., in product quality control or environmental monitoring.

Rapid determination of saccharides by CZE




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Montero CM, Dodero MCR, Sanchez DAG, Barroso CG (2004) Chromatographia 59:15–30
Liu H, Zhang S, Yu A, Qu L, Zhao Y, Huang H, Li J (2004) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14:2339–2344
Sesta G (2006) Apidologie 37:84–90
Heleno SA, Barros L, Sousa MJ, Martins A, Ferreira ICFR (2009) Microchem J 93:195–199
Wolfender JL (2009) Planta Med 75:719–734
El Rassi Z (1994) Carbohydrate analysis: high performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Cataldi TRI, Margiotta G, Zambonin GC (1998) Food Chem 62:109–115
DIONEX (2007) http://www.dionex.com/en-us/webdocs/61831-Bro_Carbohydrates_Food_Beverage_29Aug2007_LPN1971.pdf. Accessed 8 April 2012
Soga T, Serwe M (2000) Food Chem 69:339–344
Honda S (1996) J Chromatogr A 720:337–351
Žídková J, Chmelík J (2000) Chem List 94:1093–1103
Tůma P, Málková K, Samcová E, Štulík K (2011) Anal Chim Acta 698:1–5
Carvalho AZ, da Silva JAF, do Lago CL (2003) Electrophoresis 24:2138–2143
Opekar F, Coufal P, Štulík K (2009) Chem Rev 109:4487–4499
Lauer HH, Rozing GP (2010) High performance capillary electrophoresis. Agilent Technologies, Germany
Tůma P, Opekar F, Jelínek I (2000) J Chromatogr A 883:223–230
Tůma P, Opekar F, Štulík K (2002) Electrophoresis 23:3718–3724
da Silva JAF, do Lago CL (1998) Anal Chem 70:4339–4343
Novotný M, Opekar F, Jelínek I (2005) Chem List 99:132–136
Rainelli A, Hauser PC (2005) Anal Bioanal Chem 382:789–794
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports, Czech Republic, Research Project No. MSM0021620857, and the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic, grant No. P206/10/1231, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vochyánová, B., Opekar, F., Tůma, P. et al. Rapid determinations of saccharides in high-energy drinks by short-capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 404, 1549–1554 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6242-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6242-x