Abstract
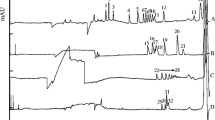
Versions of the electrophoretic determination of neutral carbohydrates by a method of indirect detection using acridone acetic and folic acids as absorbing additives (AA) are proposed. The effects of the nature and concentration of AA, alkali, and various modifiers (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, CTAB) and ionic liquids (1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride and 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride) on the electrophoretic parameters of the migration of analytes are studied. The lowest limits of detection for carbohydrates are achieved in a background electrolyte containing 2.5 mM acridone acetic acid, 75 mM KOH, 0.5 mM CTAB, and 5 vol % MeOH, and amount to 4−10 μg/mL with an efficiency of up to 350 thousand t.p. Under the conditions found, samples of buckwheat honey and human blood plasma are analyzed. It is found that in analyzing food products, it is preferable to use folic acid as a AA, because it provides the best selectivity for the separation of carbohydrates: for the sucralose−sucrose pair, the resolution factor is 7.6.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Chen, Y.F., Li, M.Y., Wang, S.R., Peng, H.J., Reid, S., Ni, N.T., Fang, H., and Xu, W.F., Carbohydrate biomarkers for future disease detection and treatment, Sci. China Chem., 2010, vol. 53, no. 1, p. 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-0021-3
Kiely, L.J. and Hickey, R.M., in Glycosylation, Davey, G.P., Ed., New York: Humana, 2022, p. 67. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1685-7_4
Nagy, G., Peng, T., and Pohl, N.L.B., Anal. Methods, 2017, vol. 9, no. 24, p. 3579. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ay01094j
Kartsova, L.A., Maliushevska, A.V., and Kolobova, E.A., J. Anal. Chem., 2023, vol. 78, no. 2, p. 156. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934823020041
Rovio, S., Yli-Kauhaluoma, J., and Siren, H., Electrophoresis, 2007, vol. 28, no. 17, p. 3129. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200600783
Alekseeva, A.V., Kartsova, L.A., and Kazachishcheva, N.V., J. Anal. Chem., 2010, vol. 65, no. 2, p. 202. )https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934810020176
Schwaiger, H., Oefner, P.J., Huber, C., Grill, E., and Bonn, G.K., Electrophoresis, 1994, vol. 15, no. 7, p. 941. https://doi.org/10.1002/ELPS.11501501138
Taga, A., Suzuki, S., and Honda, S., J. Chromatogr. A, 2001, vol. 911, no. 2, p. 259. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(01)00516-7
Soga, T. and Ross, G.A., J. Chromatogr. A, 1999, vol. 837, nos. 1–2, p. 231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(99)00092-8
Vaher, M., Koel, M., Kazarjan, J., and Kaljurand, M., Electrophoresis, 2011, vol. 32, no. 9, p. 1068. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201000575
Jiang, T.F., Chong, L., Yue, M.E., Wang, Y.H., and Lv, Z.H., Food Anal. Methods, 2015, vol. 8, no. 10, p. 2588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0157-z
Jager, A.V., Tonin, F.G., and Tavares, M.F.M., J. Sep. Sci., 2007, vol. 30, p. 586. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200600370
Dominguez, M.A., Jacksen, J., Emmer, A., and Centurion, M.E., Microchem. J., 2016, vol. 129, p. 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.05.017
Warren, C.R. and Adams, M.A., J. Exp. Bot., 2000, vol. 51, no. 347, p. 1147. https://doi.org/10.1093/JEXBOT/51.347.1147
Xu, X., Kok, W.T., and Poppe, H., J. Chromatogr. A, 1995, vol. 716, nos. 1–2, p. 231. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9673(95)00552-X
Lu, B. and Westerlund, D., Electrophoresis, 1996, vol. 17, no. 2, p. 325. https://doi.org/10.1002/ELPS.1150170207
Gürel, A., Hızal, J., Öztekin, N., and Erim, F.B., Chromatographia, 2006, vol. 64, nos 5-6, p. 321. https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-006-0032-6
Mikkers, F.E.P., Everaerts, F.M., and Verheggen, T.P.E.M., J. Chromatogr. A, 1979, vol. 169, p. 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9673(75)85028-X
Shamsi, Sh.A., in Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry: Applications, Theory and Instrumentation, Meyers, R.A., Ed., Hoboken: Wiley, 2006, p. 1. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470027318.a5404
Li, W., Zhang, M., Zhang, J., and Han, Y., Front. Chem. China, 2006, vol. 1, p. 438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11458-006-0069-y
Kolobova, E., Kartsova, L., Kravchenko, A., and Bessonova, E., Talanta, 2018, vol. 188, p. 183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.05.057
Blesic, M., Marques, M.H., Plechkova, N.V., Seddon, K.R., Rebelo, L.P.N., and Lopes, A., Green Chem., 2007, vol. 9, p. 481. https://doi.org/10.1039/b615406a
Kaper, H. and Smarsly, B., Z. Phys. Chem., 2006, vol. 220, p. 1455. https://doi.org/10.1524/zpch.2006.220.10.1455
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to the Science Park of St. Petersburg State University, the Resource Center “Methods for analyzing the composition of matter.”
Funding
The work was carried out with financial support from the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 19-13-00370.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants who gave blood plasma.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by V. Kudrinskaya
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolobova, E.A., Maliushevska, A.V. & Kartsova, L.A. Electrophoretic Determination of Carbohydrates in Samples of Natural Origin by an Indirect Detection Method. J Anal Chem 79, 224–232 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934824020102
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934824020102