Abstract
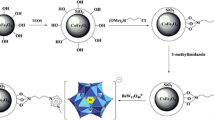
A magnetic material based on N-methylimidazolium ionic liquid and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles incorporated in a silica matrix has been used to extract and preconcentrate sulfonylurea herbicides, such as thifensulfuron methyl (TSM), metsulfuron methyl (MSM), triasulfuron (TS), tribenuron methyl (TBM) and primisulfuron methyl (PSM) from polluted water samples, prior to their analysis by capillary liquid chromatography with a diode array detector (DAD). Under the optimum conditions, this method allows the determination of TSM, MSM, TS, TBM and PSM in a linear range between 5 and 100 ng mL−1, with relative standard deviation values lower than 5.3 % (n = 10), in all cases. Detection limits ranging between 1.13 and 2.95 ng mL−1 were achieved. The usefulness of the proposed method was demonstrated by the analysis of river water samples, obtaining recoveries higher than 91 %.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quesada-Molina C, del Olmo-Iruela M, García-Campaña AM (2010) Trace determination of sulfonylurea herbicides in water and grape samples by capillary zone electrophoresis using large volume sample stacking. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:2593–2601
Fletcher JS, Pfleeger TG, Ratsch HC (1993) Potential environmental risks associated with the new sulfonylurea herbicides. Environ Sci Technol 27:2250–2252
Niu H, Shi Y, Cai Y, Wei F, Jiang G (2009) Solid-phase extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides from water samples with single-walled carbon nanotubes disk. Microchim Acta 164:431–438
Zhou Q, Liu J, Cai Y, Liu G, Jiang G (2003) Micro-porous membrane liquid-liquid extraction as an enrichment step prior to nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis determination of sulfonylurea herbicides. Microchem J 74:157–163
Qi Y, Li S, Zhan C, Peng T (2004) Simultaneous determination of sulfonylurea herbicides residues in soybeans by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Fenxi Huaxue 32:1436–1440
Sui K, Wei F, Chu X, Zhao S, Wang Y (2006) Simultaneous determination of twelve sulfonyl urea herbicide residues in rice by high performance liquid chromatography with solid-phase extraction. Sepu 24:152–156
Losito I, Amorisco A, Carbonara T, Lofiego S, Palmisano F (2006) Simultaneous determination of phenyl- and sulfonyl-urea herbicides in river water at sub-parts-per-billion level by on-line preconcentration and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 575:89–96
Bossi R, Vejrup K, Jacobsen CS (1999) Determination of sulfonylurea degradation products in soil by liquid chromatography–ultraviolet detection followed by confirmatory liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 855:575–582
Wu Q, Wang C, Liu Z, Wu C, Zeng X, Wen J, Wang Z (2009) Dispersive solid-phase extraction followed by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of some sulfonylurea herbicides in soil by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1216:5504–5510
Fang G, Chen J, Wang J, He J, Wang S (2010) N-Methylimidazolium ionic liquid-functionalized silica as a sorbent for selective solid-phase extraction of 12 sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental water and soil samples. J Chromatogr A 1217:1567–1574
Ghildyal R, Kariofillis M (1995) Determination of triasulfuron in soil: affinity chromatography as a soil extract cleanup procedure. J Biochem Biophys Methods 489(30):207–215
Degelmann P, Egger S, Jürling H, Müller J, Niessner R, Knopp D (2006) Determination of sulfonylurea herbicides in water and food samples using sol–gel glass-based immunoaffinity extraction and liquid chromatography-ultraviolet/diode array detection or liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 54:2003–2011
Degelmann P, Wenger J, Niessner R, Knopp D (2004) Development of a class-specific ELISA for sulfonylurea herbicides (sulfuron screen). Environ Sci Technol 38:6795–6802
Bastide J, Cambon JP, Breton F, Piletsky SA, Rouillon R (2005) The use of molecularly imprinted polymers for extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides. Anal Chim Acta 542:97–103
Tang K, Chen S, Gu X, Wang H, Dai J, Tang J (2008) Preparation of molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction using bensulfuron-methyl imprinted polymer and clean-up for the sulfonylurea-herbicides in soybean. Anal Chim Acta 614:112–118
Liu J, Chao J, Jiang G, Cai Y, Liu J (2003) T race analysis of sulfonylurea herbicides in water by on-line continuous flow liquid membrane extraction–C18 precolumn liquid chromatography with ultraviolet absorbance detection. J Chromatogr A 995:21–28
Chao J, Liu J, Wen M, Liu J, Cai Y, Jiang G (2002) Determination of sulfonylurea herbicides by continuous-flow liquid membrane extraction on-line coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 955:183–189
Font N, Hernández F, Hogendoorn EA, Baumann RA, van Zoonen P (1998) Microwave-assisted solvent extraction and reversed-phase liquid chromatography–UV detection for screening soils for sulfonylurea herbicides. J Chromatogr A 798:179–186
Liu JC, Anand M, Roberts CB (2006) Synthesis and extraction of ß-D-glucose-stabilized Au nanoparticles processed into low-defect, wide-area thin films and ordered arrays using CO2-expanded liquids. Langmuir 22:3964–3971
Vanderpuije BNY, Han G, Rotello VM, Vachet RW (2006) Mixed monolayer-protected gold nanoclusters as selective peptide extraction agents for MALDI-MS analysis. Anal Chem 78:5491–5496
Saiyed ZM, Parasramka M, Telang SD, Ramchand CN (2007) Extraction of DNA from agarose gel using magnetic nanoparticles (magnetite or Fe3O4). Anal Biochem 363:288–290
He XX, Huo HL, Wang KM, Tan WH, Gong P, Ge J (2007) Plasmid DNA isolation using amino-silica coated magnetic nanoparticles (ASMNPs). Talanta 73:764–769
Lin PC, Tseng MC, Su AK, Chen YJ, Lin CC (2007) Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for small-molecule isolation, identification, and quantification. Anal Chem 79:3401–3408
Chang SY, Zheng NY, Chen CS, Chen CD, Chen YY, Wang CRC (2007) Analysis of peptides and proteins affinity-bound to iron oxide nanoparticles by MALDI MS. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 18:910–918
Song YR, Zhao SL, Tchounwou P, Liu YM (2007) A nanoparticle-based solid-phase extraction method for liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometric analysis. J Chromatogr A 1166:79–84
Moeller K, Kobler J, Bein T (2007) Colloidal suspensions of nanometer-sized mesoporous silica. Adv Funct Mater 17:605–612
Klabunde KJ (2001) Nanoscale material in chemistry. Wiley Interscience, New York
Lin YS, Tsai PJ, Weng MF, Chen YC (2005) Affinity capture using vancomycin-bound magnetic nanoparticles for the MALDI-MS analysis of bacteria. Anal Chem 77:1753–1760
Smith JE, Medley CD, Tang Z, Shangguan D, Lofton C, Tan W (2007) Aptamer-conjugated nanoparticles for the collection and detection of multiple cancer cells. Anal Chem 79:3075–3082
Li Y, Qi DW, Deng CH, Yang PY, Zhang XM (2008) Cerium ion-chelated magnetic silica microspheres for enrichment and direct determination of phosphopeptides by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 7:1767–1777
Li Y, Liu YC, Tang J, Lin HQ, Yao N, Shen XZ, Deng CH, Yang PY, Zhang XM (2007) Fe3O4@Al2O3 magnetic core–shell microspheres for rapid and highly specific capture of phosphopeptides with mass spectrometry analysis. J Chromatogr A 1172:57–71
Li Y, Leng TH, Lin HQ, Deng CH, Xu XQ, Yao N, Yang PY, Zhang XM (2007) Preparation of Fe3O4@ZrO2 core-shell microspheres as affinity probes for selective enrichment and direct determination of phosphopeptides using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 6:4498–4510
Whiteaker JT, Zhao L, Zhang HY, Feng LC, Piening BD, Anderson L, Paulovich AG (2007) Antibody-based enrichment of peptides on magnetic beads for mass-spectrometry-based quantification of serum biomarkers. Anal Biochem 362:44–54
Aguilar-Arteaga K, Rodriguez JA, Barrado E (2010) Magnetic solids in analytical chemistry. Anal Chim Acta 674:157–165
Marsh KN, Boxall JA, Lichtenthaler R (2004) Room temperature ionic liquids and their mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib 219:93–98
Jonathan GH, Heather DW, Richard PS, Ann EV, Robin DR (1998) Room temperature ionic liquids as novel media for ‘clean’ liquid–liquid Extraction. Chem Commun 16:1765–1766
Fujita K, Mac-Farlane DR, Forsyth M, Yoshizawa-Fujita M, Murata K, Nakamura N, Ohno H (2007) Solubility and stability of cytochrome c in hydrated ionic liquids: effect of oxo acid residues and kosmotropicity. Biomacromolecules 8:2080–2086
Zheng ZQ, Wang J, Wu TH, Zhou XP (2007) Alkylation of ammonium salts catalyzed by imidazolium-based ionic liquid catalysts. Adv Synth Catal 349:1095–1101
Fang G, Chen J, Wang J, He J, Wang S (2010) N-Methylimidazolium ionic liquid-functionalized silica as a sorbent for selective solid-phase extraction of 12 sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental water and soil samples. J Chromatogr A 1217:1567–1574
Min LI, Patrisha JP, Charles UPLIT (2008) Selective solid-phase extraction of α-tocopherol by functionalized ionic liquid-modified mesoporous SBA-15 adsorbent. Anal Sci 24:1245–1250
Liang P, Peng L (2010) Ionic liquid-modified silica as sorbent for preconcentration of cadmium prior to its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry in water samples. Talanta 81:673–677
Bi W, Zhou J, Row KH (2011) Solid phase extraction of lactic acid from fermentation broth by anion-exchangeable silica confined ionic liquids. Talanta 83:974–979
Yang C, Wang G, Lu Z, Sun J, Zhuang J, Yang W (2005) Effect of ultrasonic treatment on dispersibility of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and synthesis of multi-core Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 15:4252–4257
Tartaj P, Serna CJ (2003) Synthesis of Monodisperse Superparamagnetic Fe/Silica Nanospherical Composites. J Am Chem Soc 125:15754–15755
Carabias-Martínez R, Rodríguez-Gonzalo E, Herrero-Hernández E, Hernández-Méndez J (2004) Simultaneous determination of phenyl- and sulfonylurea herbicides in water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with UV diode array or mass spectrometric detection. Anal Chim Acta 517:71–79
Bastide J, Cambon JP, Breton F, Piletsky SA, Rouillon R (2005) The use of molecularly imprinted polymers for extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides. Anal Chim Acta 542:97–103
Seccia S, Albrizio S, Fidente P, Montesano D (2011) Development and validation of a solid-phase extraction method coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet-diode array detection for the determination of sulfonylurea herbicide residues in bovine milk samples. J Chrmatogr A 1218:1253–1259
He C, Li Y, Wang (2008) Determination on five sulfonylurea herbicides in water by high performance liquid chromatography with solid-phase extraction. Mod Prev Med 35:538–540
Marek M (2009) Comparison of chromatographic separation of selected sulfonylurea herbicides carried out by HPLC and RR-HPLC techniques. Prog Plant Prot 49:1889–1894
Qiu W, Yun L, Chao L, Chun W, Zhi L, Yu H, Zhi W (2010) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-DAD detection for the determination of sulfonylurea herbicides in water samples. Inter J Environ Anal Chem 90:891–902
Yan C, Zhang B, Liu W, Feng F, Zhao Y, Du H (2011) Rapid determination of sixteen sulfonylurea herbicides in surface water by solid phase extraction cleanup and ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 879:3484–3489
Qiu H, Jiang S, Liu X, Zhao L (2006) Novel imidazolium stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1116:46–50
Miller JN, Miller JC (2000) Statistics and chemometrics for analytical chemistry, 4th edn. Prentice-Hall, Harrow
Directive EUC (1998) 98/83/EC on the quality of water intended for human consumption. Off J Eur Communities L 330(32):570
Coly A, Aaron J-J (1999) Sensitive and rapid floow injection analysis of sulfonylurea herbicides in water with micellar-enhanced photochemically induced fuorescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 392:255–264
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (CTQ2010-15027) is gratefully acknowledged. The support given through a “INCRECYT” research contract to M. Zougagh is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouri, M., Gurau, M., Salghi, R. et al. Ionic liquids supported on magnetic nanoparticles as a sorbent preconcentration material for sulfonylurea herbicides prior to their determination by capillary liquid chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 404, 1529–1538 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6221-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6221-2