Abstract
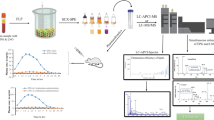
Alendronate is an important representative of bisphosphonates, strongly polar compounds that lack chromophores. With rare exceptions, derivatization of the analytes is necessary for bioanalysis. In this study, a rapid liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method employing pre-column derivatization was developed and validated for the determination of alendronate concentrations in human plasma. The procedure was based on derivatization with trimethylsilyldiazomethane during solid-phase extraction on a weak anion-exchange solid-phase cartridge, which integrated sample purification and derivatization into one step. The alendronate derivative was eluted with methanol. Chromatographic separation was performed on a Capcell PAK-C18 column. The total run time was 6.5 min. The calibration curve was linear in the range 1.00–1,000 ng/mL using d6-alendronate as the internal standard. The lower limit of quantification was 1.00 ng/mL. The intra- and inter-assay precision (in RSD) calculated from quality control samples was less than 15%, and the accuracy was between 98.1% and 100.2%. The validated method was successfully applied to characterize the pharmacokinetic profiles of alendronate following the intravenous infusion of 5 or 10 mg alendronate sodium to healthy volunteers.

Derivatization and determination procedures of alendronate in human plasma






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hosking D, Chilvers CE, Christiansen C, Ravn P, Wasnich R, Ross P, McClung M, Balske A, Thompson D, Daley M, Yates AJ (1998) Prevention of bone loss with alendronate in postmenopausal women under 60 years of age. N Engl J Med 338(8):485–492
Russell RG, Rogers MJ (1999) Bisphosphonates: from the laboratory to the clinic and back again. Bone 25(1):97–106
Finkelstein JS, Wyland JJ, Lee H, Neer RM (2010) Effects of teriparatide, alendronate, or both in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:1838–1845
Fleisch H (2003) Bisphosphonates in osteoporosis. Eur Spine J 12(Suppl 2):S142–S146
Zacharis CK, Tzanavaras PD (2008) Determination of bisphosphonate active pharmaceutical ingredients in pharmaceuticals and biological material: a review of analytical methods. J Pharm Biomed 48:483–496
Xie Z, Jiang Y, Zhang D (2006) Simple analysis of four bisphosphonates simultaneously by reverse phase liquid chromatography using n-amylamine as volatile ion-pairing agent. J Chromatogr A 1104:173–178
Tsai EW, Ip DP, Brooks MA (1992) Determination of alendronate in pharmaceutical dosage formulations by ion chromatography with conductivity detection. J Chromatogr A 596(2):217–224
Qin X, Tsai EW, Sakuma T, Ip DP (1994) Pharmaceutical application of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry: II. Ion chromatography-ion spray mass spectrometric characterization of alendronate. J Chromatogr A 686(2):205–212
Han YR, Qin X (1996) Determination of alendronate sodium by ion chromatography with refractive index detection. J Chromatogr A 719:345–352
Kline WF, Matuszewski BK (1992) Improved determination of the bisphosphonate alendronate in human plasma and urine by automated precolumn derivatization and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence and electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr 583(2):183–193
Ptáček P, Klíma J, Macek J (2002) Determination of alendronate in human urine as 9-fluorenylmethyl derivative by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 767(1):111–116
Kang H, Hwang S, Park J, Kim C (2006) HPLC method validation and pharmacokinetic study of alendronate sodium in human urine with fluorescence detection. J Liq Chromatogr R T 29:1589–1600
Apostolou C, Dotsikas Y, Kousoulos C, Tsatsou G, Colocouri F, Soumelas GS, Loukas YL (2007) Application of a semi-automated 96-well format solid-phase extraction, column-switching, fluorescence detection protocol for the determination of alendronate in human urine samples obtained from a bioequivalence study. J Pharm Biomed 43:1151–1155
Yun MH, Kwon KI (2006) High-performance liquid chromatography method for determining alendronate sodium in human plasma by detecting fluorescence: application to a pharmacokinetic study in humans. J Pharm Biomed Anal 40(1):168–172
Al Deeb SK, Hamdan II, Najjar SM (2004) Spectroscopic and HPLC methods for the determination of alendronate in tablets and urine. Talanta 64:695–702
Meng J, Meng Q, Zheng L (2009) A simple and rapid high-performance liquid chromatography method for determination of alendronate sodium in beagle dog plasma with application to preclinical pharmacokinetic study. Biomed Chromatogr 24:169–173
Jeong Y, Park J, Jin G, Park J (2011) Spectrofluorimetric determination of alendronate by conjugation with the rhodamine B sulfonyl group. Bull Korean Chem Soc 32(5):1–3
Tarcomnicu I, Silvestro L, Savu SR, Gherase A, Dulea C (2007) Development and application of a high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method to determine alendronate in human urine. J Chromatogr A 1160:21–33
Tamim MK, Gagne J-F, Nadeau F, Tanguay M, Trabelsi F, Vallee M (2010) Quantitative determination of alendronate sodium in human plasma using a validated LC- MS/MS method : application to clinical pharmacokinetic studies. www.aapsj.org/abstracts/AM_2010/M1500.pdf
Zhu LS, Lapko VN, Lee JW, Basir YJ, Kafonek C, Olsen R, Briscoe C (2006) A general approach for the quantitative analysis of bisphosphonates in human serum and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20:3421–3426
Lu Z, Diehl D, Mazzeo J, Oehrle SA, Mallet CR, Young MS, Chambers E (2008) Methods for separating and analyzing anionic compounds. Patent Application Publication US 2008/0169242 A1. http://www.freshpatents.com/Methods-for-separating-and-analyzing-anionic-compounds-dt20080717ptan20080169242.php
Preu M, Petz M Trimethylsilyldiazomethane as a methylation reagent for residue analysis-a safer and better alternative to diazomethane. www2.uni-wuppertal.de/fb9/lebensmittelchemie/Kan%20ERIV.pdf
Derivatization of carboxylic acids with diazomethane and trimethylsilyldiazomethane: convenient methods and artifacts. userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/∼tlehmann/krebs/files_diazoalkanes.pdf
Presser A, Hüfner A (2004) Trimethylsilyldiazomethane—a mild and efficient reagent for the methylation of carboxylic acids and alcohols in natural products. Monatshefte für Chemie 135(8):1015–1022
Mannur VS, Patel D, Mastiholimath VS, Shah G (2011) Selection of buffers in LC-MS/MS: an overview. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 6(1):34–37
Acknowledgment
This study was partly supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2009CB930300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 263 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Liu, K., Zhong, D. et al. Trimethylsilyldiazomethane derivatization coupled with solid-phase extraction for the determination of alendronate in human plasma by LC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 402, 791–798 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5467-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5467-4