Abstract
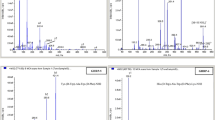
This paper describes a liquid chromatographic/tandem mass spectrometric (LC/MS–MS) method specifically designed for the screening of synthetic glucocorticosteroids in human urine. The method is designed to recognize a common mass spectral fragment formed from the particular portion of the molecular structure that is common to all synthetic glucocorticosteroids and that is fundamental to their pharmacological activity. As such, the method is also suitable for detecting unknown substances, provided they contain the portion of the molecular structure selected as the analytical target. The effectiveness of this approach was evaluated on seventeen synthetic glucocorticosteroids. Urine samples, including blank urines spiked with one or more synthetic glucocorticosteroids, were treated according to a standard procedure (enzymatic hydrolysis, liquid/liquid extraction and evaporation to dryness) and analyzed using LC/MS-MS with electrospray ionization (ESI). MS–MS acquisition was carried out in a precursor ion scan, and the results were compared with those obtained by a previously developed reference technique based on acquisition in the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. All of the glucocorticosteroids considered in this study are clearly detectable in urine, with a limit of detection in the concentration range 5–20 ng/mL, depending on the glucocorticosteroid structure. The proposed method is therefore suitable for the detection of glucocorticosteroids in urine samples taken for “in competition” sport anti-doping control tests, matching the requirements of the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) for accredited anti-doping laboratories.

Structures of the synthetic glucocorticoids considered in this study







Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Anti-Doping Agency (2007) The World Anti-Doping Code: The 2007 Prohibited List International Standard. World Anti-Doping Agency, Montreal, Canada (also available at http://www.wada-ama.org, last accessed 30 September 2007)
Catlin DH, Ahrens BD, Kucherova Y (2002) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 16:1273–1275
Catlin DH, Sekera MH, Ahrens BD, Starcevic B, Chang YC, Hatton CK (2004) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18:1245–1249
Sekera MH, Ahrens BD, Chang YC, Starcevic B, Georgakopoulos C, Catlin DH (2005) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 19:781–784
Malvey TC, Armsey TD (2005) 2nd Curr Sports Med Rep 4:227–230
Thevis M, Geyer H, Mareck U, Schänzer W (2005) In: Schänzer W, Geyer H, Gotzmann A, Mareck U (eds) Recent advances in doping analysis. Sportverlag Strauß, Köln, Germany, 13:147–155
Botrè F (2003) Toxicol In Vitro 17:509–513
Amendola L, Molaioni F, Botrè F (2000) J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 23:211–221
Nielen MWF, Bovee TFH (2001) In: Schänzer W, Geyer H, Gotzmann A, Mareck U (eds) Recent advances in doping analysis. Sport und Büch Strauß, Köln, Germany, 9:157–158
Bohets H, Annaert P, Mannens G, van Beijterveldt L, Anciaux K, Verboven P, Meuldermans W, Lavrijsen K (2001) Curr Topics Med Chem 1:367–383
Thevis M, Geyer H, Mareck U, Schanzer WJ (2005) Mass Spectrom 40:955–962
Wrona M, Mauriala Bateman TKP, Mortishire-Smith RJ, O’Connor D (2005) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 19:2597–2602
Thevis M, Schänzer W (2006) Laboratoriums Medizin 30:26–32
Thevis M, Kamber M, Schänzer W (2006) Rapid Commun Spectrom 20:870–876
Antignac J-P, Le Bizec B, Monteau F, Poulain F, André F (2000) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 14:33–39
World Anti-Doping Agency (2004) WADA Technical Document TD2004MRPL: Minimum required performance limits for detection of prohibited substances. World Anti-Doping Agency, Montreal, Canada (also available at http://www.wada-ama.org, last accessed 30 September 2007)
Mazzarino M, Botrè F (2006) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20:3465–3476
Nogrady T (1988) Medicinal chemistry: a biomedical approach, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 514
Haynes RC Jr, Murad F (1985) In: Goodman LS, Gilman A, Rall TW, Murad F (eds) Goodman and Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 7th edn. Macmillan, New York, pp 1459–1489
Norman AW, Litwack G (1991) Hormones, 2nd edn. Academic, San Diego, CA, p 558
Hofstadler SA, Sannes-Lowery KA (2006) Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:585–595
Georgakopoulus C, Vonaparti A, Stamou M, Kiousi P, Lyris E, Angelis Y, Tsoupras G, Wuest B, Nielen M, Panderi I, Koupparis M (2007) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 21:2439–2446
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by a Research Grant from the Italian Department of Health (“Ministero della Salute, Commissione per la vigilanza sul doping e sulla tutela sanitaria delle attività sportive”). The authors also wish to thank Mr. Roberto Romani for his valuable technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazzarino, M., Turi, S. & Botrè, F. A screening method for the detection of synthetic glucocorticosteroids in human urine by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry based on class-characteristic fragmentation pathways. Anal Bioanal Chem 390, 1389–1402 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1802-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1802-1