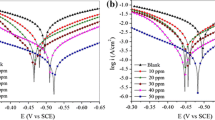
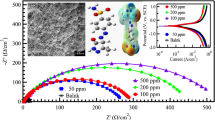
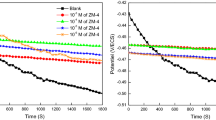
Abstract
Adsorption mechanism and inhibitive performances of alkaloids on mild steel are studied using density functional theory (DFT). Global reactivity parameters such as global hardness (ɳ), fraction of electron transfer from molecule to metal (∆N), and dipole moment (μ) are calculated to determine corrosion protection efficiency. Periodic DFT calculations show bonding interactions between heteroatoms of alkaloid and Fe atom of Fe(110) surface. Fe–-H non-classical bond formations are also observed. The order of adsorption energy (Eads) is quinine (86.6 kcal/mol) > cytisine (67.6 kcal/mol) ≈ mescaline > ephedrine > morphine ≈ atropine > nicotine > caffeine > tryptamine > codeine (50.2 kcal/mol). Highest Eads value of quinine is interpreted with its very favourable orbital energies that help to form chemical bonds via electron donation and back donation. These high Eads values confirmed chemisorption process and interpreted strong inhibition efficiencies of morphine and caffeine on mild steel as reported in experimental studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The structure information of the model systems can be obtained from the authors upon request.
References
Ameer MA, Khamis E, Al-Senani G (2000) Adsorpt Sci Technol 18:177
Bera S, Rout TK, Udayabhanu G, Narayan R (2015) Comparative study of corrosion protection of sol-gel coatings with different organic functionality on Al-2024 substrate. Prog Org Coat 88:293–303
Bera S, Rout TK, Udayabhanu G, Narayan R (2016) Water-based & eco-friendly epoxy-silane hybrid coating for enhanced corrosion protection & adhesion on galvanized steel. Prog Org Coat 101:24–44
Cadar E, Tomescu A, Erimia C, Mustafa A, Sirbu R (2015) The impact of alkaloids structures from naturalcompounds on public health. Eur Soc Sci Res 5:34–39
Chakraborty T, Gazi K, Ghosh DC (2010) Computation of the atomic radii through the conjoint action of the effective nuclear charge and the ionization energy. Mol Phys 108:2081–2092
Chattaraj PK, Sarkar U, Roy DR (2006) Electrophilicity index. Chem Rev 106:2065–2091
Costa D, Ribeiro T, Cornette P, Marcus P (2016) DFT modeling of corrosion inhibition by organic molecules: carboxylates as inhibitors of aluminum corrosion. J Phys Chem C 120:28607–28616
Davey WP (1925) Precision measurements of the lattice constants of twelve common metals. Phys Rev 25:753–761
de Souza FS, Giacomelli C, Gonçalves RS, Spinelli A (2012) Adsorption behavior of caffeine as a green corrosion inhibitor for copper. Mater Sci Eng, C 32:2436–2444
Dennis RV, Patil V, Andrews JL, Aldinger JP, Yadav GD, Banerjee S (2015) Hybrid nanostructured coatings for corrosion protection of base metals: a sustainability perspective. Mater Res Exp 2:032001
Espinoza-Vázquez A, Rodríguez-Gómez FJ (2016) Caffeine and nicotine in 3% NaCl solution with CO2 as corrosion inhibitors for low carbon steel. RSC Adv 6:70226–70236
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Li X, Caricato M, Marenich AV, Bloino J, Janesko BG, Gomperts R, Mennucci B, Hratchian HP, Ortiz JV, Izmaylov AF, Sonnenberg JL, Williams, Ding F, Lipparini F, Egidi F, Goings J, Peng B, Petrone A, Henderson T, Ranasinghe D, Zakrzewski VG, Gao J, Rega N, Zheng G, Liang W, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Throssell K, Montgomery Jr. JA, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark MJ, Heyd JJ, Brothers EN, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Keith TA, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell AP, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Millam JM, Klene M, Adamo C, Cammi R, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Farkas O, Foresman JB, Fox DJ (2016) Gaussian 16 Rev. C.01. Wallingford, CT
Gece G, Bilgiç S (2010) A theoretical study of some hydroxamic acids as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel. Corros Sci 52:3304–3308
Grimme S (2006) Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J Comput Chem 27:1787–1799
Guin AK, Nayak SK, Rout TK, Bandyopadhyay N, Sengupta DK (2012) Corrosion behavior of nanohybrid titania–silica composite coating on phosphated steel sheet. J Coat Technol Res 9:97–106
Hashimoto H, Fukuda T, Tobita H, Ray M, Sakaki S (2012) Formation of a germylyne complex: dehydrogenation of a hydrido(hydrogermylene)tungsten complex with mesityl isocyanate. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:2930–2933
Hu Z, Meng Y, Ma X, Zhu H, Li J, Li C, Cao D (2016) Experimental and theoretical studies of benzothiazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in 1M HCl. Corros Sci 112:563–575
Koopmans T (1934) Über die Zuordnung von Wellenfunktionen und Eigenwerten zu den Einzelnen Elektronen Eines Atoms. Physica 1:104–113
Kresse G, Furthmüller J (1996) Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys Rev B 54:11169–11186
Kresse G, Joubert D (1999) From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 59:1758–1775
Kumar D, Jain N, Jain V, Rai B (2020) Amino acids as copper corrosion inhibitors: A density functional theory approach. Appl Surf Sci 514:145905
Kumar D, Jain V, Rai B (2020) Imidazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for copper: A DFT and reactive force field study. Corros Sci 171:108724
Majd MT, Ramezanzadeh M, Bahlakeh G, Ramezanzadeh B (2020) Probing molecular adsorption/interactions and anti-corrosion performance of poppy extract in acidic environments. J Mol Liq 304:112750
Mendez F, Gazquez JL (1994) Chemical reactivity of enolate ions: the local hard and soft acids and bases principle viewpoint. J Am Chem Soc 116:9298–9301
Mourya P, Singh P, Tewari AK, Rastogi RB, Singh MM (2015) Relationship between structure and inhibition behaviour of quinolinium salts for mild steel corrosion: experimental and theoretical approach. Corros Sci 95:71–87
Obot IB, Obi-Egbedi NO (2010) Adsorption properties and inhibition of mild steel corrosion in sulphuric acid solution by ketoconazole: Experimental and theoretical investigation. Corros Sci 52:198–204
Oguzie EE, Adindu CB, Enenebeaku CK, Ogukwe CE, Chidiebere MA, Oguzie KL (2012) Natural products for materials protection: mechanism of corrosion inhibition of mild steel by acid extracts of piper guineense. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 116:13603–13615
Pearson RG (1988) Chemical hardness and bond dissociation energies. J Am Chem Soc 110:7684–7690
Pearson RGPaRG, (1983) Absolute hardness: companion parameter to absolute electronegativity. J Am Chem Soc 105:5
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77:3865–3868
Ray M, Nakao Y, Sato H, Sakaba H, Sakaki S (2006) Silapropargyl/silaallenyl and silylene acetylide complexes of [Cp(CO)2W]+. theoretical study of their interesting bonding nature and formation reaction. J Am Chem Soc 128:11927–11939
Ray M, Nakao Y, Sato H, Sakaki S (2007) Theoretical study of tungsten η3-Silaallyl/η3-vinylsilyl and vinyl silylene complexes: interesting bonding nature and relative stability. Organometallics 26:4413–4423
Ray M, Nakao Y, Sato H, Sakaba H, Sakaki S (2009) How to stabilize η3-silapropargyl/alkynylsilyl complex of [CpL2M]+(L = CO, PMe3, or PF3 and M = W or Mo): theoretical prediction. Organometallics 28:65–73
Ray M, Nakao Y, Sato H, Sakaki S, Watanabe T, Hashimoto H, Tobita H (2010) Experimental and theoretical study of a tungsten dihydride silyl complex: new insight into its bonding nature and fluxional behavior. Organometallics 29:6267–6281
Ray M, Saha B, Schatz GC (2012) Theoretical studies of the O(3P) + C2 reaction at hyperthermal energies. J Phys Chem C 116:26577–26585
Şahin M, Gece G, Karcı F, Bilgiç S (2008) Experimental and theoretical study of the effect of some heterocyclic compounds on the corrosion of low carbon steel in 3.5% NaCl medium. J Appl Electrochem 38:809–815
Sakaba H, Oike H, Kawai M, Takami M, Kabuto C, Ray M, Nakao Y, Sato H, Sakaki S (2011) Synthesis, structure, and bonding nature of ethynediyl-bridged bis(silylene) dinuclear complexes of tungsten and molybdenum. Organometallics 30:4515–4531
Sanderson RT (1983) Electronegativity and bond energy. J Am Chem Soc 105:2259–2261
Sastri VS, Elboujdaini M, Perumareddi JR (2005) Utility of quantum chemical parameters in the rationalization of corrosion inhibition efficiency of some organic inhibitors. Corrosion 61:933–942
Tang L, Mu G, Liu G (2003) Corros Sci 45:2251
Verma C, Olasunkanmi LO, Ebenso EE, Quraishi MA, Obot IB (2016) Adsorption behavior of glucosamine-based, pyrimidine-fused heterocycles as green corrosion inhibitors for mild steel: experimental and theoretical studies. J Phys Chem C 120:11598–11611
Verma C, Ebenso E, Bahadur I, Quraishi MA (2018) An overview on plant extracts as environmental sustainable and green corrosion inhibitors for metals and alloys in aggressive corrosive media. J Molecul Liquids 266:577–590
Vernack E, Costa D, Tingaut P, Marcus P (2020) DFT studies of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole and 2-mercaptobenzimidazole as corrosion inhibitors for copper. Corros Sci 174:108840
Wang L, Maxisch T, Ceder G (2006) Oxidation energies of transition metal oxides within the GGA+U framework. Phys Rev B 73:195107
Zhang Z, Wang F, Liu Y, Wu S, Li W, Sun W, Guo D, Jiang J (2018) Molecule adsorption and corrosion mechanism of steel under protection of inhibitor in a simulated concrete solution with 3.5% NaCl. RSC Adv 8:20648–20654
Acknowledgements
Authors sincerely thank Tata Steel Limited, India for all support.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
214_2022_2890_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Figure S1 and Figure S2. Optimized geometries and important molecular orbitals for alkaloid molecules. Figure S3. Optimized geometries for another alkaloid molecules when they are adsorbed on Fe(110) surface in favoured configuration. Figure S4. Optimized geometries for less favoured adsorption configuration of alkaloid molecules on Fe(110) surface. (DOCX 2689 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ray, M., Saha, B., Rout, T.K. et al. Adsorption mechanism and performance analysis of alkaloids as green corrosion inhibitors on mild steel. Theor Chem Acc 141, 32 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-022-02890-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-022-02890-w