Abstract
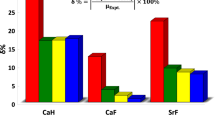
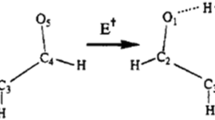
The fragmentation chemistry of protonated H–Val–Asn–OH, H–Val–Gln–OH and H–Val–Lys–OH is investigated in this work by means of modeling and density functional theory calculations. Former experimental studies indicate that the ratio of a 1 and y 1 ions cannot be explained by considering the proton affinities of the corresponding dissociating species on the a 1–y 1 pathway, while the fragmentation of other dipeptides can be understood in this way. We demonstrate that considering the correct PA value for H–Asn–OH eliminates the deviation observed for H–Val–Asn–OH. The larger than expected a 1/y 1 ratio of H–Val–Gln–OH is explained by considering the dissociation kinetics of the proton-bound dimers formed on the a 1–y 1 pathway and competition of the deamidation and a 1–y 1 channels. For H–Val–Lys–OH, it is proposed that a 1 ions are indeed formed from one of the primary products, protonated H–Val–Cap–OH.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebersold R, Goodlett DR (2001) Chem Rev 101:269
Paizs B, Suhai S (2005) Mass Spectrom Rev 24:508
Paizs B, van Stipdonk M (2008) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 19:1717 and papers in this focus issue on peptide fragmentation
Roepstorff P, Fohlmann J (1984) J Biomed Mass Spectrom 11:601
Biemann K (1988) Biomed Environ Mass Spectrom 16:99
Morgan DG, Bursey MM (1994) Org Mass Spectrom 29:354
Morgan DG, Bursey MM (1995) J Mass Spectrom 30:595
Harrison AG, Csizmadia IG, Tang TH, Tu YP (2000) J Mass Spectrom 35:683
Paizs B, Suhai S (2001) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 15:651
Paizs B, Schnölzer M, Warnken U, Suhai S, Harrison AG (2004) Phys Chem Chem Phys 6:2691
Wysocki VH, Tsaprailis G, Smith LL, Breci LA (2000) J Mass Spectrom 35:1399
Paizs B, Suhai S (2002) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 16:1699
Cooks RG, Kruger TL (1977) J Am Chem Soc 99:1279
McLuckey SA, Cameron D, Cooks RG (1981) J Am Chem Soc 103:1313
Harrison AG (1999) J Mass Spectrom 34:577
Pingitore F, Polce MJ, Wang P, Wesdemiotis C, Paizs B (2004) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 15:1025
Wyttenbach T, Paizs B, Barran P, Breci L, Liu D, Suhai S, Wysocki VH, Bowers MT (2003) J Am Chem Soc 125:13768
Paizs B, Suhai S (2004) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 15:103
Polfer NC, Oomens J, Suhai S, Paizs B (2005) J Am Chem Soc 127:17154
Harrison AG, Young AB, Bleiholder C, Suhai S, Paizs B (2006) J Am Chem Soc 128:10364
Polfer NC, Oomens J, Suhai S, Paizs B (2007) J Am Chem Soc 129:5887
Bleiholder C, Osburn S, Williams TD, Suhai S, Van Stipdonk M, Harrison AG, Paizs B (2008) J Am Chem Soc 130:17774
Case DA et al AMBER 99, University of California, San Francisco
Frisch MJ et al (1995) Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh PA
Bleiholder C, Suhai S, Paizs B (2006) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 17:1275
Harrison AG (1997) Mass Spectrom Rev 16:201
Harrison AG (2003) J Mass Spectrom 38:174
Heaton AL, Armentrout PB (2009) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 20:852
Paizs B, Suhai S (2001) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 15:2307
Dookeran NN, Yalcin T, Harrison AG (1996) J Mass Spectrom 31:500
Csonka IP, Paizs B, Lendvay G, Suhai S (2001) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 15:1457
Laerdahl JK, Uggerud E (2002) Int J Mass Spectrom 214:277
Gritsenko OV, Ensing B, Schipper PRT, Baerends EJ (2000) J Phys Chem A 104:8558
Yalcin T, Harrison AG (1996) J Mass Spectrom 31:1237
Balta B, Aviyente V, Lifshitz C (2003) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 14:1192
Acknowledgments
BP is grateful for the financial support from the DFG (SU 244/3-1). CB is grateful for a fellowship of the DKFZ International Ph.D. Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Sándor Suhai on the occasion of his 65th birthday and published as part of the Suhai Festschrift Issue.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bleiholder, C., Paizs, B. Competing gas-phase fragmentation pathways of asparagine-, glutamine-, and lysine-containing protonated dipeptides. Theor Chem Acc 125, 387–396 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-009-0658-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-009-0658-1