Abstract
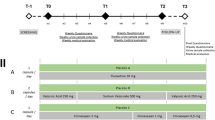
Rationale: Cocaethylene is a pharmacologically active homolog and metabolite of cocaine, formed by transesterification of cocaine in the presence of ethanol. Here we relate findings from a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study in which we examined the physiological and subjective effects and pharmacokinetics of IV administered cocaethylene in human volunteers using cocaine as a comparator. Methods: Cocaine-dependent participants randomly received one study drug, cocaethylene (0.25 or 0.5 mg/kg), cocaine (0.25 or 0.5 mg/kg), or placebo, during each experimental session which occurred on separate days. Results: Cocaethylene was less potent in elevating heart rate than equivalent doses of cocaine. Similar differences between cocaine and cocaethylene were found for subjective measures (”Cocaine High”, ”Rush”, ”Stimulated” and ”Good Drug Effects”). All active drug conditions produced significant increases in systolic blood pressure relative to placebo, but no significant effect on diastolic blood pressure was observed. Cocaethylene demonstrated a slower clearance, larger volume of distribution and correspondingly longer elimination half-life than cocaine. Conclusion: The findings from this study confirm those of previous studies that show that cocaethylene has pharmacological properties in common with cocaine, but is less potent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 July 1999 / Final version: 23 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hart, C., Jatlow, P., Sevarino, K. et al. Comparison of intravenous cocaethylene and cocaine in humans. Psychopharmacology 149, 153–162 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002139900363
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002139900363