Abstract
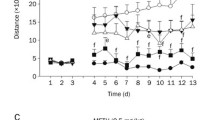
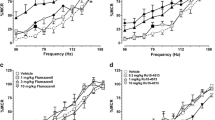
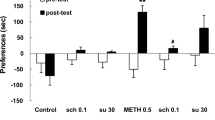
Rationale: Recent studies have suggested the involvement of excitatory amino acid (EAA) and inhibitory gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) transmission in the effects of psychostimulants such as cocaine and amphetamines. Objectives: The present study was undertaken to investigate whether drugs that are considered to inhibit glutamate release (e.g., riluzole) or increase GABAergic transmission (e.g., gabapentin) attenuate the induction and expression of sensitization to cocaine and methamphetamine (METH) in Swiss Webster mice. Methods: Sensitizationto the psychomotor stimulating effect of cocaine and METH was rendered by five daily injections of cocaine (20 mg/kg) or METH (1.0 mg/kg). Locomotor activity was measured by infrared beam interrupts. Results: Pretreatment with riluzole (2.5–20.0 mg/kg) affected neither the expression nor the induction of sensitization to cocaine. The pretreatment with riluzole (20 mg/kg) blocked the acute response to METH on day 1 and the expression of the sensitized response on day 5 but not the induction of sensitization to METH. Pretreatment with gabapentin (10 mg/kg and30 mg/kg) affected neither the expression nor the induction of sensitization to cocaine. The pretreatment with gabapentin attenuated the acute response to METH on day 1 and the expression of the sensitized response on day 5, but it failed to block the induction of sensitization to METH. Psychostimulant-induced conditioned locomotion was affected neither by riluzole nor by gabapentin. Conclusions: Riluzole and gabapentin had no effect on the induction of sensitization to cocaine and METH; however, they attenuated the expression of sensitization to METH but not to cocaine. These findings suggest that riluzole- and gabapentin-mediated changes in EAA and GABAergic transmission, respectively, had no effect on mechanisms associated with the induction of sensitization, but they may affect the expression of the sensitized response to METH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 September 1999 / Accepted: 13 January 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itzhak, Y., Martin, J. Effect of riluzole and gabapentin on cocaine- and methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice. Psychopharmacology 151, 226–233 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000394
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000394