Abstract
Rationale
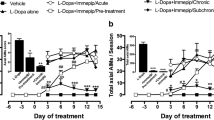
Dyskinesias induced by L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, L-Dopa (LIDs), are the major complication in the pharmacological treatment of Parkinson’s disease. LIDs induce overactivity of the glutamatergic cortico-striatal projections, and drugs that reduce glutamatergic overactivity exert antidyskinetic actions. Chronic administration of immepip, agonist at histamine H3 receptors (H3R), reduces LIDs and diminishes GABA and glutamate content in striatal dialysates (Avila-Luna et al., Psychopharmacology 236: 1937-1948, 2019).
Objectives and methods
In rats unilaterally lesioned with 6-hydroxydopamine in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc), we examined whether the chronic administration of immepip and their withdrawal modify LIDs, the effect of L-Dopa on glutamate and GABA content, and mRNA levels of dopamine D1 receptors (D1Rs) and H3Rs in the cerebral cortex and striatum.
Results
The administration of L-Dopa for 21 days induced LIDs. This effect was accompanied by increased GABA and glutamate levels in the cerebral cortex ipsi and contralateral to the lesioned SNc, and immepip administration prevented (GABA) or reduced (glutamate) these actions. In the striatum, GABA content increased in the ipsilateral nucleus, an effect prevented by immepip. L-Dopa administration had no significant effects on striatal glutamate levels. In lesioned and L-Dopa-treated animals, D1R mRNA decreased in the ipsilateral striatum, an effect prevented by immepip administration.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that chronic H3R activation reduces LIDs and the overactivity of glutamatergic cortico-striatal projections, providing further evidence for an interaction between D1Rs and H3Rs in the cortex and striatum under normal and pathological conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-Hydroxydopamine
- AIMs:
-
Abnormal involuntary movements
- D1Rs:
-
Dopamine D1 receptors
- H3Rs:
-
Histamine H3 receptors
- L-Dopa :
-
L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine
- LIDs:
-
L-Dopa-induced dyskinesias
- MSN:
-
Medium spiny neurons
- SNc:
-
Substantia nigra pars compacta
- SNr:
-
Substantia nigra pars reticulata
References
Aas JE, Laake JH, Brodal P, Ottersen OP (1992) Immunocytochemical evidence for in vitro release of glutamate and GABA from separate nerve terminal populations in the rat pontine nuclei. Exp Brain Res 89:540–548
Ahlskog JE, Muenter MD (2001) Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov Disord 16:448–458
Albin RL, Young AB, Penney JB (1989) The functional-anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci 12:366–375
Andersson M, Hilbertson A, Cenci MA (1999) Striatal fosB expression is causally linked with L-Dopa-induced abnormal involuntary movements and the associated upregulation of striatal prodynorphin mRNA in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 6:461–474
Anichtchik OV, Huotari M, Peitsaro N, Haycock JW, Männistö PT, Panula P (2000) Modulation of histamine H3 receptors in the brain of 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. Eur J Neurosci 12:3823–3832
Arias-Montaño JA, Floran B, Garcia M, Aceves J, Young JM (2001) Histamine H(3) receptor-mediated inhibition of depolarization-induced, dopamine D(1) receptor-dependent release of (3)H-gamma-aminobutryic acid from rat striatal slices. Br J Pharmacol 133:165–171
Aubert I, Guigoni C, Hakansson K, Li Q, Dovero S, Barthe N, Bioulac BH, Gross CE, Fisone G, Bloch B, Bezard E (2005) Increased D-1 dopamine receptor signaling in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol 57:17–26
Avila-Luna A, Rios C, Galvez-Rosas A, Montes S, Arias-Montano JA, Bueno-Nava A (2019) Chronic administration of the histamine H-3 receptor agonist immepip decreases L-Dopa-induced dyskinesias in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. Psychopharmacol 236:1937–1948
Bastide MF, Meissner WG, Picconi B, Fasano S, Fernagut PO, Feyder M, Francardo V, Alcacer C, Ding YM, Brambilla R, Fisone G, Stoessl AJ, Bourdenx M, Engeln M, Navailles S, De Deurwaerdere P, Ko WKD, Simola N, Morelli M et al (2015) Pathophysiology of L-Dopa-induced motor and non-motor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 132:96–168
Berthet A, Porras G, Doudnikoff E, Stark H, Cador M, Bezard E, Bloch B (2009) Pharmacological analysis demonstrates dramatic alteration of D-1 dopamine receptor neuronal distribution in the rat analog of L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia. J Neurosci 29:4829–4835
Bido S, Marti M, Morari M (2011) Amantadine attenuates levodopa-induced dyskinesia in mice and rats preventing the accompanying rise in nigral GABA levels. J Neurochem 118:1043–1055
Björklund A, Dunnett SB (2007) Dopamine neuron systems in the brain: an update. Trends Neurosci 30:194–202
Blanchet PJ, Konitsiotis S, Chase TN (1998) Amantadine reduces levodopa-induced dyskinesias in parkinsonian monkeys. Mov Disord 13:798–802
Blanchet PJ, Parent M-T, Rompre PH, Levesque D (2012) Relevance of animal models to human tardive dyskinesia. Behav Brain Funct 8:1–9
Bolam JP, Ellender TJ (2016) Histamine and the striatum. Neuropharmacol 106:74–84
Calabresi P, Pisani A, Centonze D, Bernardi G (1997) Synaptic plasticity and physiological interactions between dopamine and glutamate in the striatum. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:519–523
Calabresi P, Picconi B, Tozzi A, Ghiglieri V, Di Filippo M (2014) Direct and indirect pathways of basal ganglia: a critical reappraisal. Nat Neurosci 17:1022–1030
Capper-Loup C, Frey CM, Rebell D, Kaelin-Lang A (2013) Adaptive gene expression changes on the healthy side of parkinsonian rats. Neurosci 233:157–165
Carta M, Bezard E (2011) Contribution of pre-synaptic mechanisms to L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia. Neurosci 198:245–251
Cenci MA, Lee CS, Bjorklund A (1998) L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia in the rat is associated with striatal overexpression of prodynorphin- and glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA. Eur J Neurosci 10:2694–2706
Connolly BS, Lang AE (2014) Pharmacological treatment of parkinson disease a review. JAMA 311:1670–1683
Conti F, Defelipe J, Fariñas I, Manzoni T (1989) Glutamate-positive neurons and axon terminals in cat sensory cortex: a correlative light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 290:141–153
Dankyi BO, Amponsah SK, Allotey-Babington GL, Adams I, Goode NA, Nettey H (2020) Chitosan-coated hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose microparticles of levodopa (and Carbidopa): in vitro and rat model kinetic characteristics. Curr Ther Res 93:100612
De la Fuente-Fernandez R, Sossi V, Huang ZG, Furtado S, Lu JQ, Calne DB, Ruth TJ, Stoessl AJ (2004) Levodopa-induced changes in synaptic dopamine levels increase with progression of Parkinson’s disease: implications for dyskinesias. Brain 127:2747–2754
DeFelipe J, Fariñas I (1992) The pyramidal neuron of the cerebral cortex: morphological and chemical characteristics of the synaptic inputs. Prog Neurobiol 39:563–607
Diaz-Ruiz A, Salgado-Ceballos H, Montes S, Maldonado V, Tristan L, Alcaraz-Zubeldia M, Ríos C (2007) Acute alterations of glutamate, glutamine, GABA, and other amino acids after spinal cord contusion in rats. Neurochem Res 32:57–63
Dori I, Petrou M, Parnavelas JG (1989) Excitatory transmitter amino acid-containing neurons in the rat visual cortex: a light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol 290:169–184
Elhanany E, White EL (1990) Intrinsic circuitry: synapses involving the local axon collaterals of corticocortical projection neurons in the mouse primary somatosensory cortex. J Comp Neurol 291:43–54
Ellenbroek BA, Ghiabi B (2014) The other side of the histamine H3 receptor. Trends Neurosci 37:191–199
Ellender TJ, Huerta-Ocampo I, Deisseroth K, Capogna M, Bolam JP (2011) Differential modulation of excitatory and inhibitory striatal synaptic transmission by histamine. J Neurosci 31:15340–15351
Fahn S (2008) The history of dopamine and levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23:S497–S508
Festing MF (1994) Reduction of animal use: experimental design and quality of experiments. Lab Anim 28:212–221
Gadea A, López-Colomé AM (2001) Glial transporters for glutamate, glycine, and GABA: II. GABA transporters. J Neurosci Res 63:461–468
Gálvez-Rosas A, Avila-Luna A, Valdés-Flores M, Montes S, Bueno-Nava A (2019) GABAergic imbalance is normalized by dopamine D1 receptor activation in the striatum contralateral to the cortical injury in motor deficit-recovered rats. Psychopharmacol 236:2211–2222
Garcia M, Floran B, Arias-Montaño JA, Young JM, Aceves J (1997) Histamine H3 receptor activation selectively inhibits dopamine D1 receptor-dependent [3H] GABA release from depolarization-stimulated slices of rat substantia nigra pars reticulata. Neurosci 80:241–249
Gerfen CR, Engber TM, Mahan LC, Susel Z, Chase TN, Monsma FJ, Sibley DR (1990) D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-regulated gene expression of striatonigral and striatopallidal neurons. Science 250:1429–1432
González-Sepúlveda M, Rosell S, Hoffmann HM, Castillo-Ruiz MM, Mignon V, Moreno-Delgado D, Michel V, Díaz J, Sabriá J, Ortiz J (2013) Cellular distribution of the histamine H3 receptor in the basal ganglia: functional modulation of dopamine and glutamate neurotransmission. BG 3:109–121
Guerriero RM, Giza CC, Rotenberg A (2015) Glutamate and GABA imbalance following traumatic brain injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 15: 1-11
Healy DP, O’Rourke DA (1997) Regulation of dopamine-1A (D1A) receptor gene transcription. Clin Exp Hypertens 19:1–13
Hely MA, Morris JGL, Reid WGJ, Trafficante R (2005) Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: non-L-Dopa-responsive problems dominate at 15 years. Mov Disord 20:190–199
Huot P, Johnston TH, Koprich JB, Fox SH, Brotchie JM (2013) The pharmacology of L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol Rev 65:171–222
Johansson PA, Andersson M, Andersson KE, Cenci MA (2001) Alterations in cortical and basal ganglia levels of opioid receptor binding in a rat model of L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia. Neurobiol Dis 8:220–239
Jonkers N, Sarre S, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (2002) MK801 suppresses the L-Dopa-induced increase of glutamate in striatum of hemi-Parkinson rats. Brain Res 926:149–155
Kreitzer AC, Malenka RC (2008) Striatal plasticity and basal ganglia circuit function. Neuron 60:543–554
LeWitt PA (2015) Levodopa therapy for Parkinson’s disease: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Mov Disord 30:64–72
Lundblad M, Andersson M, Winkler C, Kirik D, Wierup N, Cenci MA (2002) Pharmacological validation of behavioural measures of akinesia and dyskinesia in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 15:120–132
Lundblad M, Usiello A, Carta M, Håkansson K, Fisone G, Cenci MA (2005) Pharmacological validation of a mouse model of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Exp Neurol 194:66–75
Martin DL, Rimvall K (1993) Regulation of γ-aminobutyric acid synthesis in the brain. J Neurochem 60:395–407
Mela F, Marti M, Dekundy A, Danysz W, Morari M, Cenci MA (2007) Antagonism of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 attenuates L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and its molecular and neurochemical correlates in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 101:483–497
Mela F, Marti M, Bido S, Cenci MA, Morari M (2012) In vivo evidence for a differential contribution of striatal and nigral D1 and D2 receptors to L-DOPA induced dyskinesia and the accompanying surge of nigral amino acid levels. Neurobiol Dis 45:573–582
Molina-Hernandez A, Nunez A, Sierra JJ, Arias-Montano JA (2001) Histamine H-3 receptor activation inhibits glutamate release from rat striatal synaptosomes. Neuropharmacol 41:928–934
Moreno E, Hoffmann H, Gonzalez-Sepulveda M, Navarro G, Casado V, Cortes A, Mallol J, Vignes M, McCormick PJ, Canela EI, Lluis C, Moratalla R, Ferre S, Ortiz J, Franco R (2011) Dopamine D-1-histamine H-3 receptor heteromers provide a selective Link to MAPK signaling in GABAergic neurons of the direct striatal pathway. J Biol Chem 286:5846–5854
Morin N, Jourdain VA, Di Paolo T (2014) Modeling dyskinesia in animal models of Parkinson disease. Exp Neurol 256:105–116
Mosharov EV, Borgkvist A, Sulzer D (2015) Presynaptic effects of levodopa and their possible role in dyskinesia. Mov Disord 30:45–53
Nieto-Alamilla G, Márquez-Gómez R, García-Gálvez A-M, Morales-Figueroa G-E, Arias-Montaño J-A (2016) The histamine H3 receptor: structure, pharmacology, and function. Mol Pharmacol 90:649–673
Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Stamelou M, Bhatia KP, Burn DJ (2014) The expanding universe of disorders of the basal ganglia. Lancet 384:523–531
Obeso JA, Stamelou M, Goetz CG, Poewe W, Lang AE, Weintraub D, Burn D, Halliday GM, Bezard E, Przedborski S, Lehericy S, Brooks DJ, Rothwell JC, Hallett M, DeLong MR, Marras C, Tanner CM, Ross GW, Langston JW et al (2017) Past, present, and future of Parkinson’s disease: a special essay on the 200th anniversary of the shaking palsy. Mov Disord 32:1264–1310
Olfert E, Cross B, Mc William A (1993) Guide for the care and use of experimental animals. Can Council Anim Care 1:211
Panula P, Nuutinen S (2013) The histaminergic network in the brain: basic organization and role in disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:472–487
Panula P, Pirvola U, Auvinen S, Airaksinen MS (1989) Histamine-immunoreactive nerve-fibers in the rat-brain. Neuroscience 28:585–610
Papathanou M, Rose S, McCreary A, Jenner P (2011) Induction and expression of abnormal involuntary movements is related to the duration of dopaminergic stimulation in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Eur J Neurosci 33:2247–2254
Papathanou M, Jenner P, Iravani M, Jackson M, Stockwell K, Strang I, Zeng B-Y, McCreary AC, Rose S (2014) The H-3 receptor agonist immepip does not affect L-Dopa-induced abnormal involuntary movements in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Eur J Pharmacol 741:304–310
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn, Academic Press, San Diego
Petroff OAC (2002) GABA and glutamate in the human brain. Neuroscientist 8:562–573
Pillot C, Heron A, Cochois V, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Ligneau X, Schwartz JC, Arrang JM (2002) A detailed mapping of the histamine H-3 receptor and its gene transcripts in rat brain. Neuroscience 114:173–193
Porras G, De Deurwaerdere P, Li Q, Marti M, Morgenstern R, Sohr R, Bezard E, Morari M, Meissner WG (2014) L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia: beyond an excessive dopamine tone in the striatum. Sci Rep 4(1):3730
Radnikow G, Misgeld U (1998) Dopamine D1 receptors facilitate GABAA synaptic currents in the rat substantia nigra pars reticulata. J Neurosci 18:2009–2016
Rapanelli M (2017) The magnificent two: histamine and the H3 receptor as key modulators of striatal circuitry. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 73:36–40
Rapanelli M, Frick LR, Horn KD, Schwarcz RC, Pogorelov V, Nairn AC, Pittenger C (2016) The histamine H3 receptor differentially modulates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Akt signaling in striatonigral and striatopallidal neurons. J Biol Chem 291:21042–21052
Reep RL, Corwin JV (1999) Topographic organization of the striatal and thalamic connections of rat medial agranular cortex. Brain Res 841:43–52
Reep RL, Cheatwood JL, Corwin JV (2003) The associative striatum: organization of cortical projections to the dorsocentral striatum in rats. J Comp Neurol 467:271–292
Rui G, Guangjian Z, Yong W, Jie F, Yanchao C, Xi J, Fen L (2013) High frequency electro-acupuncture enhances striatum DAT and D1 receptor expression, but decreases D2 receptor level in 6-OHDA lesioned rats. Behav Brain Res 237:263–269
Ryu JH, Yanai K, Iwata R, Ido T, Watanabe T (1994a) Heterogeneous distributions of histamine H3, dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in rat-brain. Neuroreport 5:621–624
Ryu JH, Yanai K, Watanabe T (1994b) Marked increase in histamine H3 receptors in the striatum and substantia nigra after 6-hydroxydopamine-induced denervation of dopaminergic neurons: an autoradiographic study. Neurosci Lett 178:19–22
Ryu JH, Yanai K, Zhao X-L, Watanabe T (1996) The effect of dopamine D1 receptor stimulation on the up-regulation of histamine H3-receptors following destruction of the ascending dopaminergic neurones. Br J Pharmacol 118:585–592
Sánchez-Lemus E, Arias-Montaño JA (2004) Histamine H-3 receptor activation inhibits dopamine D-1 receptor-induced cAMP accumulation in rat striatal slices. Neurosci Lett 364:179–184
Schousboe A (1981) Transport and metabolism of glutamate and GABA in neurons are glial cells. Int Rev Neurobiol 22:1–45
Spigolon G, Fisone G (2018) Signal transduction in L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia: from receptor sensitization to abnormal gene expression. J Neural Transm 125:1171–1186
Surmeier DJ, Ding J, Day M, Wang Z, Shen W (2007) D1 and D2 dopamine-receptor modulation of striatal glutamatergic signaling in striatal medium spiny neurons. Trends Neurosci 30:228–235
Takei H, Yamamoto K, Bae Y-C, Shirakawa T, Kobayashi M (2017) Histamine H3 heteroreceptors suppress glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission in the rat insular cortex. Front Neural Circuits 11:1–18
Waagepetersen HS, Sonnewald U, Schousboe A (2007) Glutamine, glutamate, and GABA: metabolic aspects. In: Lajtha A, Oja SS, Schousboe A, Saransaari P (eds) Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology: Amino Acids and Peptides in the Nervous System. Springer, US, Boston, MA, pp 1–21
Wu JH, Corwin JV, Reep RL (2009) Organization of the corticostriatal projection from rat medial agranular cortex to far dorsolateral striatum. Brain Res 1280:69–76
Wu X, Xu F-l, Wang B-j, Yao J (2018) Analysis of the promoter region of human dopamine receptor D1. J Mol Neurosci 65:438–443
Yoon S, Seger R (2006) The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors 24:21–44
Zheng X, Wu J, Zhu Y, Chen S, Chen Z, Chen T, Huang Z, Wei J, Li Y, Lei W (2018) A Comparative study for striatal-direct and -indirect pathway neurons to DA depletion-induced lesion in a PD rat model. Neurochem Int 118:14–22
Zhou Q-Y, Li C, Civelli R (1992) Characterization of gene organization and promoter region of the rat dopamine D1 receptor gene. J Neurochem 59:1875–1883
Acknowledgements
We thank MVZ Hugo Lecona Butrón for support with the housing, care, maintenance, and monitoring of the health of the experimental animals in INR-LGII. We also thank MVZ Javier Pérez Gallaga and Biol. Mónica Guadalupe Santamaria Olmedo for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Chronic administration of the H3R agonist immepip decreases L-Dopa-induced dyskinesias
• L-Dopa administration increases cortical GABA and glutamate levels
• Chronic immepip normalizes cortical GABA and glutamate levels
• Chronic H3R activation reduces cortico-striatal glutamatergic overactivity
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Figure S1. Representative chromatograms for glutamate, glutamine, and GABA. Panel A shows standards (10 μM). Panel B shows a striatal sample.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Avila-Luna, A., Gálvez-Rosas, A., Aguirre-Pérez, A. et al. Chronic H3R activation reduces L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia, normalizes cortical GABA and glutamate levels, and increases striatal dopamine D1R mRNA expression in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned male rats. Psychopharmacology 240, 1221–1234 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06339-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06339-1