Abstract
Rationale
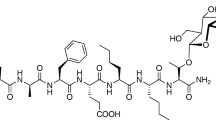
Nalfurafine is a G protein signaling-biased kappa opioid receptor (KOR) agonist approved in Japan for second-line treatment of uremic pruritus. Neither nalfurafine nor any other KOR agonist is currently approved anywhere for treatment of pain, but recent evidence suggests that G protein signaling-biased KOR agonists may have promise as candidate analgesics/antipruritics with reduced side effects compared to nonbiased or ß-arrestin-signaling-biased KOR agonists.
Objectives
This study compared nalfurafine effects in rats using assays of pain-stimulated and pain-depressed behavior used previously to evaluate other candidate analgesics. Nalfurafine effects were also examined in complementary assays of itch-stimulated and itch-depressed behavior.
Methods
Intraperitoneal lactic acid (IP acid) and intradermal serotonin (ID 5HT) served as noxious and pruritic stimuli, respectively, in male Sprague Dawley rats to stimulate stretching (IP acid) or scratching (ID 5HT) or to depress positively reinforced operant responding in an assay of intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS; both stimuli).
Results
Nalfurafine was equipotent to decrease IP acid-stimulated stretching and ID 5HT-stimulated scratching; however, doses of nalfurafine that decreased these pain/itch-stimulated behaviors also decreased control ICSS performance. Moreover, nalfurafine failed to alleviate either IP acid- or ID 5HT-induced depression of ICSS.
Conclusions
These results suggest that nalfurafine-induced decreases in pain/itch-stimulated behaviors may reflect nonselective decreases in motivated behavior rather than analgesia or antipruritus against the noxious and pruritic stimuli used here. This conclusion agrees with the absence of clinical data for nalfurafine analgesia and the weak clinical data for nalfurafine antipruritus. Nalfurafine bias for G protein signaling may not be sufficient for clinically safe and reliable analgesia or antipruritus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altarifi AA, Rice KC, Negus SS (2015) Effects of mu-opioid receptor agonists in assays of acute pain-stimulated and pain-depressed behavior in male rats: role of mu-agonist efficacy and noxious stimulus intensity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 352:208–217
Baggott MJ, Erowid E, Erowid F, Galloway GP, Mendelson J (2010) Use patterns and self-reported effects of Salvia divinorum: an internet-based survey. Drug Alcohol Depend 111:250–256
Balaskas EV, Bamihas GI, Karamouzis M, Voyiatzis G, Tourkantonis A (1998) Histamine and serotonin in uremic pruritus: effect of ondansetron in CAPD-pruritic patients. Nephron 78:395–402
Brown DC, Boston RC, Coyne JC, Farrar JT (2008) Ability of the canine brief pain inventory to detect response to treatment in dogs with osteoarthritis. J Am Vet Med Assoc 233:1278–1283
Brust TF, Morgenweck J, Kim SA, Rose JH, Locke JL, Schmid CL, Zhou L, Stahl EL, Cameron MD, Scarry SM, Aube J, Jones SR, Martin TJ, Bohn LM (2016) Biased agonists of the kappa opioid receptor suppress pain and itch without causing sedation or dysphoria. Sci Signal 9:ra117
Carlezon WA Jr, Chartoff EH (2007) Intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) in rodents to study the neurobiology of motivation. Nat Protoc 2:2987–2995
Carlezon WA Jr, Beguin C, DiNieri JA, Baumann MH, Richards MR, Todtenkopf MS, Rothman RB, Ma Z, Lee DY, Cohen BM (2006) Depressive-like effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:440–447
Carroll I, Thomas JB, Dykstra LA, Granger AL, Allen RM, Howard JL, Pollard GT, Aceto MD, Harris LS (2004) Pharmacological properties of JDTic: a novel kappa-opioid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 501:111–119
Cobos EJ, Ghasemlou N, Araldi D, Segal D, Duong K, Woolf CJ (2012) Inflammation-induced decrease in voluntary wheel running in mice: a nonreflexive test for evaluating inflammatory pain and analgesia. Pain 153:876–884
Cowan A, Kehner GB, Inan S (2015) Targeting itch with ligands selective for kappa opioid receptors. Handb Exp Pharmacol 226:291–314
Davis RE, Callahan MJ, Dickerson M, Downs DA (1992) Pharmacologic activity of CI-977, a selective kappa opioid agonist, in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:1044–1049
DiMattio KM, Ehlert FJ, Liu-Chen LY (2015) Intrinsic relative activities of kappa opioid agonists in activating Galpha proteins and internalizing receptor: differences between human and mouse receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 761:235–244
Dogra S, Yadav PN (2015) Biased agonism at kappa opioid receptors: implication in pain and mood disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 763:184–190
Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Farrar JT, Haythornthwaite JA, Jensen MP, Katz NP, Kerns RD, Stucki G, Allen RR, Bellamy N, Carr DB, Chandler J, Cowan P, Dionne R, Galer BS, Hertz S, Jadad AR, Kramer LD, Manning DC, Martin S, McCormick CG, McDermott MP, McGrath P, Quessy S, Rappaport BA, Robbins W, Robinson JP, Rothman M, Royal MA, Simon L, Stauffer JW, Stein W, Tollett J, Wernicke J, Witter J, Immpact (2005) Core outcome measures for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain 113: 9–19
Endoh T, Matsuura H, Tajima A, Izumimoto N, Tajima C, Suzuki T, Saitoh A, Suzuki T, Narita M, Tseng L, Nagase H (1999) Potent antinociceptive effects of TRK-820, a novel kappa-opioid receptor agonist. Life Sci 65:1685–1694
Endoh T, Tajima A, Suzuki T, Kamei J, Narita M, Tseng L, Nagase H (2000) Characterization of the antinociceptive effects of TRK-820 in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 387:133–140
Endoh T, Tajima A, Izumimoto N, Suzuki T, Saitoh A, Suzuki T, Narita M, Kamei J, Tseng LF, Mizoguchi H, Nagase H (2001) TRK-820, a selective kappa-opioid agonist, produces potent antinociception in cynomolgus monkeys. Jpn J Pharmacol 85:282–290
European Medicines Agency (2013) Assessment report: Winfuran. European Medicines Agency:Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use
Field MJ, Carnell AJ, Gonzalez MI, McCleary S, Oles RJ, Smith R, Hughes J, Singh L (1999) Enadoline, a selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist shows potent antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic actions in a rat model of surgical pain. Pain 80:383–389
Freitas KC, Carroll FI, Negus SS (2015) Effects of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists in assays of acute pain-stimulated and pain-depressed behaviors in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 355:341–350
Hasebe K, Kawai K, Suzuki T, Kawamura K, Tanaka T, Narita M, Nagase H, Suzuki T (2004) Possible pharmacotherapy of the opioid kappa receptor agonist for drug dependence. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1025:404–413
Hunter JC, Leighton GE, Meecham KG, Boyle SJ, Horwell DC, Rees DC, Hughes J (1990) CI-977, a novel and selective agonist for the kappa-opioid receptor. Br J Pharmacol 101:183–189
Inui S (2015) Nalfurafine hydrochloride to treat pruritus: a review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 8:249–255
Jaiswal D, Uzans D, Hayden J, Kiberd BA, Taennankore KK (2016) Targeting the opioid pathway for uremic pruritus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Kidney Health Dis In press
Jinks SL, Carstens E (2002) Responses of superficial dorsal horn neurons to intradermal serotonin and other irritants: comparison with scratching behavior. J Neurophysiol 87:1280–1289
Johnson MW, MacLean KA, Reissig CJ, Prisinzano TE, Griffiths RR (2011) Human psychopharmacology and dose-effects of salvinorin A, a kappa opioid agonist hallucinogen present in the plant Salvia divinorum. Drug Alcohol Depend 115:150–155
Kandasamy R, Lee AT, Morgan MM (2017) Depression of home cage wheel running: a reliable and clinically relevant method to assess migraine pain in rats. J Headache Pain 18:5
Kivell B, Prisinzano TE (2010) Kappa opioids and the modulation of pain. Psychopharmacology 210:109–119
Klein A, Carstens MI, Carstens E (2011) Facial injections of pruritogens or algogens elicit distinct behavior responses in rats and excite overlapping populations of primary sensory and trigeminal subnucleus caudalis neurons. J Neurophysiol 106:1078–1088
Kumagai H, Ebata T, Takamori K, Miyasato K, Muramatsu T, Nakamoto H, Kurihara M, Yanagita T, Suzuki H (2012) Efficacy and safety of a novel k-agonist for managing intractable pruritus in dialysis patients. Am J Nephrol 36:175–183
Kwilasz AJ, Negus SS (2012) Dissociable effects of the cannabinoid receptor agonists Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and CP55940 on pain-stimulated versus pain-depressed behavior in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 343:389–400
Leitl MD, Onvani S, Bowers MS, Cheng K, Rice KC, Carlezon WA Jr, Banks ML, Negus SS (2014) Pain-related depression of the mesolimbic dopamine system in rats: expression, blockade by analgesics, and role of endogenous kappa-opioids. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:614–624
Listos J, Merska A, Fidecka S (2011) Pharmacological activity of salvinorin A, the major component of Salvia divinorum. Pharmacol Rep 63:1305–1309
MacLean KA, Johnson MW, Reissig CJ, Prisinzano TE, Griffiths RR (2013) Dose-related effects of salvinorin A in humans: dissociative, hallucinogenic, and memory effects. Psychopharmacology 226:381–392
McGrath PJ, Unruh AM (2013) Measurement and assessment of pediatric pain. In: McMahon SB, Koltzenburg M, Tracey I, Turk DC (eds) Wall and Melzack’s textbook of pain, 6th Edition. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 320–327
Melzack R, Katz J (2013) Pain measurement in adult patients. In: McMahon SB, Koltzenburg M, Tracey I, Turk DC (eds) Wall and Melzack’s textbook of pain, 6th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 301–319
Nagase H, Hayakawa J, Kawamura K, Kawai K, Takezawa Y, Matsuura H, Tajima C, Endo T (1998) Discovery of a structurally novel opioid kappa-agonist derived from 4,5-epoxymorphinan. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 46:366–369
National Research Council (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academies Press, Washington DC
National_Research_Council (2003) Guidelines for the care and use of mammals in neuroscience and behavioral research. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Negus SS (2013) Expression and treatment of pain-related behavioral depression. Lab Anim (NY) 42:292–300
Negus SS, Miller LL (2014) Intracranial self-stimulation to evaluate abuse potential of drugs. Pharmacol Rev 66:869–917
Negus SS, Vanderah TW, Brandt MR, Bilsky EJ, Becerra L, Borsook D (2006) Preclinical assessment of candidate analgesic drugs: recent advances and future challenges. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:507–514
Negus SS, Morrissey EM, Rosenberg M, Cheng K, Rice KC (2010) Effects of kappa opioids in an assay of pain-depressed intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Psychopharmacology 210:149–159
Negus SS, O'Connell R, Morrissey E, Cheng K, Rice KC (2012a) Effects of peripherally restricted kappa opioid receptor agonists on pain-related stimulation and depression of behavior in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 340:501–509
Negus SS, Rosenberg MB, Altarifi AA, O'Connell RH, Folk JE, Rice KC (2012b) Effects of the delta opioid receptor agonist SNC80 on pain-related depression of intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) in rats. J Pain 13:317–327
Negus SS, Neddenriep B, Altarifi AA, Carroll FI, Leitl MD, Miller LL (2015) Effects of ketoprofen, morphine, and kappa opioids on pain-related depression of nesting in mice. Pain 156:1153–1160
Pande AC, Pyke RE, Greiner M, Cooper SA, Benjamin R, Pierce MW (1996) Analgesic efficacy of the kappa-receptor agonist, enadoline, in dental surgery pain. Clin Neuropharmacol 19:92–97
Pereira Do Carmo G, Stevenson GW, Carlezon WA, Negus SS (2009) Effects of pain- and analgesia-related manipulations on intracranial self-stimulation in rats: further studies on pain-depressed behavior. Pain 144:170–177
Rosenberg MB, Carroll FI, Negus SS (2013) Effects of monoamine reuptake inhibitors in assays of acute pain-stimulated and pain-depressed behavior in rats. J Pain 14:246–259
Runyon SP, Brieaddy LE, Mascarella SW, Thomas JB, Navarro HA, Howard JL, Pollard GT, Carroll FI (2010) Analogues of (3R)-7-hydroxy-N-[(1S)-1-{[(3R,4R)-4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dimethyl-1-piperidinyl ]methyl}-2-methylpropyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-isoquinolinecarboxamide (JDTic). Synthesis and in vitro and in vivo opioid receptor antagonist activity. J Med Chem 53:5290–5301
Schattauer SS, Kuhar JR, Song A, Chavkin C (2017) Nalfurafine is a G-protein biased agonist having significantly greater bias at the human than rodent form of the kappa opioid receptor. Cell Signal 32:59–65
Seguin L, Le Marouille-Girardon S, Millan MJ (1995) Antinociceptive profiles of non-peptidergic neurokinin1 and neurokinin2 receptor antagonists: a comparison to other classes of antinociceptive agent. Pain 61:325–343
Thomsen JS, Petersen MB, Benfeldt E, Jensen SB, Serup J (2001) Scratch induction in the rat by intradermal serotonin: a model for pruritus. Acta Derm Venereol 81:250–254
Todtenkopf MS, Marcus JF, Portoghese PS, Carlezon WA Jr (2004) Effects of kappa-opioid receptor ligands on intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Psychopharmacology 172:463–470
Togashi Y, Umeuchi H, Okano K, Ando N, Yoshizawa Y, Honda T, Kawamura K, Endoh T, Utsumi J, Kamei J, Tanaka T, Nagase H (2002) Antipruritic activity of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist, TRK-820. Eur J Pharmacol 435:259–264
Wadenberg ML (2003) A review of the properties of spiradoline: a potent and selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist. CNS Drug Rev 9:187–198
White KL, Robinson JE, Zhu H, DiBerto JF, Polepally PR, Zjawiony JK, Nichols DE, Malanga CJ, Roth BL (2015) The G protein-biased kappa-opioid receptor agonist RB-64 is analgesic with a unique spectrum of activities in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 352:98–109
Zhou L, Lovell KM, Frankowski KJ, Slauson SR, Phillips AM, Streicher JM, Stahl E, Schmid CL, Hodder P, Madoux F, Cameron MD, Prisinzano TE, Aube J, Bohn LM (2013) Development of functionally selective, small molecule agonists at kappa opioid receptors. J Biol Chem 288:36703–36716
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by NIH grants R01NS070715, R01DA039167, R01DA009045, and T32DA007027.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Lazenka contributed as a postdoctoral fellow from the Negus Lab at VCU. He conducted most of the studies, analyzed data, prepared figures, and worked with the senior author to write manuscript drafts and incorporate author comments into the final version of the manuscript.
Dr. Moerke also contributed as a postdoctoral fellow from the Negus Lab at VCU. She conducted studies, performed initial data analysis and interpretation on the studies she conducted, contributed comments to manuscript drafts, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Drs. Townsend and Freeman consulted on issues of experimental design regarding the behavioral pharmacology of nalfurafine, contributed comments to manuscript drafts, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Dr. Carroll provided JDTic, consulted on issues of experimental design regarding the behavioral pharmacology of JDTic, contributed comments to manuscript drafts, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Dr. Negus supervised all aspects of experimental design, conduct, analysis, and interpretation and worked the first author to write manuscript drafts and incorporate author comments into the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazenka, M.L., Moerke, M.J., Townsend, E.A. et al. Dissociable effects of the kappa opioid receptor agonist nalfurafine on pain/itch-stimulated and pain/itch-depressed behaviors in male rats. Psychopharmacology 235, 203–213 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4758-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4758-7