Abstract
Rationale
Although antipsychotic treatment often causes weight gain and lipid abnormalities, quantitative analyses of tissue-specific body fat content and its distribution along with adipokines have not been reported for antipsychotic-treated patients.
Objectives
The purposes of the present study were to quantitatively assess abdominal and liver fat in patients with schizophrenia on antipsychotic treatment and age- and body mass index (BMI)-matched healthy controls and to evaluate their associations with plasma leptin and adiponectin levels.
Methods
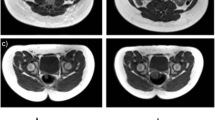
In 13 schizophrenia patients on antipsychotic treatment and 11 age- and BMI-matched controls, we simultaneously quantified visceral and subcutaneous fat content using T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and liver fat content by 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Associations of tissue-specific fat content with plasma levels of leptin and adiponectin were evaluated.
Results
Plasma adiponectin level (μg/mL) was not statistically different between groups (7.02 ± 2.67 vs. 7.59 ± 2.92), whereas plasma leptin level (ng/mL) trended to be higher in patients than in controls (11.82 ± 7.89 vs. 7.93 ± 5.25). The values of liver fat (%), visceral fat (L), and subcutaneous fat (L) were 9.64 ± 8.03 vs. 7.07 ± 7.35, 4.41 ± 1.64 vs. 3.31 ± 1.97, and 8.37 ± 3.34 vs. 7.16 ± 2.99 in patients vs. controls, respectively. Liver fat content was inversely correlated with adiponectin in controls (r = − 0.87, p < 0.001) but not in patients (r = − 0.26, p = 0.39). In both groups, visceral fat was inversely associated with adiponectin (controls : r = − 0.66, p = 0.03; patients : r = − 0.65, p = 0.02), while subcutaneous fat was positively correlated with leptin (controls : r = 0.90, p < 0.001; patients : r = 0.67, p = 0.01).
Conclusions
These findings suggest that antipsychotic treatment may disrupt the physiological relationship between liver fat content and adiponectin but does not essentially affect the associations of adiponectin and leptin with visceral and subcutaneous compartments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Press, Washington DC
Aye IL, Rosario FJ, Powell TL, Jansson T (2015) Adiponectin supplementation in pregnant mice prevents the adverse effects of maternal obesity on placental function and fetal growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:12858–12863
Baptista T, Beaulieu S (2002) Are leptin and cytokines involved in body weight gain during treatment with antipsychotic drugs? Can J Psychiatr 47:742–749
Bartoli F, Crocamo C, Clerici M, Carrà G (2015) Second-generation antipsychotics and adiponectin levels in schizophrenia: a comparative meta-analysis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 25:1767–1774
Baum T, Cordes C, Dieckmeyer M, Ruschke S, Franz D, Hauner H, Kirschke JS, Karampinos DC (2016) MR-based assessment of body fat distribution and characteristics. Eur J Radiol 85:1512–1518
Birkenaes AB, Birkeland KI, Engh JA, Faerden A, Jonsdottir H, Ringen PA, Friis S, Opjordsmoen S, Andreassen OA (2008) Dyslipidemia independent of body mass in antipsychotic-treated patients under real-life conditions. J Clin Psychopharmacol 28:132–137
Bohte AE, van Werven JR, Bipat S, Stoker J (2011) The diagnostic accuracy of US, CT, MRI and 1H-MRS for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis compared with liver biopsy: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 21:87–97
Bredella MA, Torriani M, Ghomi RH, Thomas BJ, Brick DJ, Gerweck AV, Harrington LM, Miller KK (2011) Adiponectin is inversely associated with intramyocellular and intrahepatic lipids in obese premenopausal women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19:911–916
Chan DC, Watts GF, Ng TW, Hua J, Song S, Barrett PH (2006) Measurement of liver fat by magnetic resonance imaging: relationships with body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipids in healthy men. Diabetes Obes Metab 8:698–702
de Leon J, Correa JC, Ruano G, Windemuth A, Arranz MJ, Diaz FJ (2008) Exploring genetic variations that may be associated with the direct effects of some antipsychotics on lipid levels. Schizophr Res 98:40–46
Fabbrini E, Magkos F, Mohammed BS, Pietka T, Abumrad NA, Patterson BW, Okunade A, Klein S (2009) Intrahepatic fat, not visceral fat, is linked with metabolic complications of obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:15430–15435
Fernandez-Egea E, Bernardo M, Donner T, Conget I, Parellada E, Justicia A, Esmatjes E, Garcia-Rizo C, Kirkpatrick B (2009) Metabolic profile of antipsychotic-naive individuals with non-affective psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 194:434–438
Fernández-Real JM, Castro A, Vázquez G, Casamitjana R, López-Bermejo A, Peñarroja G, Ricart W (2004) Adiponectin is associated with vascular function independent of insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 27:739–745
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (1996) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders research version (SCID-I). New York State Psychiatric Institute Biometrics Research, New York
Fox CS, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Pou KM, Maurovich-Horvat P, Liu CY, Vasan RS, Murabito JM, Meigs JB, Cupples LA, D’Agostino RB Sr, O’Donnell CJ (2007) Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 116:39–48
Fu Y (2014) Adiponectin signaling and metabolic syndrome. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 121:293–319
Gil-Campos M, Cañete RR, Gil A (2004) Adiponectin, the missing link in insulin resistance and obesity. Clin Nutr 23:963–974
Goncalves P, Araujo JR, Martel F (2015) Antipsychotics-induced metabolic alterations: focus on adipose tissue and molecular mechanisms. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 25:1–16
Hanssens L, van Winkel R, Wampers M, Van Eyck D, Scheen A, Reginster JY, Collette J, Peuskens J, De Hert M (2008) A cross-sectional evaluation of adiponectin plasma levels in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Schizophr Res 106:308–314
Henderson DC, Vincenzi B, Andrea NV, Ulloa M, Copeland PM (2015) Pathophysiological mechanisms of increased cardiometabolic risk in people with schizophrenia and other severe mental illnesses. Lancet Psychiatry 2:452–464
Hosojima H, Togo T, Odawara T, Hasegawa K, Miura S, Kato Y, Kanai A, Kase A, Uchikado H, Hirayasu Y (2006) Early effects of olanzapine on serum levels of ghrelin, adiponectin and leptin in patients with schizophrenia. J Psychopharmacol 20:75–79
Hwang JH, Stein DT, Barzilai N, Cui MH, Tonelli J, Kishore P, Hawkins M (2007) Increased intrahepatic triglyceride is associated with peripheral insulin resistance: in vivo MR imaging and spectroscopy studies. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E1663–E1669
Jin H, Meyer JM, Mudaliar S, Jeste DV (2008) Impact of atypical antipsychotic therapy on leptin, ghrelin, and adiponectin. Schizophr Res 100:70–85
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261–276
Kirk SL, Glazebrook J, Grayson B, Neill JC, Reynolds GP (2009) Olanzapine-induced weight gain in the rat: role of 5-HT2C and histamine H1 receptors. Psychopharmacology 207:119–125
Kishida K, Kim KK, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Kang HC, Shimomura I (2011) Relationships between circulating adiponectin levels and fat distribution in obese subjects. J Atheroscler Thromb 18:592–595
Koch C, Augustine RA, Steger J, Ganjam GK, Benzler J, Pracht C, Lowe C, Schwartz MW, Shepherd PR, Anderson GM, Grattan DR, Tups A (2010) Leptin rapidly improves glucose homeostasis in obese mice by increasing hypothalamic insulin sensitivity. J Neurosci 30:16180–16187
Kotronen A, Seppanen-Laakso T, Westerbacka J, Kiviluoto T, Arola J, Ruskeepaa AL, Yki-Jarvinen H, Oresic M (2010) Comparison of lipid and fatty acid composition of the liver, subcutaneous and intra-abdominal adipose tissue, and serum. Obesity(Silver Spring) 18:937–944
Kumada M, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Kobayashi H, Okamoto Y, Ohashi K, Maeda K, Nagaretani H, Kishida K, Maeda N, Nagasawa A, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2004) Adiponectin specifically increased tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 through interleukin-10 expression in human macrophages. Circulation 109:2046–2049
Lilja M, Rolandsson O, Norberg M, Söderberg S (2012) The impact of leptin and adiponectin on incident type 2 diabetes is modified by sex and insulin resistance. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 10:143–151
Livingstone RS, Begovatz P, Kahl S, Nowotny B, Strassburger K, Giani G, Bunke J, Roden M, Hwang JH (2014) Initial clinical application of modified Dixon with flexible echo times: hepatic and pancreatic fat assessments in comparison with (1)H MRS. MAGMA 27:397–405
Lu ML, Wang TN, Lin TY, Shao WC, Chang SH, Chou JY, Ho YF, Liao YT, Chen VC (2015 ) Differential effects of olanzapine and clozapine on plasma levels of adipocytokines and total ghrelin. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry: 47–50
Machann J, Thamer C, Stefan N, Schwenzer NF, Kantartzis K, Haring HU, Claussen CD, Fritsche A, Schick F (2010) Follow-up whole-body assessment of adipose tissue compartments during a lifestyle intervention in a large cohort at increased risk for type 2 diabetes. Radiology 257:353–363
Mattioli B, Straface E, Matarrese P, Quaranta MG, Giordani L, Malorni W, Viora M (2008) Leptin as an immunological adjuvant: enhanced migratory and CD8+ T cell stimulatory capacity of human dendritic cells exposed to leptin. FASEB J 22:2012–2022
Meyer JM (2002) A retrospective comparison of weight, lipid, and glucose changes between risperidone- and olanzapine-treated inpatients: metabolic outcomes after 1 year. J Clin Psychiatry 63:425–433
Meyer JM, Koro CE (2004) The effects of antipsychotic therapy on serum lipids: a comprehensive review. Schizophr Res 70:1–17
Morris DL, Rui L (2009) Recent advances in understanding leptin signaling and leptin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297:E1247–E1259
Murashita M, Inoue T, Kusumi I, Nakagawa S, Itoh K, Tanaka T, Izumi T, Hosoda H, Kangawa K, Koyama T (2007) Glucose and lipid metabolism of long-term risperidone monotherapy in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 61:54–58
Murashita M, Kusumi I, Inoue T, Takahashi Y, Hosoda H, Kangawa K, Koyama T (2005) Olanzapine increases plasma ghrelin level in patients with schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology 30:106–110
Myers MG, Cowley MA, Münzberg H (2008) Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 70:537–556
Neamat-Allah J, Johnson T, Nabers D, Hüsing A, Teucher B, Katzke V, Delorme S, Kaaks R, Kühn T (2015) Can the use of blood-based biomarkers in addition to anthropometric indices substantially improve the prediction of visceral fat volume as measured by magnetic resonance imaging? Eur J Nutr 54:701–708
Neeland IJ, Turer AT, Ayers CR, Powell-Wiley TM, Vega GL, Farzaneh-Far R, Grundy SM, Khera A, McGuire DK, de Lemos JA (2012) Dysfunctional adiposity and the risk of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in obese adults. JAMA 308:1150–1159
Ohashi K, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Nakamura T, Sumitsuji S, Kawamoto T, Matsumoto S, Nagaretani H, Kumada M, Okamoto Y, Nishizawa H, Kishida K, Maeda N, Hiraoka H, Iwashima Y, Ishikawa K, Ohishi M, Katsuya T, Rakugi H, Ogihara T, Matsuzawa Y (2004) Adiponectin I164T mutation is associated with the metabolic syndrome and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:1195–1200
Paredes RM, Quinones M, Marballi K, Gao X, Valdez C, Ahuja SS, Velligan D, Walss-Bass C (2014) Metabolomic profiling of schizophrenia patients at risk for metabolic syndrome. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17:1139–1148
Richards AA, Hickman IJ, Wang AY, Jones AL, Newell F, Mowry BJ, Whitehead JP, Prins JB, Macdonald GA (2006) Olanzapine treatment is associated with reduced high molecular weight adiponectin in serum: a potential mechanism for olanzapine-induced insulin resistance in patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 26:232–237
Skrede S, Ferno J, Vazquez MJ, Fjaer S, Pavlin T, Lunder N, Vidal-Puig A, Dieguez C, Berge RK, Lopez M, Steen VM (2012) Olanzapine, but not aripiprazole, weight-independently elevates serum triglycerides and activates lipogenic gene expression in female rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:163–179
Sporn AL, Bobb AJ, Gogtay N, Stevens H, Greenstein DK, Clasen LS, Tossell JW, Nugent T, Gochman PA, Sharp WS, Mattai A, Lenane MC, Yanovski JA, Rapoport JL (2005) Hormonal correlates of clozapine-induced weight gain in psychotic children: an exploratory study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 44:925–933
Staiger H, Tschritter O, Machann J, Thamer C, Fritsche A, Maerker E, Schick F, Häring HU, Stumvoll M (2003) Relationship of serum adiponectin and leptin concentrations with body fat distribution in humans. Obes Res 11:368–372
Starrenburg FC, Bogers JP (2009) How can antipsychotics cause diabetes mellitus? Insights based on receptor-binding profiles, humoral factors and transporter proteins. Eur Psychiatry 24:164–170
Steiger JH (1980) Tests for comparing elements of a correlation matrix. Psychol Bull 87:245–251
Stubbs B, Wang AK, Vancampfort D, Miller BJ (2016) Are leptin levels increased among people with schizophrenia versus controls? A systematic review and comparative meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 63:144–154
Sugai T, Suzuki Y, Fukui N, Ono S, Watanabe J, Tsuneyama N, Someya T (2012) Dysregulation of adipocytokines related to second-generation antipsychotics in normal fasting glucose patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 32:390–393
Tai E, Lau TN, Ho SC, Fok AC, Tan CE (2000) Body fat distribution and cardiovascular risk in normal weight women. Associations with insulin resistance, lipids and plasma leptin. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:751–757
Tanyanskiy DA, Martynikhin IA, Rotar OP, Konradi AO, Sokolian NA, Neznanov NG, Denisenko AD (2015) Association of adipokines with metabolic disorders in patients with schizophrenia: results of comparative study with mental healthy cohort. Diabetes Metab Syndr 9:163–167
Thomas EL, Frost G, Taylor-Robinson SD, Bell JD (2012a) Excess body fat in obese and normal-weight subjects. Nutr Res Rev 25:150–161
Thomas EL, Parkinson JR, Frost GS, Goldstone AP, Doré CJ, McCarthy JP, Collins AL, Fitzpatrick JA, Durighel G, Taylor-Robinson SD, Bell JD (2012b) The missing risk: MRI and MRS phenotyping of abdominal adiposity and ectopic fat. Obesity (Silver Spring) 20:76–87
Togo T, Kojima K, Shoji M, Kase A, Uchikado H, Katsuse O, Iseki E, Kosaka K (2004) Serum adiponectin concentrations during treatment with olanzapine or risperidone: a pilot study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 19:37–40
Wampers M, Hanssens L, van Winkel R, Heald A, Collette J, Peuskens J, Reginster JY, Scheen A, De Hert M (2012) Differential effects of olanzapine and risperidone on plasma adiponectin levels over time: results from a 3-month prospective open-label study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 22:17–26
Whitney Z, Procyshyn RM, Fredrikson DH, Barr AM (2015) Treatment of clozapine-associated weight gain: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 71:389–401
Woods SC, D’Alessio DA (2008) Central control of body weight and appetite. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(11 Suppl 1):S37–S50
Yan H, Chen JD, Zheng XY (2013) Potential mechanisms of atypical antipsychotic-induced hypertriglyceridemia. Psychopharmacology 229:1–7
Yang R, Barouch LA (2007) Leptin signaling and obesity: cardiovascular consequences. Circ Res 101:545–559
Zhang ZJ, Yao ZJ, Liu W, Fang Q, Reynolds GP (2004) Effects of antipsychotics on fat deposition and changes in leptin and insulin levels. Magnetic resonance imaging study of previously untreated people with schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 184:58–62
Zimmermann U, Kraus T, Himmerich H, Schuld A, Pollmacher T (2003) Epidemiology, implications and mechanisms underlying drug-induced weight gain in psychiatric patients. J Psychiatr Res 37:193–220
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2015R1C1A2A01051461), and Gachon University Gil Medical Center (Grant #2013-33). For Jong-Hoon Kim, this work was partly supported by a grant of the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (number: HI14C2750). The authors thank Prof. Jun-Young Chung for technical support with the Siemens scanner and Prof. Daniel T Stein at Albert Einstein College of Medicine (New York, USA) for fruitful discussion on the procedure of blood sampling and analyses. The authors also thank the radiographers for scanning participants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JH., Kim, JH., Park, PW. et al. Body and liver fat content and adipokines in schizophrenia: a magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy study. Psychopharmacology 234, 1923–1932 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4598-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4598-5