Abstract
Rationale
Low-efficacy mu opioid receptor agonists may be useful for some clinical indications, but clinically available low-efficacy mu agonists also have low selectivity for mu vs. kappa opioid receptors. NAQ (17-cyclopropylmethyl-3,14ß-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6α-[(3′-isoquinolyl)acetamido]morphinan) is a novel opioid receptor ligand with low-efficacy at mu receptors and greater mu-receptor selectivity than existing low-efficacy agonists.
Objectives
This study examined behavioral effects of NAQ in rats using an intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) procedure that has been used previously to examine other opioids. NAQ effects were examined before, during, and after chronic morphine treatment, and effects of NAQ were compared to effects of nalbuphine and naltrexone.
Methods
Adult male Sprague–Dawley rats were trained to respond for electrical brain stimulation delivered via electrodes implanted in the medial forebrain bundle. A range of brain stimulation frequencies maintained a wide range of baseline ICSS rates. Effects of NAQ (0.32–10 mg/kg), nalbuphine (1.0 mg/kg), and naltrexone (0.1 mg/kg) were determined before morphine treatment and during treatment with 3.2 and 18 mg/kg/day morphine. NAQ effects were also redetermined beginning 2 weeks after termination of morphine treatment.
Results
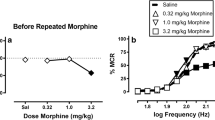
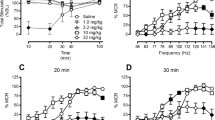
NAQ produced weak ICSS facilitation in morphine-naïve rats but more robust ICSS facilitation during and after morphine treatment and also reversed morphine withdrawal-associated depression of ICSS. These effects were similar to effects of nalbuphine.
Conclusions
These results agree with the in vitro characterization of NAQ as a low-efficacy mu agonist. Opioid exposure may enhance abuse-related effects of NAQ, but NAQ may also serve as a low-efficacy and relatively safe option for treatment of opioid withdrawal or dependence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altarifi AA, Negus SS (2011) Some determinants of morphine effects on intracranial self-stimulation in rats: dose, pretreatment time, repeated treatment, and rate dependence. Behav Pharmacol 22:663–673
Altarifi AA, Miller LL, Negus SS (2012) Role of mu-opioid receptor reserve and mu-agonist efficacy as determinants of the effects of micro-agonists on intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Behav Pharmacol 23:678–692
Altarifi AA, Rice KC, Negus SS (2013) Abuse-related effects of mu-opioid analgesics in an assay of intracranial self-stimulation in rats: modulation by chronic morphine exposure. Behav Pharmacol 24:459–470
Balster RL, Lukas SE (1985) Review of self-administration. Drug Alcohol Depend 14:249–261
Beguin C, Potter DN, Dinieri JA, Munro TA, Richards MR, Paine TA, Berry L, Zhao Z, Roth BL, Xu W, Liu-Chen LY, Carlezon WA Jr, Cohen BM (2008) N-methylacetamide analog of salvinorin A: a highly potent and selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist with oral efficacy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324:188–195
Emmerson PJ, Liu MR, Woods JH, Medzihradsky F (1994) Binding affinity and selectivity of opioids at mu, delta and kappa receptors in monkey brain membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:1630–1637
Emmerson PJ, Clark MJ, Mansour A, Akil H, Woods JH, Medzihradsky F (1996) Characterization of opioid agonist efficacy in a C6 glioma cell line expressing the mu opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:1121–1127
Gear RW, Bogen O, Ferrari LF, Green PG, Levine JD (2014) NOP receptor mediates anti-analgesia induced by agonist–antagonist opioids. Neuroscience 257:139–148
Gutstein H, Akil H (2006) Opioid analgesics. In: Brunton L, Lazo J, Parker K (eds) Goodman and Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 11th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 547–590
Hoskin PJ, Hanks GW (1991) Opioid agonist–antagonist drugs in acute and chronic pain states. Drugs 41:326–344
Hursh SR, Winger G (1995) Normalized demand for drugs and other reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav 64:373–384
Kenny PJ, Chen SA, Kitamura O, Markou A, Koob GF (2006) Conditioned withdrawal drives heroin consumption and decreases reward sensitivity. J Neurosci 26:5894–5900
Koob GF, Spector NH, Meyerhoff JL (1975) Effects of heroin on lever pressing for intracranial self-stimulation, food and water in the rat. Psychopharmacologia 42:231–234
Kornetsky C, Esposito RU (1979) Euphorigenic drugs: effects on the reward pathways of the brain. Fed Proc 38:2473–2476
Kornetsky C, Esposito RU, McLean S, Jacobson JO (1979) Intracranial self-stimulation thresholds: a model for the hedonic effects of drugs of abuse. Arch Gen Psychiatry 36:289–292
Kreek MJ, LaForge KS, Butelman E (2002) Pharmacotherapy of addictions. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:710–726
Li G, Aschenbach LC, Chen J, Cassidy MP, Stevens DL, Gabra BH, Selley DE, Dewey WL, Westkaemper RB, Zhang Y (2009) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 6alpha- and 6beta-N-heterocyclic substituted naltrexamine derivatives as mu opioid receptor selective antagonists. J Med Chem 52:1416–1427
Liu J, Schulteis G (2004) Brain reward deficits accompany naloxone-precipitated withdrawal from acute opioid dependence. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79(1):101–108
Negus SS, Altarifi A (2013) Mu, delta and kappa opioid agonist effects in novel assays of pain-depressed behavior. In: Ko H, Husbands SM (eds) Research and development of opioid-related ligands. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 163–176
Negus SS, Banks ML (2013) Medications development for opioid abuse. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3:a012104
Negus SS, Miller LL (2014) Intracranial self-stimulation to evaluate abuse potential of drugs. Pharmacol Rev 66(3):869–917
Negus SS, Morrissey EM, Rosenberg M, Cheng K, Rice KC (2010) Effects of kappa opioids in an assay of pain-depressed intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 210:149–159
Negus SS, O’Connell R, Morrissey E, Cheng K, Rice KC (2012a) Effects of peripherally restricted kappa opioid receptor agonists on pain-related stimulation and depression of behavior in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 340:501–509
Negus SS, Rosenberg MB, Altarifi AA, O’Connell RH, Folk JE, Rice KC (2012b) Effects of the delta opioid receptor agonist SNC80 on pain-related depression of intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) in rats. J Pain 13:317–327
Peng X, Knapp BI, Bidlack JM, Neumeyer JL (2007) Pharmacological properties of bivalent ligands containing butorphan linked to nalbuphine, naltrexone, and naloxone at mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors. J Med Chem 50:2254–2258
Pereira Do Carmo G, Folk JE, Rice KC, Chartoff E, Carlezon WA Jr, Negus SS (2009) The selective non-peptidic delta opioid agonist SNC80 does not facilitate intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 604:58–65
Pfeiffer A, Brantl V, Herz A, Emrich HM (1986) Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors. Science 233:774–776
Pick CG, Paul D, Pasternak GW (1992) Nalbuphine, a mixed kappa 1 and kappa 3 analgesic in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 262:1044–1050
Preston KL, Jasinski DR (1991) Abuse liability studies of opioid agonist-antagonists in humans. Drug Alcohol Depend 28:49–82
Raynor K, Kong H, Chen Y, Yasuda K, Yu L, Bell GI, Reisine T (1994) Pharmacological characterization of the cloned kappa-, delta-, and mu-opioid receptors. Mol Pharmacol 45:330–334
Remmers AE, Clark MJ, Mansour A, Akil H, Woods JH, Medzihradsky F (1999) Opioid efficacy in a C6 glioma cell line stably expressing the human kappa opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:827–833
Selley DE, Liu Q, Childers SR (1998) Signal transduction correlates of mu opioid agonist intrinsic efficacy: receptor-stimulated [35S]GTP gamma S binding in mMOR-CHO cells and rat thalamus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:496–505
Steinfels GF, Young GA, Khazan N (1981) The new mixed agonist–antagonist analgesics, nalbuphine and butorphanol, vs. pentazocine: relapse and substitution in morphine-addict rats. NIDA Res Monogr 34:138–144
Stoker AK, Markou A (2011) The intracranial self-stimulation procedure provides quantitative measures of brain reward function. In: Gould TD (ed) Mood and anxiety related phenotypes in mice: characterization using behavioral tests, volume II. Neuromethods volume 63. Humana, Totowa, pp 307–331
Todtenkopf MS, Marcus JF, Portoghese PS, Carlezon WA Jr (2004) Effects of kappa-opioid receptor ligands on intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 172:463–470
Vlachou S, Markou A (2011) Intracranial self-stimulation. In: Olmstead MC (ed) Animal models of drug addiction. Humana, New York, pp 3–56
Walsh SL, Strain EC, Abreu ME, Bigelow GE (2001) Enadoline, a selective kappa opioid agonist: comparison with butorphanol and hydromorphone in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 157:151–162
Wines JD Jr, Gruber AJ, Pope HG Jr, Lukas SE (1999) Nalbuphine hydrochloride dependence in anabolic steroid users. Am J Addict 8:161–164
Wise RA (1996) Addictive drugs and brain stimulation reward. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:319–340
Yuan Y, Li G, He H, Stevens DL, Kozak P, Scoggins KL, Mitra P, Gerk PM, Selley DE, Dewey WL, Zhang Y (2011) Characterization of 6alpha- and 6beta-N-heterocyclic substituted naltrexamine derivatives as novel leads to development of mu opioid receptor selective antagonists. ACS Chem Neurosci 2:346–351
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NIH grants R01-NS070715, R01-DA026946, and R01-DA024022.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altarifi, A.A., Yuan, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Effects of the novel, selective and low-efficacy mu opioid receptor ligand NAQ on intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Psychopharmacology 232, 815–824 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3719-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3719-7