Abstract
Rationale
Chronic treatment with dopamine (DA) receptor agonists and antagonists can differentially affect measures of DA D2/D3 receptor number and function, but the effects of chronic treatment with a partial D2/D3 receptor agonist are not clear.
Objective
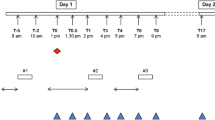
We used a within-subjects design in male cynomolgus monkeys to determine the effects of repeated (17-day) treatment with the D2/D3 receptor partial agonist aripiprazole (ARI; 0.03 mg/kg and 0.1 mg/kg i.m.) on food-reinforced behavior (n = 5) and on D2/D3 receptor availability as measured with positron emission tomography (PET; n = 9).
Methods
Five monkeys responded under a fixed-ratio 50 schedule of food reinforcement and D2/D3 receptor availability was measured before and 4 days after ARI treatment using PET and the D2/D3 receptor-selective radioligand [18F]fluoroclebopride (FCP). Four additional monkeys were studied using [11C]raclopride and treated sequentially with each dose of ARI for 17 days.
Results
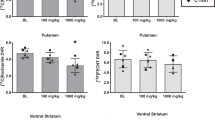
ARI decreased food-maintained responding with minimal evidence of tolerance. Repeated ARI administration increased FCP and raclopride distribution volume ratios (DVRs) in the caudate nucleus and putamen in most monkeys, but decreases were observed in monkeys with the highest baseline DVRs.
Conclusions
The results indicate that repeated treatment with a low-efficacy DA receptor partial agonist produces effects on brain D2/D3 receptor availability that are qualitatively different from those of both high-efficacy receptor agonists and antagonists, and suggest that the observed individual differences in response to ARI treatment may reflect its partial agonist activity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes TR, Edwards JG (1993) The side-effects of antipsychotic drugs. I. CNS and neuromuscular effects, in: Barnes, T.R.E. (Ed.), Antipsychotic drugs and their side-effects. Neuroscience Perspectives. Academic, Harcourt Brace, pp. 213–247
Beaulieu J-M, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63:182–217
Bettinardi V (1999) An automatic classification technique for attenuation correction in positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 26:447–458
Burris KD, Molski TF, Xu C, Ryan E, Tottori K, Kikuchi T, Yocca FD, Molinoff PB (2002) Aripiprazole, a novel antipsychotic, is a high-affinity partial agonist at human dopamine D2 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:381–389
Burt DR, Creese I, Snyder SH (1977) Antischizophrenic drugs: chronic treatment elevates dopamine receptor binding in brain. Science 196:326–328
Czoty PW, Nader MA (2013) Effects of dopamine D2/D3 receptor ligands on food-cocaine choice in socially housed male cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 344:329–338
Czoty PW, Gage HD, Nader MA (2005) PET imaging of striatal dopamine D2 receptors in nonhuman primates: increases in availability produced by chronic raclopride treatment. Synapse 58:215–219
Farde L, Ehrin E, Eriksson L, Greitz T, Hall H, Hedstrom C-G, Litton J-E, Sedvall G (1985) Substituted benzamides as ligands for visualization of dopamine receptor binding in the human brain by positron emission tomography. Proc Natl Acad Sci 82:3863–3867
Farde L, Nordstrom AL, Wiesel FA, Pauli S, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1992) Positron emission tomographic analysis of central D1 and D2 dopamine receptor occupancy in patients treated with classical neuroleptics and clozapine. Relation to extrapyramidal side effects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:538–544
Fujikawa M, Nagashima M, Inoue T, Yamada K, Furukawa T (1996) Partial agonistic effects of OPC-14597, a potential antipsychotic agent, on yawning behavior in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:903–909
Gerlach J (2002) Improving outcome in schizophrenia: the potential importance of EPS and neuroleptic dysphoria. Ann Clin Psychiatry 14:47–57
Ginovart N, Farde L, Halldin C, Swahn CG (1999) Changes in striatal D2-receptor density following chronic treatment with amphetamine as assessed with PET in nonhuman primates. Synapse 31:154–162
Ginovart N, Wilson AA, Hussey D, Houle S, Kapur S (2009) D2-receptor upregulation is dependent upon temporal course of D2-occupancyL a longitudinal [11C]-raclopride PET study in cats. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:662–671
Heusler P, Newman-Tancredi A, Castro-Fernandez A, Cussac D (2007) Differential agonist and antagonist profile of antipsychotics at D2L receptors coupled to GIRK potassium channels. Neuropharmacology 52:1106–1113
Hirose T, Uwahodo Y, Yamada S, Miwa T, Kitagawa H, Burris KD, Altar CA, Nabeshima T (2004) Mechanism of action of aripiprazole predicts clinical efficacy and a favourable side-effect profile. J Psychopharmacol 18:375–383
Howell LL, Byrd LD (1992) Enhanced sensitivity to the behavioral effects of cocaine after chronic administration of D2-selective dopamine antagonists in the squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 262:907–915
Howell LL, Murnane KS (2011) Nonhuman primate positron emission tomography neuroimaging in drug abuse research. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 337:324–334
Kim E, Howes OD, Turkheimer FE, Kim B-H, Jeong JM, Kim JW, Lee JS, Jang I-J, Shin S-G, Kapur S, Kwon JS (2013) The relationship between antipsychotic D2 occupancy and changes in frontal metabolism and working memory: A dual [11C]raclopride and [18F]FDG imaging study with aripiprazole. Psychopharmacology 227:221–229
Kinahan PE, Rogers JG (1989) Analytic 3-D image reconstruction using all detected events. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 36:964–968
Klawans HL Jr, Rubovits R (1972) An experimental model of tardive dyskinesia. J Neural Transm 33:235–246
Klewe IV, Nielsen SM, Tarpo L, Urizar E, Dipace C, Javitch JA, Gether U, Egebjerg J, Christensen KV (2008) Recruitment of beta-arrestin2 to the dopamine D2 receptor: insights into anti-psychotic and anti-parkinsonian drug receptor signaling. Neuropharmacology 54:1215–1222
Koener B, Goursaud S, Van De Stadt M, Calas A-G, Jeanjean AP, Maloteaux J-M, Hermans E (2011) Pharmacological blockade of dopamine D2 receptors by aripiprazole is not associated with striatal sensitization. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 383:65–77
Lidow MS, Goldman-Rakic PS (1994) A common action of clozapine, haloperidol, and remoxipride on D1- and D2-dopaminergic receptors in the primate cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:4353–4356
Lieberman JA (2004) Dopamine partial agonists: a new class of antipsychotic. CNS Drugs 18:251–267
Lile JA, Stoops WW, Vansickel AR, Glaser PE, Hays LR, Rush CR (2005) Aripiprazole attenuates the discriminative-stimulus effects of d-amphetamine in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:2103–2114
Lile JA, Stoops WW, Hays LR, Rush CR (2008) The safety, tolerability, and subject-rated effects of acute intranasal cocaine administration during aripiprazole maintenance II: increased aripiprazole dose and maintenance period. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 34:721–729
Linazasoro G, Obeso JA, Gomez JC, Martinez M, Antonini A, Leenders KL (1999) Modification of dopamine D2 receptor activity by pergolide in Parkinson's disease: an in vivo study by PET. Clin Neuropharmacol 22:277–280
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wolf AP, Dewey SL, Schlyer DJ, MacGregor RR, Hitzemann R, Bendriem B, Gatley SJ et al (1990) Graphical analysis of reversible radioligand binding from time- activity measurements applied to [N-11C-methyl]-(−)-cocaine PET studies in human subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10:740–747
Mach RH, Elder ST, Morton TE, Nowak PA, Evora PH, Scripko JG, Luedtke RR, Unsworth CD, Filtz T, Rao AV et al (1993a) The use of [18F]4-fluorobenzyl iodide (FBI) in PET radiotracer synthesis: model alkylation studies and its application in the design of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-based imaging agents. Nucl Med Biol 20:777–794
Mach RH, Luedtke RR, Unsworth CD, Boundy VA, Nowak PA, Scripko JG, Elder ST, Jackson JR, Hoffman PL, Evora PH et al (1993b) 18F-labeled benzamides for studying the dopamine D2 receptor with positron emission tomography. J Med Chem 36:3707–3720
Martinez D, Carpenter KM, Liu F, Slifstein M, Broft A, Friedman AC, Kumar D, Van Heertum R, Kleber HD, Nunes E (2011) Imaging dopamine transmission in cocaine dependence: link between neurochemistry and response to treatment. Am J Psych 168:634–641
Meini M, Moncini M, Cecconi D, Cellesi V, Biasci L, Simoni G, Ameglio M, Pellegrini M, Forgione RN, Rucci P (2011) Safety, tolerability, and self-rated effects of aripiprazole and ropinirole treatment for cocaine dependence: a pilot study. Am J Addict 20:179–180
Muller P, Seeman P (1977) Brain neurotransmitter receptors after long-term haloperidol: dopamine, acetylcholine, serotonin, alpha-noradrenergic and naloxone receptors. Life Sci 21:1751–1758
Nader MA, Grant KA, Gage HD, Ehrenkaufer RL, Kaplan JR, Mach RH (1999) PET imaging of dopamine D2 receptors with [18F]fluoroclebopride in monkeys: effects of isoflurane- and ketamine-induced anesthesia. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:589–596
Nader MA, Daunais JB, Moore T, Nader SH, Moore RJ, Smith HR, Friedman DP, Porrino LJ (2002) Effects of cocaine self-administration on striatal dopamine systems in rhesus monkeys: initial and chronic exposure. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:35–46
Nader MA, Morgan D, Gage HD, Nader SH, Calhoun TL, Buchheimer N et al (2006) PET imaging of dopamine D2 receptors during chronic cocaine self-administration in monkeys. Nat Neurosci 9:1050–1056
Platt DM, Rowlett JK, Spealman RD (2002) Behavioral effects of cocaine and dopaminergic strategies for preclinical medication development. Psychopharmacology 163:265–282
Semba J, Watanabe A, Kito S, Toru M (1995) Behavioural and neurochemical effects of OPC-14597, a novel antipsychotic drug, on dopaminergic mechanisms in rat brain. Neuropharmacology 34:785–791
Shapiro DA, Shapiro DA, Renock S, Arrington E, Chiodo LA, Liu LX, Sibley DR, Roth BL, Mailman R (2003) Aripiprazole, a novel atypical antipsychotic drug with a unique and robust pharmacology. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1400–1411
Silvestri S, Seeman MV, Negrete J-C, Houle S et al (2000) Increased dopamine D2 receptor binding after long-term treatment with antipsychotics in humans: a clinical PET study. Psychopharmacology 152:174–180
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres M-P, Bouthenet M-L, Schwartz J-C (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature (Lond) 347:146–151
Stoops WW, Lile JA, Lofwall MR, Rush CR (2007) The safety, tolerability, and subject-rated effects of acute intranasal cocaine administration during aripiprazole maintenance. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 33:769–776
Swainston-Harrison T, Perry CM (2004) Aripiprazole: a review of its use in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Drugs 64:1715–1736
Takahata K, Ito H, Takano H, Arakawa R, Fujiwara H, Kimura Y, Kodaka F, Sasaki T, Nogami T, Suzuki M, Nagashima T, Shimada H, Kato M, Mimura M, Suhara T (2012) Striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptor occupancy by the partial agonist antipsychotic drug aripiprazole in the human brain: a positron emission tomography study with [11C]raclopride and [11C]FLB457. Psychopharmacology 222:165–172
Tanahashi S, Yamamura S, Nakagawa M, Motomura E, Okada M (2012) Dopamine D2 and serotonin1A receptors mediate the actions of aripiprazole in mesocortical and mesoaccumbens transmission. Neuropharmacology 62:765–774
Tayarani-Binazir K, Jackson MJ, Rose S, McCreary AC, Jenner P (2010) The partial dopamine agonist pardoprunox (SLV308) administered in combination with l-dopa improves efficacy and decreases dyskinesia in MPTP treated common marmosets. Exp Neurol 226:320–327
Thomsen M, Fink-Jensen A, Woldbye DPD, Wortwein G, Sager TN, Holm R, Pepe LM, Caine SB (2008) Effects of acute and chronic aripiprazole treatment on choice between cocaine self-administration and food under a concurrent schedule of reinforcement in rats. Psychopharmacology 201:43–54
Urban JD, Vargas GA, von Zastrow M, Mailman RB (2007) Aripiprazole has functionally selective actions at dopamine D2 receptor-mediated signaling pathways. Neuropharmacology 32:1106–1113
Vergne DE, Anton RF (2010) Aripiprazole: a drug with a novel mechanism of action and possible efficacy for alcohol dependence. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 9:50–54
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Hitzemann R, Logan J, Schlyer DJ, Dewey SL, Wolf AP (1993) Decreased dopamine D2 receptor availability is associated with reduced frontal metabolism in cocaine abusers. Synapse 14:169–177
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ (1999) Imaging studies on the role of dopamine in cocaine reinforcement and addiction in humans. J Psychopharmacol 13:337–345
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (DA 10584, DA 12460 and DA 14637). The authors thank Michael Coller, Michelle Icenhower Bell, and Michael Bounds for their assistance in conducting these experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Czoty, P.W., Gage, H.D., Garg, P.K. et al. Effects of repeated treatment with the dopamine D2/D3 receptor partial agonist aripiprazole on striatal D2/D3 receptor availability in monkeys. Psychopharmacology 231, 613–619 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3274-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3274-7