Abstract
Rationale
With its high palatability, near-beer has been successfully used in rats as a vehicle to induce ethanol oral self-administration.
Objectives
The study aimed to develop an operant model of oral alcoholic beer self-administration promoting a stable intake of pharmacologically relevant amounts of ethanol in free-feeding C57BL/6J mice. It also aimed to assess the model's predictive validity by evaluating the influence of baclofen, a GABAB agonist, and BHF177, a GABAB positive allosteric modulator, on alcoholic beer self-administration.
Methods
Mice were trained to self-administer, under a fixed ratio three schedule of reinforcement, 10 μl of beer containing increasing ethanol concentrations (0–18% v/v) in daily 30-min sessions. The effects on motor coordination (rotarod), locomotor activity (open field, automated cages) and anxiety-like behavior (elevated plus maze, EPM) were examined. Baclofen (1.25–5 mg/kg, intraperitoneal, i.p.) and BHF177 (3.75–30 mg/kg, i.p.) were used to see the effects on 9% alcoholic beer and near-beer self-administration.
Results
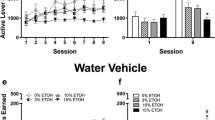
Near-beer stably maintained operant oral self-administration in mice. Adding ethanol to near-beer reduced the number of active lever presses, while the corresponding amount of ethanol self-administration increased (0.8–1.0 g/kg/session). Motor impairment was observed when more than 1.3 g/kg/session of ethanol was self-administered with beer and slight but consistent hyperlocomotion with more than 0.9–1.0 g/kg/session. BHF177 (15 mg/kg) preferentially reduced 9% alcoholic beer self-administration, while the higher dose (30 mg/kg)—like baclofen 5 mg/kg—also reduced near-beer self-administration.
Conclusions
The operant model of oral alcoholic beer self-administration in C57BL/6J mice should prove useful for studying ethanol-reinforced behaviors and to identify candidate compounds for the pharmacological management of alcohol addiction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addolorato G, Leggio L (2010) Safety and efficacy of baclofen in the treatment of alcohol-dependent patients. Curr Pharm Des 16:2113–2117
Anstrom KK, Cromwell HC, Markowski T, Woodward DJ (2003) Effect of baclofen on alcohol and sucrose self-administration in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:900–908
Bachmanov AA, Tordoff MG, Beauchamp GK (2000) Intake of umami-tasting solutions by mice: a genetic analysis. J Nutr 130:935S–941S
Bachmanov AA, Reed DR, Li X, Li S, Beauchamp GK, Tordoff MG (2002) Voluntary ethanol consumption by mice: genome-wide analysis of quantitative trait loci and their interactions in a C57BL/6ByJ x 129P3/J F2 intercross. Genome Res 12:1257–1268
Bechtholt AJ, Cunningham CL (2005) Ethanol-induced conditioned place preference is expressed through a ventral tegmental area dependent mechanism. Behav Neurosci 119:213–223
Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, Young ER (1993) Voluntary consumption of ethanol in 15 inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 112:503–510
Bell SM, Stewart RB, Thompson SC, Meisch RA (1997) Food-deprivation increases cocaine-induced conditioned place preference and locomotor activity in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 131:1–8
Besheer J, Lepoutre V, Hodge CW (2004) GABA(B) receptor agonists reduce operant ethanol self-administration and enhance ethanol sedation in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174:358–366
Besheer J, Lepoutre V, Hodge CW (2009) Preclinical evaluation of riluzole: assessments of ethanol self-administration and ethanol withdrawal symptoms. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1460–1468
Boehm SL II, Piercy MM, Bergstrom HC, Phillips TJ (2002) Ventral tegmental area region governs GABAB receptor modulation of ethanol-stimulated activity in mice. Neuroscience 115:185–200
Brebner K, Phelan R, Roberts DC (2000) Effect of baclofen on cocaine self-administration in rats reinforced under fixed-ratio 1 and progressive-ratio schedules. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 148:314–321
Cabeza de Vaca S, Carr KD (1998) Food restriction enhances the central rewarding effect of abused drugs. J Neurosci 18:7502–7510
Caine SB, Lintz R, Koob GF (1993) Intravenous drug self-administration techniques in animals. In: Sangal A (ed) Behavioural neuroscience, vol II, a practical approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 117–143
Caine SB, Negus SS, Mello NK (2000) GABA agonist effects on cocaine- and food-maintained responding in rats: influence of cocaine dose and liquid food concentration. Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Scientific Meeting of College on Problems of Drug Dependence, San Juan, Puerto Rico, p 21
Carr KD (2002) Augmentation of drug reward by chronic food restriction: behavioral evidence and underlying mechanisms. Physiol Behav 76:353–364
Carr KD (2007) Chronic food restriction: enhancing effects on drug reward and striatal cell signaling. Physiol Behav 91:459–472
Chu K, Koob GF, Cole M, Zorrilla EP, Roberts AJ (2007) Dependence-induced increases in ethanol self-administration in mice are blocked by the CRF1 receptor antagonist antalarmin and by CRF1 receptor knockout. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86:813–821
Corrigall WA, Coen KM, Zhang J, Adamson KL (2001) GABA mechanisms in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus influence particular aspects of nicotine self-administration selectively in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 158:190–197
Corwin RL, Wojnicki FH (2009) Baclofen, raclopride, and naltrexone differentially affect intake of fat and sucrose under limited access conditions. Behav Pharmacol 20:537–548
Cox WM, Mertz JE (1985) Do rats prefer water, near beer, or beer with ethanol? Bull Psychon Soc 23:335–338
Crabbe JC, Phillips TJ (2004) Pharmacogenetic studies of alcohol self-administration and withdrawal. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174:539–560
Crabbe JC Jr, Johnson NA, Gray DK, Kosobud A, Young ER (1982) Biphasic effects of ethanol on open-field activity: sensitivity and tolerance in C57BL/6 N and DBA/2 N mice. J Comp Physiol Psychol 96:440–451
Crabbe JC, Metten P, Cameron AJ, Wahlsten D (2005) An analysis of the genetics of alcohol intoxication in inbred mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:785–802
Cryan JF, Kelly PH, Chaperon F, Gentsch C, Mombereau C, Lingenhoehl K, Froestl W, Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Spooren WP (2004) Behavioral characterization of the novel GABAB receptor-positive modulator GS39783 (N, N′-dicyclopentyl-2-methylsulfanyl-5 nitro-pyrimidine-4,6-diamine): anxiolytic-like activity without side effects associated with baclofen or benzodiazepines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:952–963
Di Chiara G, Imperato A (1988) Drugs abused by humans preferentially increase synaptic dopamine concentrations in the mesolimbic system of freely moving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5274–5278
Ebenezer IS (1995) Intraperitoneal administration of baclofen increases consumption of both solid and liquid diets in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 273:183–185
Elliott J, Brown T, Wren S, Lancaster F (1995) Beer drinking by young Sprague–Dawley rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 19:16A
Elmer GI, Meisch RA, George FR (1986) Oral ethanol reinforced behavior in inbred mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:1417–1421
Elmer GI, Meisch RA, Goldberg SR, George FR (1988) Fixed-ratio schedules of oral ethanol self-administration in inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 96:431–436
Faccidomo S, Spanos M, Besheer J, Wilkie MB, Hodge CW (2007) Modulation of voluntary drinking and operant responding for ethanol in male C57BL/6J mice by the map kinase inhibitor, SL 327. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:89
Faccidomo S, Besheer J, Stanford PC, Hodge CW (2009) Increased operant responding for ethanol in male C57BL/6J mice: specific regulation by the ERK1/2, but not JNK, MAP kinase pathway. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 204:135–147
Fachin-Scheit DJ, Frozino Ribeiro A, Pigatto G, Oliveira Goeldner F, Boerngen de Lacerda R (2006) Development of a mouse model of ethanol addiction: naltrexone efficacy in reducing consumption but not craving. J Neural Transm 113:1305–1321
Filip M, Frankowska M (2007) Effects of GABAB receptor agents on cocaine priming, discrete contextual cue and food induced relapses. Eur J Pharmacol 571:166–173
Filip M, Frankowska M, Przegalinski E (2007) Effects of GABAB receptor antagonist, agonists and allosteric positive modulator on the cocaine induced self-administration and drug discrimination. Eur J Pharmacol 574:148–157
Ford MM, Fretwell AM, Mark GP, Finn DA (2007) Influence of reinforcement schedule on ethanol consumption patterns in non-food restricted male C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol 41:21–29
Gallate JE, McGregor IS (1999) The motivation for beer in rats: effects of ritanserin, naloxone and SR141716. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 142:302–308
Gallate JE, Morley KC, Ambermoon P, McGregor IS (2003) The consequences of beer consumption in rats: acute anxiolytic and ataxic effects and withdrawal-induced anxiety. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 166:51–60
Gallate JE, Mallet PE, McGregor IS (2004) Combined low dose treatment with opioid and cannabinoid receptor antagonists synergistically reduces the motivation to consume alcohol in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 173:210–216
Guery S, Floersheim P, Kaupmann K, Froestl W (2007) Syntheses and optimization of new GS39783 analogues as positive allosteric modulators of GABA B receptors. Bioorg Chem Med Lett 17:6206–6211
Gulick D, Gould TJ (2009) Interactive effects of ethanol and nicotine on learning, anxiety, and locomotion in C57BL/6 mice in the plus-maze discriminative avoidance task. Neuropharmacology 57:302–310
Hale RL, Johnston AL, Becker HC (1990) Indomethacin does not antagonize the anxiolytic action of ethanol in the elevated plus-maze. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 101:203–207
Hargreaves GA, McGregor IS (2007) Topiramate moderately reduces the motivation to consume alcohol and has a marked antidepressant effect in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:1900–1907
Hayward MD, Hansen ST, Pintar JE, Low MJ (2004) Operant self-administration of ethanol in C57BL/6 mice lacking beta-endorphin and enkephalin. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79:171–181
Heidbreder CA, Andreoli M, Marcon C, Hutcheson DM, Gardner EL, Ashby CR Jr (2007) Evidence for the role of dopamine D3 receptors in oral operant alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior in mice. Addict Biol 12:35–50
Hodge CW, Miles MF, Sharko AC, Stevenson RA, Hillmann JR, Lepoutre V, Besheer J, Schroeder JP (2006) The mGluR5 antagonist MPEP selectively inhibits the onset and maintenance of ethanol self-administration in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:429–438
Hopf FW, Chang SJ, Sparta DR, Bowers MS, Bonci A (2010) Motivation for alcohol becomes resistant to quinine adulteration after 3 to 4 months of intermittent alcohol self-administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:1565-1573
Janak PH, Gill TM (2003) Comparison of the effects of allopregnanolone with direct GABAergic agonists on ethanol self-administration with and without concurrently available sucrose. Alcohol 30:1–7
Johnson BA (2010) Medication treatment of different types of alcoholism. Am J Psychiatry 167:630–639
Jones LC, Duggan K, Bellingham WP, Ward LC (1988) Effect of alcohol content on beer consumption by rats. Drug Alcohol Depend 22:101–104
Kalivas PW, Duffy P, Eberhardt H (1990) Modulation of A10 dopamine neurons by gamma-aminobutyric acid agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:858–866
Koob GF (2003) Alcoholism: allostasis and beyond. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:232–243
Korkosz A, Scinska A, Rogowski A, Mierzejewski P, Kostowski W, Kukwa A, Bienkowski P (2003) Chorda tympani nerve transaction does not alter operant oral self-administration of ethanol in the rat. Alcohol 30:211–215
Lancaster F, Spiegel K, Zaman M (1987) Voluntary beer drinking in rats. Alcohol Drug Res 7:393–403
Leite-Morris KA (2004) The effects tegmental baclofen on ethanol-induced motor stimulation and sensitization in DBA⁄ 2 mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:182A
Leite-Morris KA, Czachowski CL (2006) Intra-ventral tegmental area microinjections of a GABA receptor agonist dose-dependently attenuate ethanol seeking in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:182A
Lhuillier L, Mombereau C, Cryan JF, Kaupmann K (2007) GABAB receptor-positive modulation decreases selective molecular and behavioral effects of cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:388–398
Liang JH, Chen F, Krstew E, Cowen MS, Carroll FY, Crawford D, Beart PM, Lawrence AJ (2006) The GABAB receptor allosteric modulator CGP7930, like baclofen, reduces operant self-administration of ethanol in alcohol-preferring rats. Neuropharmacology 50:632–639
Lister RG (1987) The use of a plus-maze to measure anxiety in the mouse. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 92:180–185
Maccioni P, Colombo G (2009) Role of the GABA(B) receptor in alcohol-seeking and drinking behavior. Alcohol 43:555–558
Maccioni P, Serra S, Vacca G, Orrù A, Pes D, Agabio R, Addolorato G, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2005) Baclofen-induced reduction of alcohol reinforcement in alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol 36:161–168
Maccioni P, Pes D, Orrù A, Froestl W, Gessa GL, Carai MAM, Colombo G (2007) Reducing effect of the positive allosteric modulator of the GABA-B receptor, GS30783, on alcohol self-administration in alcohol preferring rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 193:171–178
Maccioni P, Fantini N, Froestl W, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2008) Specific reduction of alcohol's motivational properties by the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, GS39783—comparison with the effect of the GABAB receptor direct agonist, baclofen. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:1558–1564
Maccioni P, Carai MAM, Kaupmann K, Guery S, Froestl W, Leite-Morris KA, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2009) Reduction of alcohol's reinforcing and motivational properties by the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, BHF177, in alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1749–1756
Maccioni P, Thomas AW, Carai MA, Gessa GL, Malherbe P, Colombo G (2010) The positive allosteric modulator of the GABA(B) receptor, rac-BHFF, suppresses alcohol self-administration. Drug Alcohol Depend 109:96–103
Malherbe P, Masciadri R, Norcross RD, Knoflach F, Kratzeisen C, Zenner M-T, Kolb Y, Marcuz A, Huwyler J, Nakagawa T, Porter RHP, Thomas AW, Wettstein JG, Sleight AJ, Spooren W, Prinssen EP (2008) Characterization of (R, S)-5,7-di-tert-butyl-3-hydroxy-3-trifluoromethyl-3H-benzofuran-2-one as a positive allosteric modulator of GABAB receptors. Br J Pharmacol 154:797–811
McClearn GE, Rodgers DA (1959) Differences in alcohol preference among inbred strains of mice. Q J Stud Alcohol 20:691–695
McGregor IS, Gallate JE (2004) Rats on the grog: novel pharmacotherapies for alcohol craving. Addict Behav 29:1341–1357
McGregor IS, Saharov T, Hunt GE, Topple AN (1999) Beer consumption in rats: the influence of ethanol content, food deprivation, and cocaine. Alcohol 17:47–56
Middaugh LD, Kelley BM (1999) Operant ethanol reward in C57BL/6 mice: influence of gender and procedural variables. Alcohol 17:185–194
Middaugh LD, Boggan WO, Randall CL (1987) Stimulatory effects of ethanol in C57BL/6 mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 27:421–424
Middaugh LD, Frackelton WF, Boggan WO, Onofrio A, Shepherd CL (1992) Gender differences in the effects of ethanol on C57BL/6 mice. Alcohol 9:257–260
Middaugh LD, Lee AM, Bandy AL (2000) Ethanol reinforcement in non deprived mice: effects of abstinence and naltrexone. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:1172–1179
Mombereau C, Lhuillier L, Kaupmann K, Cryan JF (2007) GABAB receptor-positive modulation-induced blockade of the rewarding properties of nicotine is associated with a reduction in nucleus accumbens DeltaFosB accumulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:172–177
Munzar P, Kutkat SW, Miller CR, Goldberg SR (2000) Failure of baclofen to modulate discriminative-stimulus effects of cocaine or methamphetamine in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 408:169–174
Murata Y, Nakashima K, Yamada A, Shigemura N, Sasamoto K, Ninomiya Y (2003) Gurmarin suppression of licking responses to sweetener-quinine mixtures in C57BL mice. Chem Sense 28:237–243
Nguyen SA, Deleon CP, Malcolm RJ, Middaugh LD (2005) Tiagabine reduces ethanol reward in C57BL/6 mice under acute and chronic administration regimens. Synapse 56:135–146
Orrù A, Lai P, Lobina C, Maccioni P, Piras P, Scanu L, Froestl W, Gessa GL, Carai MAM, Colombo G (2005) Reducing effect of the positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor, CGP7930 and GS39783, on alcohol intake in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 525:105–111
Orrù A, Lobina C, Maccioni P, Gessa GL, Carai MAM, Colombo G (2007) Repeated exposure to alcoholic beer does not induce long-lasting changes in alcohol self-administration and intake in Sardinian alcohol-preferring and Sardinian non-preferring rats. Alcohol Alcohol 42:513–524
Paterson NE, Vlachou S, Guery S, Kaupmann K, Froestl W, Markou A (2008) Positive modulation of GABA(B) receptors decreased nicotine self-administration and counteracted nicotine-induced enhancement of brain reward function in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:306–314
Pellow S, File SE (1986) Anxiolytic and anxiogenic drug effects on exploratory activity in an elevated plus-maze: a novel test of anxiety in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:525–529
Pothos EN, Creese I, Hoebel BG (1995) Restricted eating with weight loss selectively decreases extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and alters dopamine response to amphetamine, morphine, and food intake. J Neurosci 15:6640–6650
Quertemont E, Tambour S, Bernaerts P, Zimatkin SM, Tirelli E (2004) Behavioral characterization of acetaldehyde in C57BL/6J mice: locomotor, hypnotic, anxiolytic and amnesic effects. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 177:84–92
Rhodes JS, Ford MM, Yu CH, Brown LL, Finn DA, Garland T Jr, Crabbe JC (2007) Mouse inbred strain differences in ethanol drinking to intoxication. Genes Brain Behav 6:1–18
Richards JK, Simms JA, Bartlett SE (2009) Conditioned cues and yohimbine induce reinstatement of beer and near-beer seeking in Long–Evans rats. Addict Biol 14:144–151
Risinger FO, Brown MM, Doan AM, Oakes RA (1998) Mouse strain differences in oral operant ethanol reinforcement under continuous access conditions. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:677–684
Risinger FO, Freeman PA, Greengard P, Fienberg AA (2001) Motivational effects of ethanol in DARPP-32 knock-out mice. J Neurosci 21:340–348
Roberts DC, Andrews MM, Vickers GJ (1996) Baclofen attenuates the reinforcing effects of cocaine in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:417–423
Salling MC, Faccidomo S, Hodge CW (2008) Non selective suppression of operant ethanol and sucrose self-administration by the mGluR7 positive allosteric modulator AMN082. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:14–20
Samson HH, Denning C, Chappelle AM (1996) The use of non alcoholic beer as the vehicle for ethanol consumption in rats. Alcohol 13:365–368
Schroeder JP, Iller KA, Hodge CW (2003) Neuropeptide-Y Y5 receptors modulate the onset and maintenance of operant ethanol self-administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:1912–1920
Slattery DA, Markou A, Froestl W, Cryan JF (2005) The GABAB receptor positive modulator GS39783 and the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen attenuate the reward-facilitating effects of cocaine: intracranial self-stimulation studies in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:2065–2072
Smith MA, Yancey DL, Morgan D, Froestl W, Roberts DC (2004) Effects of positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor on cocaine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 173:105–111
Sparta DR, Ferraro FM 3rd, Fee JR, Knapp DJ, Breese GR, Thiele TE (2009) The alcohol deprivation effect in C57BL/6 J mice is observed using operant self-administration procedures and is modulated by CRF-1 receptor signaling. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:31–42
Tanchuck MA, Yoneyama N, Ford MM, Fretwell AM, Finn DA (2011) Assessment of GABA-B, metabotropic glutamate, and opioid receptor involvement in an animal model of binge drinking. Alcohol 45:33–44
Thomsen M, Caine SB (2007) Intravenous drug self-administration in mice: practical considerations. Behav Genet 37:101–118
Topple AN, Hunt GE, McGregor IS (1998) Possible neural substrates of beer-craving in rats. Neurosci Lett 252:99–102
Tsiang MT, Janak PH (2006) Alcohol seeking in C57BL/6 mice induced by conditioned cues and contexts in the extinction-reinstatement model. Alcohol 38:81–88
Urwyler S, Pozza MF, Lingenhoehl K, Mosbacher J, Lampert C, Froestl W, Koller M, Kaupmann K (2003) N, N′-Dicyclopentyl-2-methylsulfanyl-5-nitro-pyrimidine-4,6-diamine (GS39783) and structurally related compounds: novel allosteric enhancers of gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:322–330
Wirtshafter D, Sheppard AC (2001) Localization of GABAB receptors in midbrain monoamine containing neurons in the rat. Brain Res Bull 56:1–5
Wu YN, Mercuri NB, Johnson SW (1995) Presynaptic inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid B-mediated synaptic current by adenosine recorded in vitro in midbrain dopamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273:576–581
Xi ZX, Stein EA (1999) Baclofen inhibits heroin self-administration behavior and mesolimbic dopamine release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 90:1369–1374
Yoneyama N, Crabbe JC, Ford MM, Murillo A, Finn DA (2008) Voluntary ethanol consumption in 22 inbred mouse strains. Alcohol 42:149–160
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Klemens Kaupmann, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, Basel, Switzerland for the generous gift of BHF117 and to J.D. Baggott for language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orrù, A., Fujani, D., Cassina, C. et al. Operant, oral alcoholic beer self-administration by C57BL/6J mice: effect of BHF177, a positive allosteric modulator of GABAB receptors. Psychopharmacology 222, 685–700 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2672-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2672-6