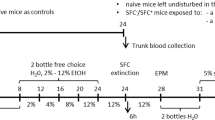
Abstract
Rationale
Anxiety disorders and alcohol use disorders frequently co-occur in humans perhaps because alcohol relieves anxiety. Studies in humans and rats indicate that alcohol may have greater anxiolytic effects in organisms with increased genetic propensity for high alcohol consumption.
Objectives and methods
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of moderate doses of alcohol (0.5, 1.0, 1.5 g/kg) on the acquisition and expression of anxiety-related behavior using a fear-potentiated startle (FPS) procedure. Experiments were conducted in two replicate pairs of mouse lines selectively bred for high- (HAP1 and HAP2) and low- (LAP1 and LAP2) alcohol preference; these lines have previously shown a genetic correlation between alcohol preference and FPS (HAP > LAP; Barrenha and Chester, Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:1081–1088, 2007). In a control experiment, the effect of diazepam (4.0 mg/kg) on the expression of FPS was tested in HAP2 and LAP2 mice.
Results
The 1.5 g/kg alcohol dose moderately decreased the expression of FPS in both HAP lines but not LAP lines. Alcohol had no effect on the acquisition of FPS in any line. Diazepam reduced FPS to a similar extent in both HAP2 and LAP2 mice.
Conclusions
HAP mice may be more sensitive to the anxiolytic effects of alcohol than LAP mice when alcohol is given prior to the expression of FPS. These data collected in two pairs of HAP/LAP mouse lines suggest that the anxiolytic response to alcohol in HAP mice may be genetically correlated with their propensity toward high alcohol preference and robust FPS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams K, Kushner M, Medina KL, Voight A (2001) The pharmacologic and expectancy effects of alcohol on social anxiety in individuals with social phobia. Drug Alcohol Depend 64:219–231
Abreu-Villaca Y, Nunes F, Queiroz-Gomes F, Manhaes AC, Filgueiras CC (2008) Combined exposure to nicotine and ethanol in adolescent mice differentially affects anxiety levels during exposure, short-term, and long-term withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:599–610
Barrenha GD, Chester JA (2007) Genetic correlation between innate alcohol preference and fear-potentiated startle in selected mouse lines. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:1081–1088
Blanchard RJ, Magee L, Veniegas R, Blanchard DC (1993) Alcohol and anxiety: ethopharmacological approaches. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 17:171–182
Boehm SL, Reed CL, McKinnon CS, Phillips TJ (2002) Shared genes influence sensitivity to the effects of ethanol on locomotor and anxiety-like behaviors, and the stress axis. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 161:54–63
Bowen RC, Cipywnyk D, D'Arcy C, Keegan D (1984) Alcoholism, anxiety disorders, and agoraphobia. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 8:48–50
Brady KT, Killeen TK, Brewerton T, Lucerini S (2000) Comorbidity of psychiatric disorders and posttraumatic stress disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 61(Suppl 7):22–32
Brown PJ, Sout RL, Gannon-Rowley J (1998) Substance use disorder-PTSD comorbidity. Patients’ perceptions of symptom interplay and treatment issues. J Subst Abuse Treat 15:445–448
Cappell H, Herman CP (1972) Alcohol and tension reduction: a review. Q J Stud Alcohol 33:33–64
Colombo G, Agabio R, Lobina C, Reali R, Zocchi A, Fadda F, Gessa GL (1995) Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats: a genetic animal model of anxiety. Physiol Behav 57:1181–1185
Conger JJ (1956) Alcoholism: theory, problem and challenge II. Reinforcement theory and the dynamics of alcoholism. Q J Stud Alcohol 17:296–305
Correia D, Ribeiro AF, Brunialti Godard AL, Boerngen-Lacerda R (2009) Trait anxiety and ethanol: anxiolysis in high-anxiety mice and no relation to intake behavior in an addiction model. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:880–888
Costall B, Kelly ME, Naylor RJ (1988) The anxiolytic and anxiogenic actions of ethanol in a mouse model. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:197–202
Crabbe JC, Phillips TJ, Kosobud A, Belknap JK (1990) Estimation of genetic correlation: interpretation of experiments using selectively bred and inbred animals. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 14:141–151
Croissant B, Olbrich R (2004) Stress response dampening indexed by cortisol in subjects at risk for alcoholism. J Stud Alcohol 65:701–707
Curtin JJ, Lang AR, Patrick CJ, Stritzke WG (1998) Alcohol and fear-potentiated startle: the role of competing cognitive demands in the stress-reducing effects of intoxication. J Abnorm Psychol 107:547–557
Davidson JR, Kudler HS, Saunders WB, Smith RD (1990) Symptom and comorbidity patterns in World War II and Vietnam veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Compr Psychiatry 31:162–170
Davis M (1979) Diazepam and flurazepam: effects on conditioned fear as measured with the potentiated startle paradigm. Psychopharmacology 62:1–7
Davis M (2006) Neural systems involved in fear and anxiety measured with fear-potentiated startle. Am Psychol 61:741–756
Durcan MJ, Lister RG (1988) Time course of ethanol's effects on locomotor activity, exploration and anxiety in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 96:67–72
Fendt M, Fanselow MS (1999) The neuroanatomical and neurochemical basis of conditioned fear. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:743–760
File SE (1976) Are central cholinergic paths involved in habituation of exploration and distraction? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 4:695–702
File SE, Hyde J, Pool M (1976) Effects of ethanol and chlordiazepoxide on social interaction in rats [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol 58:465
Finn PR, Pihl RO (1987) Men at high risk for alcoholism: the effect of alcohol on cardiovascular response to unavoidable shock. J Abnorm Psychol 93:230–236
Gould TJ (2003) Ethanol disrupts fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice. J Psychopharmacol 17:77–81
Grahame NJ, Li TK, Lumeng L (1999) Limited access alcohol drinking in high- and low-alcohol preferring selected lines of mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1015–1022
Grahame NJ, Rodd-Henricks K, Li TK, Lumeng L (2000) Ethanol locomotor sensitization, but not tolerance correlates with selection for alcohol preference in high- and low-alcohol preferring mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 151:252–260
Grillon C (2002) Startle reactivity and anxiety disorders: aversive conditioning, context and neurobiology. Biol Psychiatry 52:958–975
Gulick D, Gould TJ (2007) Acute ethanol has biphasic effects on short- and long- term memory in both foreground and background contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:1528–1537
Gulick D, Gould TJ (2009a) Effects of ethanol and caffeine on behavior in C57BL/6 mice in the plus-maze discriminative avoidance task. Behav Neurosci 123:1271–1278
Gulick D, Gould TJ (2009b) Interactive effects of ethanol and nicotine on learning, anxiety, and locomotion in C57BL/6 mice in the plus-maze discriminative avoidance task. Neuropsychopharmacology 57:302–310
Hijzen TH, Houtzager SW, Joordens RJ, Olivier B, Slangen JL (1995) Predictive validity of the potentiated startle response as a behavioral model for anxiolytic drugs. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 118:150–154
Himle JA, Abelson JL, Haghightgou H, Hill EM, Nesse RM, Curtis GC (1999) Effect of alcohol on social phobic anxiety. Am J Psychiatry 156:1237–1243
Hoge CW, Castro CA, Messer SC, McGurk D, Cotting DI, Koffman RL (2004) Combat duty in Iraq and Afghanistan, mental health problems, and barriers to care. N Engl J Med 351:13–22
Kameda SR, Frussa-Filho R, Carvalho RC, Takatsu-Coleman AL, Ricardo VP, Patti CL et al (2007) Dissociation of the effects of ethanol on memory, anxiety, and motor behavior in mice tested in the plus-maze discriminative avoidance task. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 192:39–48
Kang HK, Hyams KC (2005) Mental health care needs among recent war veterans. N Engl J Med 352:1289
Kessler RC, Nelson CB, McGonagle KA, Edlund MJ, Frank RG, Leaf PJ (1996) The epidemiology of co-occurring addictive and mental disorders: implications for prevention and service utilization. Am J Orthopsychiatry 66:17–31
Kim JJ, Jung MW (2006) Neural circuits and mechanisms involved in Pavlovian fear conditioning: a critical review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:188–202
Kolb LC (1984) The post-traumatic stress disorders of combat: a subgroup with a conditioned emotional response. Mil Med 149:237–243
LaBuda CJ, Fuchs PN (2002) Catecholamine depletion by reserpine blocks the anxiolytic actions of ethanol in the rat. Alcohol 26:55–59
Land C, Spear NE (2004) Fear conditioning is impaired in adult rats by ethanol doses that do not affect periadolescents. Int J Dev Neurosci 22:355–362
Lattal KM (2007) Effects of ethanol on the encoding, consolidation, and expression of extinction following contextual fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci 121:1280–1292
Levenson RW, Sher KJ, Grossman LM, Newman J, Newlin DB (1980) Alcohol and stress response dampening: pharmacological effects, expectancy, and tension-reduction. J Abnorm Psychol 89:528–538
Levenson RW, Oyama ON, Meek PS (1987) Greater reinforcement from alcohol for those at risk: parental risk, personality risk, and sex. J Abnorm Psychol 96:242–253
Logue SF, Paylor R, Wehner JM (1997) Hippocampal lesions cause learning deficits in inbred mice in the Morris water maze and conditioned-fear task. Behav Neurosci 111:104–113
Löw K, Crestani F, Keist R, Benke D, Brunig I, Benson JA et al (2000) Molecular and neuronal substrate for the selective attenuation of anxiety. Science 290:131–134
Maier W, Minges J, Lichtermann D (1993) Alcoholism and panic disorder: co-occurrence and co-transmission in families. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 243:205–211
McBride WJ (2002) Central nucleus of the amygdala and the effects of alcohol and alcohol-drinking behavior in rodents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:509–515
McDougle CJ, Krystal JH, Price LH, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1995) Noradrenergic response to acute ethanol administration in healthy subjects: comparison with intravenous yohimbine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 118:127–135
McFarlane AC (1998) Epidemiological evidence about the relationship between PTSD and alcohol abuse: the nature of the association. Addict Behav 23:813–825
McKinzie DL, Sajdyk TJ, McBride WJ, Murphy JM, Lumeng L, Li TK, Shekhar A (2000) Acoustic startle and fear-potentiated startle in alcohol-preferring (P) and -nonpreferring (NP) lines of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:691–696
Melia KR, Ryabinin AE, Corodimas KP, Wilson MC, Ledoux JE (1996) Hippocampal-dependent learning and experience-dependent activation of the hippocampus are preferentially disrupted by ethanol. Neuroscience 74:313–322
Merikangas KR, Risch NJ, Weissman MM (1994) Comorbidity and co-transmission of alcoholism, anxiety and depression. Psychol Med 24:69–80
Merikangas KR, Stevens DE, Fenton B, Stolar M, O'Malley S, Woods SW, Risch N (1998) Co-morbidity and familial aggregation of alcoholism and anxiety disorders. Psychol Med 28:773–788
Miller NE, Barry H 3rd (1960) Motivational effects of drugs: methods which illustrate some general problems in psychopharmacology. Psychopharmacologia 1:169–199
Milliken CS, Auchterlonie JL, Hoge CW (2007) Longitudinal assessment of mental health problems among active and reserve component soldiers returning from the Iraq war. JAMA 298:2141–2148
Moberg CA, Curtin JJ (2009) Alcohol selectively reduces anxiety but not fear: startle response during unpredictable versus predictable threat. J Abnorm Psychol 118:335–347
Munjack DJ, Moss HB (1981) Affective disorder and alcoholism in families of agoraphobics. Arch Gen Psychiatry 38:869–871
Naftolowitz DF, Vaughn BV, Ranc J, Tancer ME (1994) Response to alcohol in social phobia. Anxiety 1:96–99
Nesic J, Duka T (2006) Gender specific effects of a mild stressor on alcohol cue reactivity in heavy social drinkers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 83:239–248
Pandey SC, Zhang H, Roy A (2005) Deficits in amygdaloid cAMP-responsive element-binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism. J Clin Invest 115:2762–2773, Erratum in J Clin Invest (2006) 116:3292
Phillips RG, LeDoux JE (1992) Differential contribution of amygdala and hippocampus to cued and contextual fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci 106:274–285
Risbrough VB, Brodkin JD, Geyer MA (2003) GABA-A and 5HT1A receptor agonists block expression of fear-potentiated startle in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:654–663
Roberto M, Madamba SG, Moore SD, Tallent MK, Siggins GR (2003) Ethanol increases GABAergic transmission at both pre- and postsynaptic sites in rat central amygdala neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2053–2058
Rorick LM, Finn PR, Steinmetz JE (2003) Moderate doses of ethanol partially reverse avoidance learning deficits in high-alcohol-drinking rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:89–102
Ryabinin AE, Criado JR, Henriksen SJ, Bloom FE, Wilson MC (1997) Differential sensitivity of c-Fos expression in hippocampus and other brain regions to moderate and low doses of alcohol. Mol Psychiatry 2:32–43
Sayette MA, Contrada RJ, Wilson GT (1990) Alcohol and correspondence between self-report and physiological measures of anxiety. Behav Res Ther 28:351–354
Schuckit MA, Engstrom D, Alpert R, Duby J (1981) Differences in muscle-tension response to ethanol in young men with and without family histories of alcoholism. J Stud Alcohol 42:918–924
Sher KJ (1987) Stress response dampening. In: Blane HT, Leonard KE (eds) Psychological Theories of Drinking and Alcoholism. Guilford Press, New York
Sher KJ, Levenson RW (1982) Risk for alcoholism and individual differences in the stress-response-dampening effect of alcohol. J Abnorm Psychol 91:350–367
Sinha R, Robinson J, O'Malley S (1998) Stress response dampening: effects of gender and family history of alcoholism and anxiety disorders. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 137:311–320
Smith KS, Meloni EG, Myers KM, Van't Veer A, Carlezon WA Jr, Rudolph U (2011) Reduction of fear-potentiated startle by benzodiazepines in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 213:697–706
Spanagel R, Montkowski A, Allingham K, Stohr T, Shoaib M, Holsboer F et al (1995) Anxiety: a potential predictor of vulnerability to the initiation of ethanol self administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 122:373
Stewart SH (1996) Alcohol abuse in individuals exposed to trauma: a critical review. Psychol Bull 120:83–112
Stewart SH, Finn PR, Pihl RO (1992) The effects of alcohol on the cardiovascular stress response in men at high risk for alcoholism: a dose response study. J Stud Alcohol 53:499–506
Stewart RB, Gatto GJ, Lumeng L, Li TK, Murphy JM (1993) Comparison of alcohol-preferring (P) and nonpreferring (NP) rats on tests of anxiety and for the anxiolytic effects of ethanol. Alcohol 10:1–10
Stromberg MF, Hammond LJ (1997) The effects of ethanol on a measure of conditioned fear in mice. Alcohol 14:403–407
Terra MB, Figueira I, Barros HM (2004) Impact of alcohol intoxication and withdrawal syndrome on social phobia and panic disorder in alcoholic inpatients. Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Sao Paulo 59:187–192
Thomas SE, Randall CL, Carrigan MH (2003) Drinking to cope in socially anxious individuals: a controlled study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:1937–1943
Walker DL, Davis M (2002) Quantifying fear potentiated startle using absolute versus proportional increase scoring methods: implications for the neurocircuitry of fear and anxiety. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 164:318–328
Wehner JM, Keller JJ, Keller AB, Picciotto MR, Paylor R, Booker TK, Beaudet A, Heinemann SF, Balogh SA (2004) Role of neuronal nicotinic receptors in the effects of nicotine and ethanol on contextual fear conditioning. Neuroscience 129:11–24
Weiss KJ, Rosenberg DJ (1985) Prevalence of anxiety disorder among alcoholics. J Clin Psychiatry 46:3–5
Weitemier AZ, Ryabinin AE (2003) Alcohol-induced memory impairment in trace fear conditioning: a hippocampus-specific effect. Hippocampus 13:305–315
Zack M, Poulos CX, Aramakis VB, Khamba BK, MacLeod CM (2007) Effects of drink-stress sequence and gender on alcohol stress response dampening in high and low anxiety sensitive drinkers. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:411–422
Zimmermann U, Spring K, Wittchen HU, Holsboer F (2004) Effects of ethanol administration and induction of anxiety-related affective states on the acoustic startle reflex in sons of alcohol-dependent fathers. Alcoholism Clin Exp Res 28:424–432
Zimmermann US, Buchmann AF, Spring C, Uhr M, Holsboer F, Wittchen HU (2009) Ethanol administration dampens the prolactin response to psychosocial stress exposure in sons of alcohol-dependent fathers. Psychoneuroendocrinology 34:996–1003
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by AA016843 for JAC. We are grateful to Dr. Nicholas J. Grahame for providing the breeders for the HAP1/LAP1 and HAP2/LAP2 lines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrenha, G.D., Coon, L.E. & Chester, J.A. Effects of alcohol on the acquisition and expression of fear-potentiated startle in mouse lines selectively bred for high and low alcohol preference. Psychopharmacology 218, 191–201 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2285-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2285-5