Abstract
Rationale
Dopamine agonists have been implicated in the treatment of depression. Cabergoline is an ergot derivative with a high affinity to dopamine D2-like receptors; however, there have been few preclinical studies on its antidepressant-like effects.
Materials and methods
Behavioral effects of cabergoline were examined in rats using forced swimming (FST), novelty-suppressed feeding (NST), open field (OFT), and elevated-plus maze (EPT) tests. In a single treatment paradigm, behaviors of rats were analyzed 4 h after single injection of cabergoline (s.c., 0–4 µmol/kg). In a repeated-treatment paradigm, OFT, EPT, and FST were conducted on days 11, 12, and13–14, respectively, during daily cabergoline injections (s.c., 0.5 µmol/kg), and then hippocampus was removed 24 h after the last injection. NST was conducted in a separate experiment at day 14. Western blotting was used for the analysis of the protein levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and the activation of intracellular signaling molecules.
Results
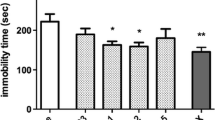
Single injection of cabergoline demonstrated decreased immobility in FST and distance traveled during 0–10 min in OFT, while time spent and entry into open arms were increased at 4 µmol/kg. When cabergoline was repeatedly administered, immobility in FST and the latency of feeding in NSF were significantly reduced, while vertical movement was increased in OFT. The time in closed arms was tended to be decreased in EPT. Expression of BDNF and activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 were up-regulated after the chronic administration of cabergoline.
Conclusions
Cabergoline exerts antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects, which may be mediated by potentiation of intracellular signaling of BDNF.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi N, Kunugi H (2008) Impaired secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuropsychiatric diseases. Open Neurosci J 2:59–64
Angelucci F, Mathé AA, Aloe L (2000) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and tyrosine kinase receptor TrkB in rat brain are significantly altered after haloperidol and risperidone administration. J Neurosci Res 60:783–794
Basso AM, Gallagher KB, Bratcher NA, Brioni JD, Moreland RB, Hsieh GC, Drescher K, Fox GB, Decker MW, Rueter LE (2005) Antidepressant-like effect of D(2/3) receptor-, but not D(4) receptor-activation in the rat forced swim test. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1257–1268
Bodnoff SR, Suranyi-Cadotte B, Quirion R, Meaney MJ (1989) A comparison of the effects of diazepam versus several typical and atypical anti-depressant drugs in an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 97:277–279
Castrén E, Võikar V, Rantamäki T (2007) Role of neurotrophic factors in depression. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:18–21
Chen B, Dowlatshahi D, MacQueen GM, Wang JF, Young LT (2001) Increased hippocampal BDNF immunoreactivity in subjects treated with antidepressant medication. Biol Psychiatry 50:260–265
Dawson NM, Hamid EH, Egan MF, Meredith GE (2001) Changes in the pattern of brain-derived neurotrophic factor immunoreactivity in the rat brain after acute and subchronic haloperidol treatment. Synapse 39:70–81
De La Garza RII, Mahoney JJ III (2004) A distinct neurochemical profile in WKY rats at baseline and in response to acute stress: implications for animal models of anxiety and depression. Brain Res 1021:209–218
Detke MJ, Rickels M, Lucki I (1995) Active behaviors in the rat forced swimming test differentially produced by serotonergic and noradrenergic antidepressants. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 121:66–72
Du F, Li R, Huang Y, Li X, Le W (2005) Dopamine D3 receptor-preferring agonists induce neurotrophic effects on mesencephalic dopamine neurons. Eur J Neurosci 22:2422–2430
Duman RS, Monteggia LM (2006) A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 59:1116–1127
Dunham JS, Deakin JF, Miyajima F, Payton A, Toro CT (2009) Expression of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its receptors in Stanley consortium brains. J Psychiatr Res 43:1175–1184
Dunlop BW, Nemeroff CB (2007) The role of dopamine in the pathophysiology of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:327–337
Dwivedi Y, Rizavi HS, Roberts RC, Conley RC, Tamminga CA, Pandey GN (2001) Reduced activation and expression of ERK1/2 MAP kinase in the post-mortem brain of depressed suicide subjects. J Neurochem 77:916–928
Eilam D, Szechtman H (1989) Biphasic effect of D-2 agonist quinpirole on locomotion and movements. Eur J Pharmacol 161:151–157
Einat H, Yuan P, Gould TD, Li J, Du J, Zhang L, Manji HK, Chen G (2003) The role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in mood modulation. J Neurosci 23:7311–7316
Feng P, Guan Z, Yang X, Fang J (2003) Impairments of ERK signal transduction in the brain in a rat model of depression induced by neonatal exposure of clomipramine. Brain Res 991:195–205
Fumagalli F, Molteni R, Bedogni F, Gennarelli M, Perez J, Racagni G, Riva MA (2004) Quetiapine regulates FGF-2 and BDNF expression in the hippocampus of animals treated with MK-801. NeuroReport 15:2109–2112
Fumagalli F, Molteni R, Calabrese F, Frasca A, Racagni G, Riva MA (2005) Chronic fluoxetine administration inhibits extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation in rat brain. J Neurochem 93:1551–1560
Gambarana C, Scheggi S, Tagliamonte A, Tolu P, De Montis MG (2001) Animal models for the study of antidepressant activity. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 7:11–20
Grønli J, Bramham C, Murison R, Kanhema T, Fiske E, Bjorvatn B, Ursin R, Portas CM (2006) Chronic mild stress inhibits BDNF protein expression and CREB activation in the dentate gyrus but not in the hippocampus proper. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85:842–849
Hetman M, Kanning K, Cavanaugh JE, Xia Z (1999) Neuroprotection by brain-derived neurotrophic factor is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 274:22569–22580
Huang EJ, Reichardt LF (2001) Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:677–736
Inoue T, Tsuchiya K, Miura J, Sakakibara S, Denda K, Kasahara T, Koyama T (1996) Bromocriptine treatment of tricyclic and heterocyclic antidepressant-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 40:151–153
Izumi T, Inoue T, Kitagawa N, Nishi N, Shimanaka S, Takahashi Y, Kusumi I, Odagaki Y, Denda K, Ohmori T, Koyama T (2000) Open pergolide treatment of tricyclic and heterocyclic antidepressant-resistant depression. J Affect Disord 61:127–132
Kaplan DR, Miller FD (1997) Signal transduction by the neurotrophin receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:213–221
Keller MB (2005) Issues in treatment-resistant depression. J Clin Psychiatry 66(Suppl 8):5–12
Koeltzow TE, Austin JD, Vezina P (2003) Behavioral sensitization to quinpirole is not associated with increased nucleus accumbens dopamine overflow. Neuropharmacology 44:102–110
Kumamaru E, Numakawa T, Adachi N, Yagasaki Y, Izumi A, Niyaz M, Kudo M, Kunugi H (2008) Glucocorticoid prevents brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated maturation of synaptic function in developing hippocampal neurons through reduction in the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol 22:546–558
Küppers E, Beyer C (2001) Dopamine regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in cultured embryonic mouse striatal cells. NeuroReport 12:1175–1179
Lattanzi L, Dell’Osso L, Cassano P, Pini S, Rucci P, Houck PR, Gemignani A, Battistini G, Bassi A, Abelli M, Cassano GB (2002) Pramipexole in treatment-resistant depression: a 16-week naturalistic study. Bipolar Disord 4:307–314
Leentjens AF, Koester J, Fruh B, Shephard DT, Barone P, Houben JJ (2009) The effect of pramipexole on mood and motivational symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of placebo-controlled studies. Clin Ther 31:89–98
Lemke MR (2008) Depressive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol 15(Suppl 1):21–25
Lemke MR, Brecht HM, Koester J, Kraus PH, Reichmann H (2005) Anhedonia, depression, and motor functioning in Parkinson’s disease during treatment with pramipexole. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 17:214–220
Lemke MR, Brecht HM, Koester J, Reichmann H (2006) Effects of the dopamine agonist pramipexole on depression, anhedonia and motor functioning in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 248:266–270
López-Rubalcava C, Lucki I (2000) Strain differences in the behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs in the rat forced swimming test. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:191–199
Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A (2002) Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:791–804
Millan MJ, Brocco M, Papp M, Serres F, La Rochelle CD, Sharp T, Peglion JL, Dekeyne A (2004a) S32504, a novel naphtoxazine agonist at dopamine D3/D2 receptors: III. Actions in models of potential antidepressive and anxiolytic activity in comparison with ropinirole. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:936–950
Millan MJ, Seguin L, Gobert A, Cussac D, Brocco M (2004b) The role of dopamine D3 compared with D2 receptors in the control of locomotor activity: a combined behavioural and neurochemical analysis with novel, selective antagonists in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174:341–357
Miyagi M, Arai N, Taya F, Itoh F, Komatsu Y, Kojima M, Isaji M (1996) Effect of cabergoline, a long-acting dopamine D2 agonist, on reserpine-treated rodents. Biol Pharm Bull 19:1499–1502
Nibuya M, Morinobu S, Duman RS (1995) Regulation of BDNF and trkB mRNA in rat brain by chronic electroconvulsive seizure and antidepressant drug treatments. J Neurosci 15:7539–7547
Numakawa T, Nakayama H, Suzuki S, Kubo T, Nara F, Numakawa Y, Yokomaku D, Araki T, Ishimoto T, Ogura A, Taguchi T (2003) Nerve growth factor-induced glutamate release is via p75 receptor, ceramide, and Ca(2+) from ryanodine receptor in developing cerebellar neurons. J Biol Chem 278:41259–41269
Numakawa T, Ishimoto T, Suzuki S, Numakawa Y, Adachi N, Matsumoto T, Yokomaku D, Koshimizu H, Fujimori KE, Hashimoto R, Taguchi T, Kunugi H (2004) Neuronal roles of the integrin-associated protein (IAP/CD47) in developing cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 279:43245–43253
Numakawa T, Kumamaru E, Adachi N, Yagasaki Y, Izumi A, Kunugi H (2009) Glucocorticoid receptor interaction with TrkB promotes BDNF-triggered PLC-gamma signaling for glutamate release via a glutamate transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:647–652
Ohta K, Kuno S, Mizuta I, Fujinami A, Matsui H, Ohta M (2003) Effects of dopamine agonists bromocriptine, pergolide, cabergoline, and SKF-38393 on GDNF, NGF, and BDNF synthesis in cultured mouse astrocytes. Life Sci 73:617–626
Ohta K, Fujinami A, Kuno S, Sakakimoto A, Matsui H, Kawahara Y, Ohta M (2004) Cabergoline stimulates synthesis and secretion of nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor by mouse astrocytes in primary culture. Pharmacology 71:162–168
Paré WP (1989) Stress ulcer susceptibility and depression in Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats. Physiol Behav 46:993–998
Parikh V, Khan MM, Mahadik SP (2004) Olanzapine counteracts reduction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB receptors in rat hippocampus produced by haloperidol. Neurosci Lett 356:135–139
Poo MM (2001) Neurotrophins as synaptic modulators. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:24–32
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 266:730–732
Qi X, Lin W, Li J, Pan Y, Wang W (2006) The depressive-like behaviors are correlated with decreased phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in rat brain following chronic forced swim stress. Behav Brain Res 175:233–240
Qi X, Lin W, Li J, Li H, Wang W, Wang D, Sun M (2008) Fluoxetine increases the activity of the ERK-CREB signal system and alleviates the depressive-like behavior in rats exposed to chronic forced swim stress. Neurobiol Dis 31:278–285
Rektorová I, Rektor I, Bares M, Dostál V, Ehler E, Fanfrdlová Z, Fiedler J, Klajblová H, Kulist’ák P, Ressner P, Svátová J, Urbánek K, Velísková J (2003) Pramipexole and pergolide in the treatment of depression in Parkinson’s disease: a national multicentre prospective randomized study. Eur J Neurol 10:399–406
Rogers DC, Costall B, Domeney AM, Gerrard PA, Greener M, Kelly ME, Hagan JJ, Hunter AJ (2000) Anxiolytic profile of ropinirole in the rat, mouse and common marmoset. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 151:91–97
Rogóz Z, Skuza G, Kłodzińska A (2004) Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of 7-OH-DPAT, preferential dopamine D3 receptor agonist, in rats. Pol J Pharmacol 56:519–526
Rowlett JK, Mattingly BA, Bardo MT (1995) Repeated quinpirole treatment: locomotor activity, dopamine synthesis, and effects of selective dopamine antagonists. Synapse 20:209–216
Szechtman H, Talangbayan H, Canaran G, Dai H, Eilam D (1994) Dynamics of behavioral sensitization induced by the dopamine agonist quinpirole and a proposed central energy control mechanism. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 115:95–104
Takahashi H, Yoshida K, Higuchi H, Shimizu T, Inoue T, Koyama T (2003) Addition of a dopamine agonist, cabergoline, to a serotonin-noradrenalin reuptake inhibitor, milnacipran as a therapeutic option in the treatment of refractory depression: two case reports. Clin Neuropharmacol 26:230–232
Tejani-Butt S, Kluczynski J, Paré WP (2003) Strain-dependent modification of behavior following antidepressant treatment. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:7–14
Yagasaki Y, Numakawa T, Kumamaru E, Hayashi T, Su TP, Kunugi H (2006) Chronic antidepressants potentiate via sigma-1 receptors the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced signaling for glutamate release. J Biol Chem 281:12941–12949
Yamamoto M (2001) Depression in Parkinson’s disease: its prevalence, diagnosis, and neurochemical background. J Neurol 248(Suppl 3):III5–III11
Yaroslavsky I, Colletti M, Jiao X, Tejani-Butt S (2006) Strain differences in the distribution of dopamine (DA-2 and DA-3) receptor sites in rat brain. Life Sci 79:772–776
Ying SW, Futter M, Rosenblum K, Webber MJ, Hunt SP, Bliss TV, Bramham CR (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces long-term potentiation in intact adult hippocampus: requirement for ERK activation coupled to CREB and upregulation of Arc synthesis. J Neurosci 22:1532–1540
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants (Research on Psychiatric and Neurological Diseases and Mental Health; Clinical Research for Development of Preventive Medicine and New Therapeutics) (H.K.), the JST, CREST (T.N., H.K), the Program for Promotion of Fundamental Studies in Health Sciences of the National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (NIBIO) (H.K.), and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (H.K.). The authors declare no conflict of interest. The experiments comply with the current laws of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiba, S., Numakawa, T., Ninomiya, M. et al. Cabergoline, a dopamine receptor agonist, has an antidepressant-like property and enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling. Psychopharmacology 211, 291–301 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1894-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1894-8