Abstract
Rationale
Lithium and several antiepileptic drugs have mood-stabilizing effects in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Both disorders are characterized by deficits in prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response.
Objectives
Using the DBA/2 model of naturally low PPI, which is reliably increased by antipsychotics, five mood stabilizers in clinical use were tested to determine whether they would also increase PPI in this model. All drugs were administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) 30 min before testing.
Results
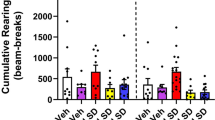
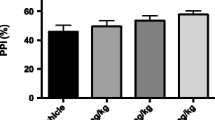
Lithium chloride (30 mg/kg), topiramate (100 and 300 mg/kg), carbamazepine (30, 60, and 100 mg/kg), valproic acid (178 and 316 mg/kg), and lamotrigine (3, 10, and 30 mg/kg) increased percent PPI. The antiepileptic drugs carbamazepine, valproic acid, and lamotrigine at high doses also decreased no-stimulus amplitudes and increased startle amplitudes. At high doses of carbamazepine, valproic acid, and lamotrigine, increases in percent PPI were independent of the increases in startle amplitude.
Conclusions
The demonstrated efficacy of five mood stabilizers in the DBA/2 model of naturally low PPI points to the translational value of this model in predicting therapeutic activity in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder of compounds with diverse mechanisms of action.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braff DL, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR (2001) Human studies of prepulse inhibition of startle: normal subjects, patient groups, and pharmacological studies. Psychopharmacology 156:234–258
Brody SA, Geyer MA, Large CH (2003) Lamotrigine prevents ketamine but not amphetamine-induced deficits in prepulse inhibition in mice. Psychopharmacology 169:240–246
Browman KE, Komater VA, Curzon P, Rueter LE, Hancock AA, Decker MW, Fox GB (2004) Enhancement of prepulse inhibition of startle in mice by the H3 receptor antagonists thioperamide and ciproxifan. Behav Brain Res 153:69–76
Coyle JT (2006) Glutamate and schizophrenia: beyond the dopamine hypothesis. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:365–384
Depoortère R, Dargazanli G, Estenne-Bouhtou G, Coste A, Lanneau C, Desvignes C, Poncelet M, Heaulme M, Santucci V, Decobert M, Cudennec A, Voltz C, Boulay D, Terranova JP, Stemmelin J, Roger P, Marabout B, Sevrin M, Vigé X, Biton B, Steinberg R, Françon D, Alonso R, Avenet P, Oury-Donat F, Perrault G, Griebel G, George P, Soubrié P, Scatton B (2005) Neurochemical, electrophysiological and pharmacological profiles of the selective inhibitor of the glycine transporter-1 SSR504734, a potential new type of antipsychotic. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1963–1985
Donato Di Paola E, Gareri P, Davoli A, Gratteri S, Scicchitano F, Naccari C, De Sarro G (2007) Influence of levetiracetam on the anticonvulsant efficacy of conventional antiepileptic drugs against audiogenic seizures in DBA/2 mice. Epilepsy Res 75:112–121
Fisher RS (1989) Animal models of the epilepsies. Brain Res Rev 14:245–278
Flood DG, Gasior M, Marino MJ (2007) Variables affecting prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex and the response to antipsychotics in DBA/2NCrl mice. Psychopharmacology 195:203–211
Fox GB, Esbenshade TA, Pan JB, Radek RJ, Krueger KM, Yao BB, Browman KE, Buckley MJ, Ballard ME, Komater VA, Miner H, Zhang M, Faghih R, Rueter LE, Bitner RS, Drescher KU, Wetter J, Marsh K, Lemaire M, Porsolt RD, Bennani YL, Sullivan JP, Cowart MD, Decker MW, Hancock AA (2005) Pharmacological properties of ABT-239 [4-(2-{2-[(2R)-2-methylpyrrolidinyl]ethyl}-benzofuran-5-yl) benzonitrile]: II. neurophysiological characterization and broad preclinical efficacy in cognition and schizophrenia of a potent and selective histamine H3 receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:176–190
Frau R, Orrù M, Fà M, Casti A, Manunta M, Fais N, Mereu G, Gessa G, Bortolato M (2007) Effects of topiramate on the prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:320–331
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology 156:117–154
Grunze HCR (2008) The effectiveness of anticonvulsants in psychiatric disorders. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 10:77–89
Kato T (2008) Molecular biology of bipolar disorder: a disease of ‘mood-stabilizing neurons’? Trends Neurosci 31:495–503
Kinney GG, Sur C, Burno M, Mallorga PJ, Williams JB, Figueroa DJ, Wittmann M, Lemaire W, Conn PJ (2003) The glycine transporter type 1 inhibitor N-[3-(4′-fluorophenyl)-3-(4′-phenylphenoxy) propyl]sarcosine potentiates NMDA receptor-mediated responses in vivo and produces an antipsychotic profile in rodent behavior. J Neurosci 23:7586–7591
Ligneau X, Landais L, Perrin D, Piriou J, Uguen M, Denis E, Robert P, Parmentier R, Anaclet C, Lin J-S, Burban A, Arrang J-M, Schwartz JC (2007) Brain histamine and schizophrenia: potential therapeutic applications of H3-receptor inverse agonists studied with BF2.649. Biochem Pharmacol 73:1215–1224
Marino MJ, Conn PJ (2002) Direct and indirect modulation of the N-methyl D-aspartate receptor: potential for the development of novel antipsychotic therapies. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 1:1–16
McCaughran J Jr, Mahjubi E, Decena E, Hitzemann R (1997) Genetics, haloperidol-induced catalepsy and haloperidol-induced changes in acoustic startle and prepulse inhibition. Psychopharmacology 134:131–139
Olivier B, Leahy C, Mullen T, Paylor R, Groppi VE, Sarnyai Z, Brunner D (2001) The DBA/2J strain and prepulse inhibition of startle: a model system to test antipsychotics? Psychopharmacology 156:284–290
Ong JC, Brody SA, Large CH, Geyer MA (2005) An investigation of the efficacy of mood stabilizers in rodent models of prepulse inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Therap 315:1163–1171
Paylor R, Crawley JN (1997) Inbred strain differences in prepulse inhibition of the mouse startle response. Psychopharmacology 132:169–180
Perry W, Minassian A, Feifel D, Braff DL (2001) Sensorimotor gating deficits in bipolar disorder patients with acute psychotic mania. Biol Psychiatry 50:418–424
Rogawski MA, Löscher W (2004a) The neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:553–563
Rogawski MA, Löscher W (2004b) The neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs for the treatment of nonepileptic conditions. Nat Med 10:685–692
Rosenberg JM, Salzman C (2007) Update: new uses for lithium and anticonvulsants. CNS Spectr 12:831–841
Sanacora G, Zarate CA, Krystal JH, Manji HK (2008) Targeting the glutamatergic system to develop novel, improved therapeutics for mood disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:426–437
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA (2000) Animal models of deficient sensorimotor gating: what we know, what we think we know, and what we hope to know soon. Behav Pharmacol 11:185–204
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Taaid N, Geyer MA (1994) Assessing the validity of an animal model of deficient sensorimotor gating in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:139–154
Swerdlow NR, Platten A, Shoemaker J, Pitcher L, Auerbach P (2001) Effects of pergolide on sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology 158:230–240
Swerdlow NR, Shoemaker JM, Bongiovanni MJ, Neary AC, Tochen LS, Saint Marie RL (2007) Strain differences in the disruption of prepulse inhibition of startle after systemic and intra-accumbens amphetamine administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 87:1–10
Swerdlow NR, Weber M, Qu Y, Light GA, Braff DL (2008) Realistic expectations of prepulse inhibition in translational models for schizophrenia research. Psychopharmacology 199:331–388
Thase ME, Denko T (2008) Pharmacotherapy of mood disorders. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 4:53–91
Umeda K, Suemaru K, Todo N, Egashira N, Mishima K, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M, Araki H (2006) Effects of mood stabilizers on the disruption of prepulse inhibition induced by apomorphine or dizocilpine in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 553:157–162
Yamada S, Harano M, Annoh N, Nakamura K, Tanaka M (1999) Involvement of serotonin 2A receptors in phencyclidine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats. Biol Psychiatry 46:832–838
Acknowledgments
Cephalon, Inc. employs the authors and sponsored this research. The experiments described in this manuscript comply with the current laws and regulations of the USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flood, D.G., Choinski, M., Marino, M.J. et al. Mood stabilizers increase prepulse inhibition in DBA/2NCrl mice. Psychopharmacology 205, 369–377 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1547-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1547-y