Abstract
Rationale
Cognitive deficits, including memory impairment, are regarded as a core feature of schizophrenia. Aripiprazole, an atypical antipsychotic drug, has been shown to improve disruption of prepulse inhibition and social interaction in an animal model of schizophrenia induced by phencyclidine (PCP); however, the effects of aripiprazole on recognition memory remain to be investigated.
Objectives
In this study, we examined the effect of aripiprazole on cognitive impairment in mice treated with PCP repeatedly.
Materials and methods
Mice were repeatedly administered PCP at a dose of 10mg/kg for 14days, and their cognitive function was assessed using a novel-object recognition task. We investigated the therapeutic effects of aripiprazole (0.01–1.0mg/kg) and haloperidol (0.3 and 1.0mg/kg) on cognitive impairment in mice treated with PCP repeatedly.
Results
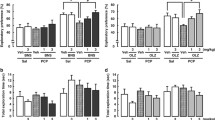
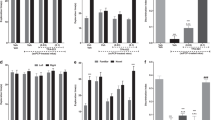
Single (1.0mg/kg) and repeated (0.03 and 0.1mg/kg, for 7days) treatment with aripiprazole ameliorated PCP-induced impairment of recognition memory, although single treatment significantly decreased the total exploration time during the training session. In contrast, both single and repeated treatment with haloperidol (0.3 and 1.0mg/kg) failed to attenuate PCP-induced cognitive impairment. The ameliorating effect of aripiprazole on recognition memory in PCP-treated mice was blocked by co-treatment with a dopamine D1 receptor antagonist, SCH23390, and a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, WAY100635; however, co-treatment with a D2 receptor antagonist raclopride had no effect on the ameliorating effect of aripiprazole.
Conclusions
These results suggest that the ameliorative effect of aripiprazole on PCP-induced memory impairment is associated with dopamine D1 and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggleton JP, Brown MW (1999) Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal–anterior thalamic axis. Behav Brain Sci 22:425–444
Allen RM, Young SJ (1978) Phencyclidine-induced psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 135:1081–1084
Bakshi VP, Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1994) Clozapine antagonizes phencyclidine-induced deficits in sensorimotor gating of the startle response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:787–794
Bantick RA, Deakin JF, Grasby PM (2001) The 5-HT1A receptor in schizophrenia: a promising target for novel atypical neuroleptics. J Psychopharmacol 15:37–46
Bortolozzi A, Díaz-Mataix L, Toth M, Celada P, Artigas F (2007) In vivo actions of aripiprazole on serotonergic and dopaminergic systems in rodent brain. Psychopharmacology 191:745–758
Bruins Slot LA, Kleven MS, Newman-Tancredi A (2005) Effects of novel antipsychotics with mixed D2 antagonist/5-HT1A agonist properties on PCP-induced social interaction deficits in the rat. Neuropharmacology 49:996–1006
Burnet PW, Eastwood SL, Harrison PJ (1996) 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptor mRNAs and binding site densities are differentially altered in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:442–455
Burris KD, Molski TF, Xu C, Ryan E, Tottori K, Kikuchi T, Yocca FD, Molinoff PB (2002) Aripiprazole, a novel antipsychotic, is a high-affinity partial agonist at human dopamine D2 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:381–389
DeLeon A, Patel NC, Crismon ML (2004) Aripiprazole: a comprehensive review of its pharmacology, clinical efficacy, and tolerability. Clin Ther 26:649–666
Dias R, Robbins TW, Roberts AC (1996a) Dissociation in prefrontal cortex of affective and attentional shifts. Nature 380:69–72
Dias R, Robbins TW, Roberts AC (1996b) Primate analogue of the Wisconsin card sorting test: Effects of excitotoxic lesions of the prefrontal cortex in the marmoset. Behav Neurosci 110:872–886
Díaz-Mataix L, Scorza MC, Bortolozzi A, Toth M, Celada P, Artigas F (2005) Involvement of 5-HT1A receptors in prefrontal cortex in the modulation of dopaminergic activity: role in atypical antipsychotic action. J Neurosci 25:10831–10843
Ennaceur A, Delacour J (1988) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: Behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31:47–59
Enomoto T, Noda Y, Mouri A, Shin EJ, Wang D, Murai R, Hotta K, Furukawa H, Nitta A, Kim HC, Nabeshima T (2005) Long-lasting impairment of associative learning is correlated with a dysfunction of N-methyl-d-aspartate-extracellular signaling-regulated kinase signaling in mice after withdrawal from repeated administration of phencyclidine. Mol Pharmacol 68:1765–1774
Fejgin K, Safonov S, Pålsson E, Wass C, Engel JA, Svensson L, Klamer D (2007) The atypical antipsychotic, aripiprazole, blocks phencyclidine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition in mice. Psychopharmacology 191:377–385
Grayson B, Idris NF, Neill JC (2007) Atypical antipsychotics attenuate a sub-chronic PCP-induced cognitive deficit in the novel object recognition task in the rat. Behav Brain Res 184:31–38
Green B (2004) Focus on aripiprazole. Curr Med Res Opin 20:207–213
Gurevich EV, Joyce JN (1997) Alterations in the cortical serotonergic system in schizophrenia: a postmortem study. Biol Psychiatry 42:529–545
Hagiwara H, Fujita Y, Ishima T, Kunitachi S, Shirayama Y, Iyo M, Hashimoto K (2008) Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice are improved by subsequent subchronic administration of the antipsychotic drug perospirone: role of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18:448–454
Hashimoto K, Fujita Y, Shimizu E, Iyo M (2005) Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice are improved by subsequent subchronic administration of clozapine, but not haloperidol. Eur J Pharmacol 519:114–117
Hirose T, Kikuchi T (2005) Aripiprazole, a novel antipsychotic agent: dopamine D2 receptor partial agonist. J Med Invest 52:284–290
Ichikawa J, Ishii H, Bonaccorso S, Fowler WL, O’Laughlin IA, Meltzer HY (2001) 5-HT2A and D2 receptor blockade increases cortical DA release via 5-HT1A receptor activation: a possible mechanism of atypical antipsychotic-induced cortical dopamine release. J Neurochem 76:1521–1531
Inoue T, Domae M, Yamada K, Furukawa T (1996) Effects of the novel antipsychotic agent 7-(4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyloxy)-3,4-dihydro -2(1H)-quinolinone (OPC-14597) on prolactin release from the rat anterior pituitary gland. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:137–143
Ito M, Nagai T, Mizoguchi H, Fukakusa A, Nakanishi Y, Kamei H, Nabeshima T, Takuma K, Yamada K (2007a) Possible involvement of protease-activated receptor-1 in the regulation of morphine-induced dopamine release and hyperlocomotion by the tissue plasminogen activator-plasmin system. J Neurochem 101:1392–1399
Ito Y, Takuma K, Mizoguchi H, Nagai T, Yamada K (2007b) A novel azaindolizinone derivative ZSET1446 (spiro[imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3,2-indan]-2(3H)-one) improves methamphetamine-induced impairment of recognition memory in mice by activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:819–827
Javitt DC, Zukin SR (1991) Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 148:1301–1308
Jordan S, Koprivica V, Chen R, Tottori K, Kikuchi T, Altar CA (2002) The antipsychotic aripiprazole is a potent, partial agonist at the human 5-HT1A receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 441:137–140
Joyce JN, Shane A, Lexow N, Winokur A, Casanova MF, Kleinman JE (1993) Serotonin uptake sites and serotonin receptors are altered in the limbic system of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol 8:315–336
Kamei H, Nagai T, Nakano H, Togan Y, Takayanagi M, Takahashi K, Kobayashi K, Yoshida S, Maeda K, Takuma K, Nabeshima T, Yamada K (2006) Repeated methamphetamine treatment impairs recognition memory through a failure of novelty-induced ERK1/2 activation in the prefrontal cortex of mice. Biol Psychiatry 59:75–84
Kapur S, Zipursky R, Jones C, Remington G, Houle S (2000) Relationship between dopamine D2 occupancy, clinical response, and side effects: a double-blind PET study of first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 157:514–520
Keefe RS, Bilder RM, Davis SM, Harvey PD, Palmer BW, Gold JM, Meltzer HY, Green MF, Capuano G, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO, Davis CE, Hsiao JK, Lieberman JA, CATIE InvestigatorsNeurocognitive Working Group (2007) Neurocognitive effects of antipsychotic medications in patients with chronic schizophrenia in the CATIE Trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:633–647
Kikuchi T, Tottori K, Uwahodo Y, Hirose T, Miwa T, Oshiro Y, Morita S (1995) 7-(4-[4-(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyloxy)-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone (OPC-14597), a new putative antipsychotic drug with both presynaptic dopamine autoreceptor agonistic activity and postsynaptic D2 receptor antagonistic activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:329–336
Lerner SE, Burns RS (1986) Legal issues associated with PCP abuse-the role of the forensic expert. NIDA Res Monogr 64:229–236
Li Z, Ichikawa J, Dai J, Meltzer HY (2004) Aripiprazole, a novel antipsychotic drug, preferentially increases dopamine release in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 493:75–83
Lopez-Figueroa AL, Norton CS, Lopez-Figueroa MO, Armellini-Dodel D, Burke S, Akil H, Lopez JF, Watson SJ (2004) Serotonin 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, and 5-HT2A receptor mRNA expression in subjects with major depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 55:225–233
Maddox VH, Godefroi EF, Parcell RF (1965) The synthesis of phencyclidine and other 1-arylcyclohexylamines. J Med Chem 56:230–235
McQuade RD, Burris KD, Jordan S, Tottori K, Kurahashi N, Kikuchi T (2002) Aripiprazole: a dopamine–serotonin system stabilizer. Int Neuropsychopharmacol 5(Suppl. 1):S176
Meltzer HY (1999) The role of serotonin in antipsychotic drug action. Neuropsychopharmacol 21:106S–115S
Mishara AL, Goldberg TE (2004) A meta-analysis and critical review of the effects of conventional neuroleptic treatment on cognition in schizophrenia: opening a closed book. Biol Psychiatry 55:1013–1022
Mouri A, Noda Y, Enomoto T, Nabeshima T (2007a) Phencyclidine animal models of schizophrenia: approaches from abnormality of glutamatergic neurotransmission and neurodevelopment. Neurochem Int 51:173–184
Mouri A, Noda Y, Noda A, Nakamura T, Tokura T, Yura Y, Nitta A, Furukawa H, Nabeshima T (2007b) Involvement of a dysfunctional dopamine-D1/N-methyl-d-aspartate-NR1 and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II pathway in the impairment of latent learning in a model of schizophrenia induced by phencyclidine. Mol Pharmacol 71:1598–1609
Murai R, Noda Y, Matsui K, Kamei H, Mouri A, Matsuba K, Nitta A, Furukawa H, Nabeshima T (2007) Hypofunctional glutamatergic neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex is involved in the emotional deficit induced by repeated treatment with phencyclidine in mice: implications for abnormalities of glutamate release and NMDA-CaMKII signaling. Behav Brain Res 180:152–160
Nagai T, Yamada K, Kim HC, Kim YS, Noda Y, Imura A, Nabeshima Y, Nabeshima T (2003) Cognition impairment in the genetic model of aging klotho gene mutant mice: a role of oxidative stress. FASEB J 17:50–52
Nagai T, Takuma K, Kamei H, Ito Y, Nakamichi N, Ibi D, Nakanishi Y, Murai M, Mizoguchi H, Nabeshima T, Yamada K (2007) Dopamine D1 receptors regulate protein synthesis-dependent long-term recognition memory via extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in the prefrontal cortex. Learn Mem 14:117–125
Newcomer JW (2005) Second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics and metabolic effects: a comprehensive literature review. CNS Drugs 19(Suppl 1):1–93
Newman-Tancredi A, Verriele L, Touzard M, Millan MJ (2001) Efficacy of antipsychotic agents at human 5-HT1A receptors determined by [3H]WAY100,635 binding affinity ratios: relationship to efficacy for G-protein activation. Eur J Pharmacol 428:177–184
Noda Y, Yamada K, Furukawa H, Nabeshima T (1995) Enhancement of immobility in a forced swimming test by subacute or repeated treatment with phencyclidine: a new model of schizophrenia. Br J Pharmacol 116:2531–2537
Noda Y, Mamiya T, Furukawa H, Nabeshima T (1997) Effects of antidepressants on phencyclidine-induced enhancement of immobility in a forced swimming test in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 324:135–140
Noda Y, Kamei H, Mamiya T, Furukawa H, Nabeshima T (2000) Repeated phencyclidine treatment induces negative symptom-like behavior in forced swimming test in mice: imbalance of prefrontal serotonergic and dopaminergic functions. Neuropsychopharmacology 23:375–387
Nuechterlein KH, Barch DM, Gold JM, Goldberg TE, Green MF, Heaton RK (2004) Identification of separable cognitive factors in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 72:29–39
Pearlson GD (2000) Neurobiology of schizophrenia. Ann Neurol 48:556–566
Qiao H, Noda Y, Kamei H, Nagai T, Furukawa H, Miura H, Kayukawa Y, Ohta T, Nabeshima T (2001) Clozapine, but not haloperidol, reverses social behavior deficit in mice during withdrawal from chronic phencyclidine treatment. Neuroreport 12:11–15
Rainey Jr JM, Crowder MK (1975) Prolonged psychosis attributed to phencyclidine: report of three cases. Am J Psychiatry 132:1076–1078
Rivas-Vasquez RA (2003) Aripiprazole: a novel antipsychotic with dopamine-stabilising properties. Prof Psychol: Res Prac 34:108–111
Rollema H, Lu Y, Schmidt AW, Sprouse JS, Zorn SH (2000) 5-HT1A receptor activation contributes to ziprasidone-induced dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex. Biol Psychiatry 48:229–237
Rössler W, Salize HJ, van Os J, Riecher-Rössler A (2005) Size of burden of schizophrenia and psychotic disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 15:399–409
Sawaguchi T, Goldman-Rakic PS (1991) D1 dopamine receptors in prefrontal cortex: involvement in working memory. Science 251:947–950
Shapiro DA, Renock S, Arrington E, Chiodo LA, Liu LX, Sibley DR, Roth BL, Mailman R (2003) Aripiprazole, a novel atypical antipsychotic drug with a unique and robust pharmacology. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1400–1411
Shimokawa Y, Akiyama H, Kashiyama E, Koga T, Miyamoto G (2005) High performance liquid chromatographic methods for the determination of aripiprazole with ultraviolet detection in rat plasma and brain: application to the pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 821:8–14
Sprouse JS, Reynolds LS, Braselton JP, Rollema H, Zorn SH (1999) Comparison of the novel antipsychotic ziprasidone with clozapine and olanzapine: inhibition of dorsal raphe cell firing and the role of 5-HT1A receptor activation. Neuropsychopharmacol 21:622–631
Stark AD, Jordan S, Allers KA, Bertekap RL, Chen R, Mistry Kannan T, Molski TF, Yocca FD, Sharp T, Kikuchi T, Burris KD (2007) Interaction of the novel antipsychotic aripiprazole with 5-HT1A and 5-HT 2A receptors: functional receptor-binding and in vivo electrophysiological studies. Psychopharmacology 190:373–382
Sumiyoshi T, Matsui M, Nohara S, Yamashita I, Kurachi M, Sumiyoshi C, Jayathilake K, Meltzer HY (2001a) Enhancement of cognitive performance in schizophrenia by addition of tandospirone to neuroleptic treatment. Am J Psychiatry 158:1722–1725
Sumiyoshi T, Matsui M, Yamashita I, Nohara S, Kurachi M, Uehara T, Sumiyoshi S, Sumiyoshi C, Meltzer HY (2001b) The effect of tandospirone, a serotonin-1A agonist, on memory function in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 49:861–868
Tamminga CA (2002) Partial dopamine agonists in the treatment of psychosis. J Neural Transm 109:411–420
Tamminga CA (2006) The neurobiology of cognition in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 67:9–13
Tan HY, Callicott JH, Weinberger DR (2007) Dysfunctional and compensatory prefrontal cortical systems, genes and the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Cereb Cortex 17:i171–i181
Tang YP, Shimizu E, Dube GR, Rampon C, Kerchner GA, Zhuo M, Liu G, Tsien JZ (1999) Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 401:63–69
Vincent SL, Khan Y, Benes FM (1995) Cellular colocalization of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in rat medial prefrontal cortex. Synapse 19:112–120
Woodward ND, Purdon SE, Meltzer HY, Zald DH (2005) A meta-analysis of neuropsychological change to clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone in schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 8:457–472
Zocchi A, Fabbri D, Heidbreder CA (2005) Aripiprazole increases dopamine but not noradrenaline and serotonin levels in the mouse prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Lett 387:157–161
Acknowledgements
This work was supported, in part, as Research on Regulatory Science of Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices, and Research on Risk of Chemical Substances, Health and Labour Sciences Research Grants from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan, Academic Frontier Project for Private Universities (2007–2011) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and from Uehara Memorial Foundation, International Research Project supported by The Meijo Asian Research Center (MARC). We are grateful to Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. for providing the aripiprazole.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM Supplemental Fig. 1
Effect of single administrations of aripiprazole on PCP-induced cognitive impairment in novel object recognition. Eight days after withdrawal from repeated PCP (10 mg/kg, s.c., for 14 days) treatment, mice were subjected to the novel-object recognition test. Objects A and B were used in the training. Object B was replaced by object C in the retention session. Aripiprazole (0.01–1.0 mg/kg, p.o.) or vehicle (0.1% CMC) was administered 1 h before the training session. A paired comparisons test for each group comparing the time spent on objects in the training session (a) and retention session (b). Values indicate the mean ± S.E. (n = 8–16). **p < 0.01 compared with object A. (DOC 54.0 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, T., Murai, R., Matsui, K. et al. Aripiprazole ameliorates phencyclidine-induced impairment of recognition memory through dopamine D1 and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. Psychopharmacology 202, 315–328 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1240-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1240-6