Abstract
Rationale
The mechanisms mediating tobacco addiction remain elusive. Nicotine, the psychoactive component in tobacco, is generally believed to be the main cause of reward and addiction. However, tobacco smoke contains thousands of constituents, some of which may interact with nicotine to enhance reward. It has previously been shown that monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibition, known to result from smoking, can enhance nicotine self-administration. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the role of noradrenergic systems in mediating this enhancement of nicotine reward.
Objective
The objective of this study was to test the hypothesis that MAO inhibitor pretreatment enhances nicotine self-administration by activation of noradrenergic pathways that regulate dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens (NAc).
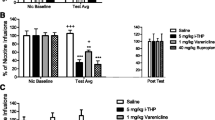
Methods
The effect of prazosin (0.0625–0.5 mg/kg, i.p.), a specific α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist, was examined on male rats pretreated with tranylcypromine (3 mg/kg), an irreversible inhibitor of MAO A and B. Acquisition of nicotine (10 μg kg−1 inj−1, i.v.) self-administration behavior was examined over a 5-day period. Nicotine (60 μg kg−1 inj−1, i.v.)-induced increase in NAc extracellular dopamine levels was examined by in vivo microdialysis in non-self-administering animals.
Results
We have shown that (1) tranylcypromine enhances nicotine self-administration, (2) prazosin pretreatment blocks both the acquisition and the expression of nicotine self-administration, and (3) prazosin pretreatment diminishes nicotine-induced dopamine release in the NAc.
Conclusion
These data indicate that the stimulation of α1-adrenergic receptors is critical for tranylcypromine enhancement of nicotine reward and suggest a critical interplay between the noradrenergic and dopaminergic systems in tobacco addiction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson JL, Marcus M, Nomikos GG, Svensson TH (1994) Prazosin modulates the changes in firing pattern and transmitter release induced by raclopride in the mesolimbic, but not in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 349:236–243
Antelman SM, Caggiula AR (1977) Norepinephrine-dopamine interactions and behavior. Science 195:646–653
Auclair A, Cotecchia S, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (2002) d-Amphetamine fails to increase extracellular dopamine levels in mice lacking alpha 1b-adrenergic receptors: relationship between functional and nonfunctional dopamine release. J Neurosci 22:9150–9154
Auclair A, Drouin C, Cotecchia S, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (2004) 5-HT2A and alpha1b-adrenergic receptors entirely mediate dopamine release, locomotor response and behavioural sensitization to opiates and psychostimulants. Eur J Neurosci 20:3073–3084
Baker GB, Coutts RT, McKenna KF, Sherry-McKenna RL (1992) Insights into the mechanisms of action of the MAO inhibitors phenelzine and tranylcypromine: a review. J Psychiatry Neurosci 17:206–214
Balfour D, Benowitz N, Fagerstrom K, Kunze M, Keil U (2000) Diagnosis and treatment of nicotine dependence with emphasis on nicotine replacement therapy. A status report. Eur Heart J 21:438–445
Belluzzi JD, Wang R, Leslie FM (2005) Acetaldehyde enhances acquisition of nicotine self-administration in adolescent rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 30(4):705–712
Berlin I, Said S, Spreux-Varoquaux O, Launay JM, Olivares R, Millet V, Lecrubier Y, Puech AJ (1995) A reversible monoamine oxidase A inhibitor (moclobemide) facilitates smoking cessation and abstinence in heavy, dependent smokers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 58(4):444–452
Biberman R, Neumann R, Katzir I, Gerber Y (2003) A randomized controlled trial of oral selegiline plus nicotine skin patch compared with placebo plus nicotine skin patch for smoking cessation. Addiction 98(10):1403–1407
Blanc G, Trovero F, Vezina P, Herve D, Godeheu AM, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (1994) Blockade of prefronto-cortical alpha 1-adrenergic receptors prevents locomotor hyperactivity induced by subcortical d-amphetamine injection. Eur J Neurosci 6:293–298
Caine SB, Lintz R, Koob GF (1993) Intravenous drug self-administration techniques in animals. In: Sahagal A (ed) Behavioural neuroscience, vol. II: A practical approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 117–143
Carr DB, Sesack SR (2000) Projections from the rat prefrontal cortex to the ventral tegmental area: target specificity in the synaptic associations with mesoaccumbens and mesocortical neurons. J Neurosci 20:3864–3873
CDC (1989) Reducing the health consequences of smoking: 25 years of progress—a report of the Surgeon General, chap. 2. US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, DHHS publication, Rockville, MD, USA, pp 79–92
Champtiaux N, Gotti C, Cordero-Erausquin M, David DJ, Przybylski C, Lena C, Clementi F, Moretti M, Rossi FM, Le Novere N et al (2003) Subunit composition of functional nicotinic receptors in dopaminergic neurons investigated with knock-out mice. J Neurosci 23:7820–7829
Chergui K, Charléty P, Akaoka H, Saunier C, Brunet J, Buda M, Svensson T, Chouvet G (1993) Tonic activation of NMDA receptors causes spontaneous burst discharge of rat midbrain dopamine neurons. In Vivo Eur J Neurosci 5:137–144
Dani JA, Heinemann S (1996) Molecular and cellular aspects of nicotine abuse. Neuron 16:905–908
Darracq L, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (1998) Importance of the noradrenaline-dopamine coupling in the locomotor activating effects of d-amphetamine. J Neurosci 18:2729–2739
Darracq L, Drouin C, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (2001) Stimulation of metabotropic but not ionotropic glutamatergic receptors in the nucleus accumbens is required for the d-amphetamine-induced release of functional dopamine. Neuroscience 103:395–403
Di Chiara G (2000) Role of dopamine in the behavioural actions of nicotine related to addiction. Eur J Pharmacol 393:295–314
Di Chiara G, Tanda G, Bassareo V, Pontieri F, Acquas E, Fenu S, Cadoni C, Carboni E (1999) Drug addiction as a disorder of associative learning. Role of nucleus accumbens shell/extended amygdala dopamine. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:461–485
Drouin C, Blanc G, Villégier AS, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (2002a) Critical role of alpha1-adrenergic receptors in acute and sensitized locomotor effects of d-amphetamine, cocaine, and GBR 12783: influence of preexposure conditions and pharmacological characteristics. Synapse 43:51–61
Drouin C, Darracq L, Trovero F, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Cotecchia S, Tassin JP (2002b) Alpha1b-adrenergic receptors control locomotor and rewarding effects of psychostimulants and opiates. J Neurosci 22:2873–2884
Engberg G, Hajos M (1994) Nicotine-induced activation of locus coeruleus neurons-an analysis of peripheral versus central induction. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 349:443–446
Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Pappas N, Logan J, MacGregor R, Alexoff D, Shea C, Schlyer D, Wolf AP, et al (1996a) Inhibition of monoamine oxidase B in the brains of smokers. Nature 379:733–736
Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Pappas N, Logan J, Shea C, Alexoff D, MacGregor RR, Schlyer DJ, Zezulkova I, Wolf AP (1996b) Brain monoamine oxidase A inhibition in cigarette smokers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14065–14069
Fowler JS, Logan J, Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Telang F, Zhu W, Franceschi D, Pappas N, Ferrieri R, Shea C et al (2003) Low monoamine oxidase B in peripheral organs in smokers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:11600–11605
Fu Y, Matta SG, McIntosh JM, Sharp BM (1999a) Inhibition of nicotine-induced hippocampal norepinephrine release in rats by alpha-conotoxins MII and AuIB microinjected into the locus coeruleus. Neurosci Lett 266:113–116
Fu Y, Matta SG, Sharp BM (1999b) Local alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic receptors modulate hippocampal norepinephrine release by systemic nicotine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:133–139
Gariano RF, Groves PM (1988) Burst firing induced in midbrain dopamine neurons by stimulation of the medial prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortices. Brain Res 462:194–198
George TP, Vessicchio JC, Termine A, Jatlow PI, Kosten TR, O’Malley SS (2003) A preliminary placebo-controlled trial of selegiline hydrochloride for smoking cessation. Biol Psychiatry 53(2):136–143
Grenhoff J, Svensson TH (1993) Prazosin modulates the firing pattern of dopamine neurons in rat ventral tegmental area. Eur J Pharmacol 233:79–84
Grenhoff J, Nisell M, Ferre S, Aston-Jones G, Svensson TH (1993) Noradrenergic modulation of midbrain dopamine cell firing elicited by stimulation of the locus coeruleus in the rat. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 93:11–25
Griebel G, Curet O, Perrault G, Sanger DJ (1998) Behavioral effects of phenelzine in an experimental model for screening anxiolytic and anti-panic drugs: correlation with changes in monoamine-oxidase activity and monoamine levels. Neuropharmacology 37:927–935
Guillem K, Vouillac C, Azar MR, Parsons LH, Koob GF, Cador M, Stinus L (2005) Monoamine oxidase inhibition dramatically increases the motivation to self-administer nicotine in rats. J Neurosci 25:8593–8600
Henningfield JE, Benowitz NL, Slade J, Houston TP, Davis RM, Deitchman SD (1998) Reducing the addictiveness of cigarettes. Council on Scientific Affairs, American Medical Association. Tob Control 7:281–293
Hooks MS, Jones GH, Smith AD, Neill DB, Justice JB Jr (1991) Response to novelty predicts the locomotor and nucleus accumbens dopamine response to cocaine. Synapse 9:121–128
Kokkinidis L, Anisman H (1978) Involvement of norepinephrine in startle arousal after acute and chronic d-amphetamine administration. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 59:285–292
Lategan AJ, Marien MR, Colpaert FC (1990) Effects of locus coeruleus lesions on the release of endogenous dopamine in the rat nucleus accumbens and caudate nucleus as determined by intracerebral microdialysis. Brain Res 523:134–138
Lena C, de Kerchove D’Exaerde A, Cordero-Erausquin M, Le Novere N, del Mar Arroyo-Jimenez M, Changeux JP (1999) Diversity and distribution of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the locus ceruleus neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12126–12131
Leslie FM, Gallardo KA, Park MK (2002) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated release of [3H]norepinephrine from developing and adult rat hippocampus: direct and indirect mechanisms. Neuropharmacology 42:653–661
Lewis A, Miller JH, Lea RA (2007) Monoamine oxidase and tobacco dependence. Neurotoxicology 28:182–195
Li X, Eisenach JC (2002) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor regulation of spinal norepinephrine release. Anesthesiology 96:1450–1456
Li Y, Hu XT, Berney TG, Vartanian AJ, Stine CD, Wolf ME, White FJ (1999) Both glutamate receptor antagonists and prefrontal cortex lesions prevent induction of cocaine sensitization and associated neuroadaptations. Synapse 34:169–180
Linner L, Endersz H, Ohman D, Bengtsson F, Schalling M, Svensson TH (2001) Reboxetine modulates the firing pattern of dopamine cells in the ventral tegmental area and selectively increases dopamine availability in the prefrontal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:540–546
Lu W, Chen H, Xue CJ, Wolf ME (1997) Repeated amphetamine administration alters the expression of mRNA for AMPA receptor subunits in rat nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex. Synapse 26:269–280
McManus DJ, Greenshaw AJ (1991a) Differential effects of antidepressants on GABAB and beta-adrenergic receptors in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem Pharmacol 42:1525–1528
McManus DJ, Greenshaw AJ (1991b) Differential effects of chronic antidepressants in behavioural tests of beta-adrenergic and GABAB receptor function. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 103:204–208
Mitchell SN, Brazell MP, Joseph MH, Alavijeh MS, Gray JA (1989) Regionally specific effects of acute and chronic nicotine on rates of catecholamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 167:311–322
Nisell M, Nomikos GG, Hertel P, Panagis G, Svensson TH (1996) Condition-independent sensitization of locomotor stimulation and mesocortical dopamine release following chronic nicotine treatment in the rat. Synapse 22:369–381
O’Brien C, Ehrman R, Terns J (1986) Classical conditionning in human. In: Goldberg S, Stlerman I (eds) Behavioral analysis of drug dependence. Academic, London, pp 329–338
O’Leary KT, Leslie FM (2003) Developmental regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated [3H]norepinephrine release from rat cerebellum. J Neurochem 84:952–959
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, New York
Piazza PV, Deminiere JM, Le Moal M, Simon H (1989) Factors that predict individual vulnerability to amphetamine self-administration. Science 245:1511–1513
Sesack SR, Pickel VM (1992) Prefrontal cortical efferents in the rat synapse on unlabeled neuronal targets of catecholamine terminals in the nucleus accumbens septi and on dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area. J Comp Neurol 320:145–160
Shi WX, Pun CL, Zhang XX, Jones MD, Bunney BS (2000) Dual effects of d-amphetamine on dopamine neurons mediated by dopamine and nondopamine receptors. J Neurosci 20:3504–3511
Shiffman S (1991) Refining models of dependence: variations across persons and situations. Br J Addict 86:611–615
Spear LP (2000) The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:417–463
Stolerman IP, Jarvis MJ (1995) The scientific case that nicotine is addictive. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 117:2–10
Summers KL, Giacobini E (1995) Effects of local and repeated systemic administration of (−)nicotine on extracellular levels of acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin in rat cortex. Neurochem Res 20:753–759
Tassin JP (1998) Norepinephrine-dopamine interactions in the prefrontal cortex and the ventral tegmental area: relevance to mental diseases. Adv Pharmacol 42:712–716
Todd KG, Baker GB (1995) GABA-elevating effects of the antidepressant/antipanic drug phenelzine in brain: effects of pretreatment with tranylcypromine, (−)-deprenyl and clorgyline. J Affect Disord 35:125–129
Trovero F, Marin P, Tassin JP, Premont J, Glowinski J (1994) Accelerated resensitization of the D1 dopamine receptor-mediated response in cultured cortical and striatal neurons from the rat: respective role of α1 adrenergic and N-methyl aspartate receptor. J Neurosci 14:6208–6218
Vezina P (1993) Amphetamine injected into the ventral tegmental area sensitizes the nucleus accumbens dopaminergic response to systemic amphetamine: an in vivo microdialysis study in the rat. Brain Res 605:332–337
Villégier AS, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (2003) Transient behavioral sensitization to nicotine becomes long-lasting with monoamine oxidases inhibitors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:267–274
Villégier AS, Loftipour S, Belluzzi J, Leslie FM (2005) Involvement of α1-adrenergic receptors in tranylcypromine enhancement of nicotine self-administration. 2005 Abstract Viewer/Itinerary Planner, Session No. 1027. Program No. 1027.5, Society for Neuroscience, Washington, DC, USA (online)
Villégier AS, Salomon L, Granon S, Changeux JP, Belluzzi JD, Leslie FM, Tassin JP (2006) Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Allow Locomotor and Rewarding Responses to Nicotine. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(8):1704–1713
Villégier AS, Loftipour S, McQuown CS, Belluzzi J, Leslie FM (2007) Tranylcypromine enhancement of nicotine self-administration. Neuropharmacology 52(6):1415–1425
Zhang XY, Kosten TA (2005) Prazosin, an alpha-1 adrenergic antagonist, reduces cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking. Biol Psychiatry 57:1202–1204
Zhang XY, Kosten TA (2006) Previous exposure to cocaine enhances cocaine self-administration in an alpha 1-adrenergic receptor dependent manner. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(3):638–645
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by PHS Grant DA21267 and a fellowship from TRDRP 13DT-0033 (S.L). Experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed. All experimental procedures were performed in compliance with NIH Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH No 85-23, rev. 1985) and approved by the UCI Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villégier, AS., Lotfipour, S., Belluzzi, J.D. et al. Involvement of alpha1-adrenergic receptors in tranylcypromine enhancement of nicotine self-administration in rat. Psychopharmacology 193, 457–465 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0799-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0799-7